Ruhui Ma
Fedcompass: Federated Clustered and Periodic Aggregation Framework for Hybrid Classical-Quantum Models
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Federated learning enables collaborative model training across decentralized clients under privacy constraints. Quantum computing offers potential for alleviating computational and communication burdens in federated learning, yet hybrid classical-quantum federated learning remains susceptible to performance degradation under non-IID data. To address this,we propose FEDCOMPASS, a layered aggregation framework for hybrid classical-quantum federated learning. FEDCOMPASS employs spectral clustering to group clients by class distribution similarity and performs cluster-wise aggregation for classical feature extractors. For quantum parameters, it uses circular mean aggregation combined with adaptive optimization to ensure stable global updates. Experiments on three benchmark datasets show that FEDCOMPASS improves test accuracy by up to 10.22% and enhances convergence stability under non-IID settings, outperforming six strong federated learning baselines.
Hermes: Memory-Efficient Pipeline Inference for Large Models on Edge Devices
Sep 09, 2024



Abstract:The application of Transformer-based large models has achieved numerous success in recent years. However, the exponential growth in the parameters of large models introduces formidable memory challenge for edge deployment. Prior works to address this challenge mainly focus on optimizing the model structure and adopting memory swapping methods. However, the former reduces the inference accuracy, and the latter raises the inference latency. This paper introduces PIPELOAD, a novel memory-efficient pipeline execution mechanism. It reduces memory usage by incorporating dynamic memory management and minimizes inference latency by employing parallel model loading. Based on PIPELOAD mechanism, we present Hermes, a framework optimized for large model inference on edge devices. We evaluate Hermes on Transformer-based models of different sizes. Our experiments illustrate that Hermes achieves up to 4.24 X increase in inference speed and 86.7% lower memory consumption than the state-of-the-art pipeline mechanism for BERT and ViT models, 2.58 X increase in inference speed and 90.3% lower memory consumption for GPT-style models.
SkyMask: Attack-agnostic Robust Federated Learning with Fine-grained Learnable Masks
Dec 19, 2023



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is becoming a popular paradigm for leveraging distributed data and preserving data privacy. However, due to the distributed characteristic, FL systems are vulnerable to Byzantine attacks that compromised clients attack the global model by uploading malicious model updates. Most existing Byzantine-robust FL systems statistically analyze the weights of whole individual model updates uploaded by clients to defend against Byzantine attacks. With the development of layer-level and parameter-level fine-grained attacks, the attacks' stealthiness and effectiveness have been significantly improved. Due to unawareness or overreaction, the existing model-level defense methods degrade the training efficiency and model performance. To address this problem, we propose SkyMask, a new attack-agnostic robust FL system that leverages fine-grained learnable masks to identify malicious model updates at the parameter-level. Specifically, the FL server applies parameter-level masks to model updates uploaded by clients and trains the masks over a small clean dataset (i.e., root dataset) to learn the subtle difference between benign and malicious model updates in a high-dimension space. Our extensive experiments involve different models on three public datasets under state-of-the-art (SOTA) attacks, where the results show that SkyMask achieves up to 10% higher testing accuracy compared with SOTA defense strategies and successfully defends against attacks with malicious clients of a high fraction up to 80%. In the meantime, the experimental results demonstrate the scalability of our approach and the weak dependence on the data distribution of the root dataset.
PFLlib: Personalized Federated Learning Algorithm Library
Dec 08, 2023

Abstract:Amid the ongoing advancements in Federated Learning (FL), a machine learning paradigm that allows collaborative learning with data privacy protection, personalized FL (pFL) has gained significant prominence as a research direction within the FL domain. Whereas traditional FL (tFL) focuses on jointly learning a global model, pFL aims to achieve a balance between the global and personalized objectives of each client in FL settings. To foster the pFL research community, we propose PFLlib, a comprehensive pFL algorithm library with an integrated evaluation platform. In PFLlib, We implement 34 state-of-the-art FL algorithms (including 7 classic tFL algorithms and 27 pFL algorithms) and provide various evaluation environments with three statistically heterogeneous scenarios and 14 datasets. At present, PFLlib has already gained 850 stars and 199 forks on GitHub.
