Roy Rinberg
Beyond Laplace and Gaussian: Exploring the Generalized Gaussian Mechanism for Private Machine Learning
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Differential privacy (DP) is obtained by randomizing a data analysis algorithm, which necessarily introduces a tradeoff between its utility and privacy. Many DP mechanisms are built upon one of two underlying tools: Laplace and Gaussian additive noise mechanisms. We expand the search space of algorithms by investigating the Generalized Gaussian mechanism, which samples the additive noise term $x$ with probability proportional to $e^{-\frac{| x |}{\sigma}^{\beta} }$ for some $\beta \geq 1$. The Laplace and Gaussian mechanisms are special cases of GG for $\beta=1$ and $\beta=2$, respectively. In this work, we prove that all members of the GG family satisfy differential privacy, and provide an extension of an existing numerical accountant (the PRV accountant) for these mechanisms. We show that privacy accounting for the GG Mechanism and its variants is dimension independent, which substantially improves computational costs of privacy accounting. We apply the GG mechanism to two canonical tools for private machine learning, PATE and DP-SGD; we show empirically that $\beta$ has a weak relationship with test-accuracy, and that generally $\beta=2$ (Gaussian) is nearly optimal. This provides justification for the widespread adoption of the Gaussian mechanism in DP learning, and can be interpreted as a negative result, that optimizing over $\beta$ does not lead to meaningful improvements in performance.
Attribute-to-Delete: Machine Unlearning via Datamodel Matching
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Machine unlearning -- efficiently removing the effect of a small "forget set" of training data on a pre-trained machine learning model -- has recently attracted significant research interest. Despite this interest, however, recent work shows that existing machine unlearning techniques do not hold up to thorough evaluation in non-convex settings. In this work, we introduce a new machine unlearning technique that exhibits strong empirical performance even in such challenging settings. Our starting point is the perspective that the goal of unlearning is to produce a model whose outputs are statistically indistinguishable from those of a model re-trained on all but the forget set. This perspective naturally suggests a reduction from the unlearning problem to that of data attribution, where the goal is to predict the effect of changing the training set on a model's outputs. Thus motivated, we propose the following meta-algorithm, which we call Datamodel Matching (DMM): given a trained model, we (a) use data attribution to predict the output of the model if it were re-trained on all but the forget set points; then (b) fine-tune the pre-trained model to match these predicted outputs. In a simple convex setting, we show how this approach provably outperforms a variety of iterative unlearning algorithms. Empirically, we use a combination of existing evaluations and a new metric based on the KL-divergence to show that even in non-convex settings, DMM achieves strong unlearning performance relative to existing algorithms. An added benefit of DMM is that it is a meta-algorithm, in the sense that future advances in data attribution translate directly into better unlearning algorithms, pointing to a clear direction for future progress in unlearning.
Have it your way: Individualized Privacy Assignment for DP-SGD
Mar 29, 2023Abstract:When training a machine learning model with differential privacy, one sets a privacy budget. This budget represents a maximal privacy violation that any user is willing to face by contributing their data to the training set. We argue that this approach is limited because different users may have different privacy expectations. Thus, setting a uniform privacy budget across all points may be overly conservative for some users or, conversely, not sufficiently protective for others. In this paper, we capture these preferences through individualized privacy budgets. To demonstrate their practicality, we introduce a variant of Differentially Private Stochastic Gradient Descent (DP-SGD) which supports such individualized budgets. DP-SGD is the canonical approach to training models with differential privacy. We modify its data sampling and gradient noising mechanisms to arrive at our approach, which we call Individualized DP