Eliminating Domain Bias for Federated Learning in Representation Space
Nov 25, 2023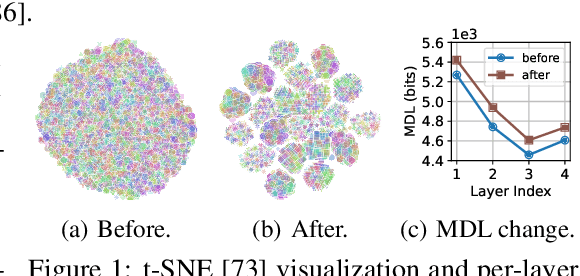
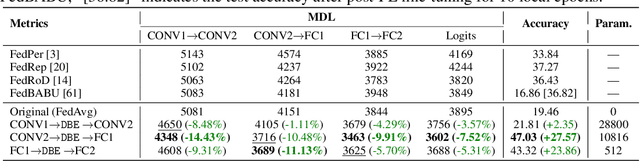
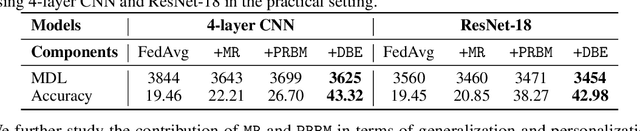
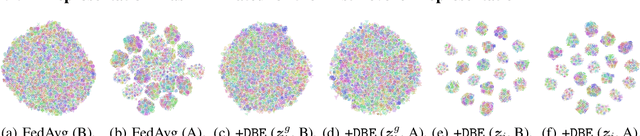
Abstract:Recently, federated learning (FL) is popular for its privacy-preserving and collaborative learning abilities. However, under statistically heterogeneous scenarios, we observe that biased data domains on clients cause a representation bias phenomenon and further degenerate generic representations during local training, i.e., the representation degeneration phenomenon. To address these issues, we propose a general framework Domain Bias Eliminator (DBE) for FL. Our theoretical analysis reveals that DBE can promote bi-directional knowledge transfer between server and client, as it reduces the domain discrepancy between server and client in representation space. Besides, extensive experiments on four datasets show that DBE can greatly improve existing FL methods in both generalization and personalization abilities. The DBE-equipped FL method can outperform ten state-of-the-art personalized FL methods by a large margin. Our code is public at https://github.com/TsingZ0/DBE.
GPFL: Simultaneously Learning Global and Personalized Feature Information for Personalized Federated Learning
Aug 20, 2023
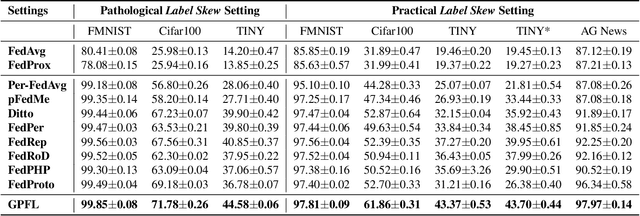
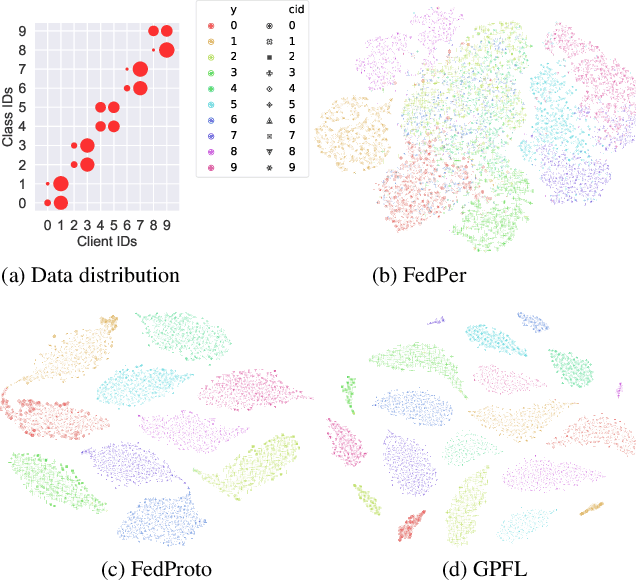
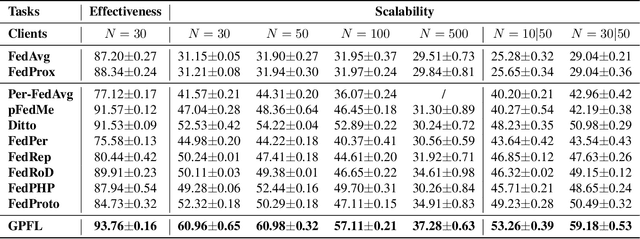
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is popular for its privacy-preserving and collaborative learning capabilities. Recently, personalized FL (pFL) has received attention for its ability to address statistical heterogeneity and achieve personalization in FL. However, from the perspective of feature extraction, most existing pFL methods only focus on extracting global or personalized feature information during local training, which fails to meet the collaborative learning and personalization goals of pFL. To address this, we propose a new pFL method, named GPFL, to simultaneously learn global and personalized feature information on each client. We conduct extensive experiments on six datasets in three statistically heterogeneous settings and show the superiority of GPFL over ten state-of-the-art methods regarding effectiveness, scalability, fairness, stability, and privacy. Besides, GPFL mitigates overfitting and outperforms the baselines by up to 8.99% in accuracy.
FedCP: Separating Feature Information for Personalized Federated Learning via Conditional Policy
Jul 01, 2023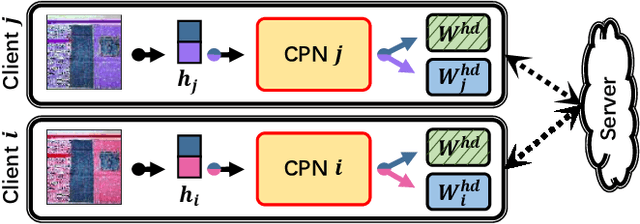

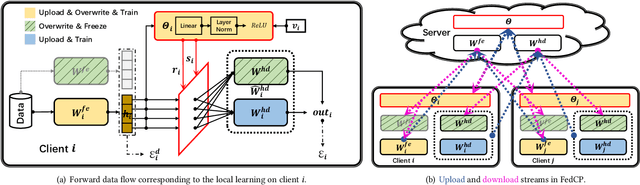
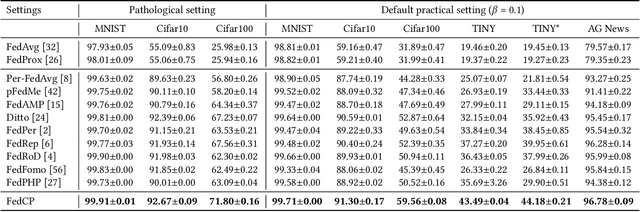
Abstract:Recently, personalized federated learning (pFL) has attracted increasing attention in privacy protection, collaborative learning, and tackling statistical heterogeneity among clients, e.g., hospitals, mobile smartphones, etc. Most existing pFL methods focus on exploiting the global information and personalized information in the client-level model parameters while neglecting that data is the source of these two kinds of information. To address this, we propose the Federated Conditional Policy (FedCP) method, which generates a conditional policy for each sample to separate the global information and personalized information in its features and then processes them by a global head and a personalized head, respectively. FedCP is more fine-grained to consider personalization in a sample-specific manner than existing pFL methods. Extensive experiments in computer vision and natural language processing domains show that FedCP outperforms eleven state-of-the-art methods by up to 6.69%. Furthermore, FedCP maintains its superiority when some clients accidentally drop out, which frequently happens in mobile settings. Our code is public at https://github.com/TsingZ0/FedCP.
Adversarial Example Does Good: Preventing Painting Imitation from Diffusion Models via Adversarial Examples
Feb 09, 2023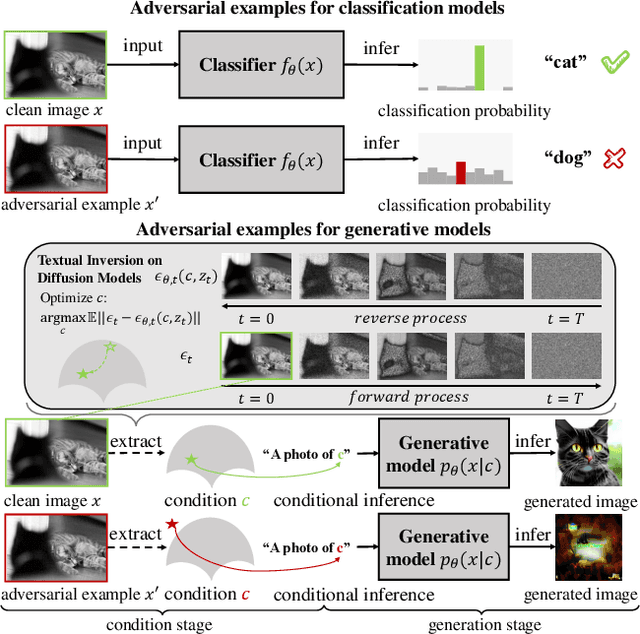
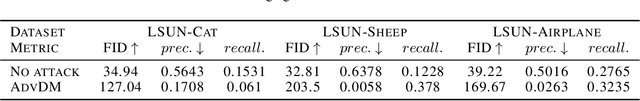
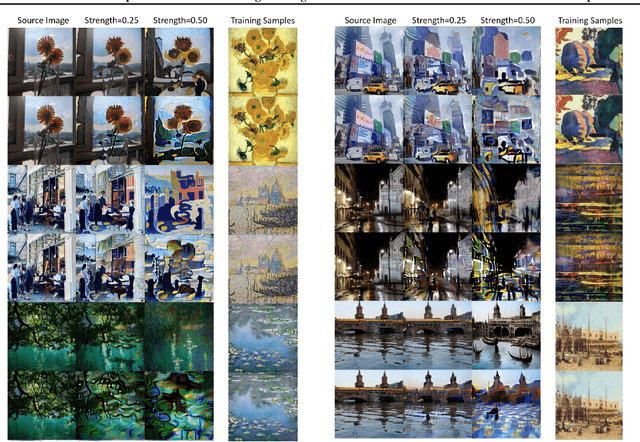
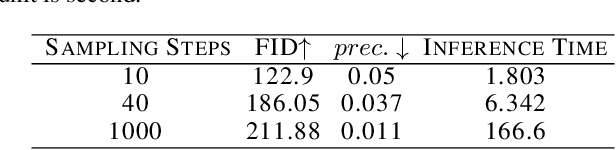
Abstract:Diffusion Models (DMs) achieve state-of-the-art performance in generative tasks, boosting a wave in AI for Art. Despite the success of commercialization, DMs meanwhile provide tools for copyright violations, where infringers benefit from illegally using paintings created by human artists to train DMs and generate novel paintings in a similar style. In this paper, we show that it is possible to create an image $x'$ that is similar to an image $x$ for human vision but unrecognizable for DMs. We build a framework to define and evaluate this adversarial example for diffusion models. Based on the framework, we further propose AdvDM, an algorithm to generate adversarial examples for DMs. By optimizing upon different latent variables sampled from the reverse process of DMs, AdvDM conducts a Monte-Carlo estimation of adversarial examples for DMs. Extensive experiments show that the estimated adversarial examples can effectively hinder DMs from extracting their features. Our method can be a powerful tool for human artists to protect their copyright against infringers with DM-based AI-for-Art applications.
FedALA: Adaptive Local Aggregation for Personalized Federated Learning
Dec 02, 2022



Abstract:A key challenge in federated learning (FL) is the statistical heterogeneity that impairs the generalization of the global model on each client. To address this, we propose a method Federated learning with Adaptive Local Aggregation (FedALA) by capturing the desired information in the global model for client models in personalized FL. The key component of FedALA is an Adaptive Local Aggregation (ALA) module, which can adaptively aggregate the downloaded global model and local model towards the local objective on each client to initialize the local model before training in each iteration. To evaluate the effectiveness of FedALA, we conduct extensive experiments with five benchmark datasets in computer vision and natural language processing domains. FedALA outperforms eleven state-of-the-art baselines by up to 3.27% in test accuracy. Furthermore, we also apply ALA module to other federated learning methods and achieve up to 24.19% improvement in test accuracy.
Fast and Accurate Scene Parsing via Bi-direction Alignment Networks
May 25, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we propose an effective method for fast and accurate scene parsing called Bidirectional Alignment Network (BiAlignNet). Previously, one representative work BiSeNet~\cite{bisenet} uses two different paths (Context Path and Spatial Path) to achieve balanced learning of semantics and details, respectively. However, the relationship between the two paths is not well explored. We argue that both paths can benefit each other in a complementary way. Motivated by this, we propose a novel network by aligning two-path information into each other through a learned flow field. To avoid the noise and semantic gaps, we introduce a Gated Flow Alignment Module to align both features in a bidirectional way. Moreover, to make the Spatial Path learn more detailed information, we present an edge-guided hard pixel mining loss to supervise the aligned learning process. Our method achieves 80.1\% and 78.5\% mIoU in validation and test set of Cityscapes while running at 30 FPS with full resolution inputs. Code and models will be available at \url{https://github.com/jojacola/BiAlignNet}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge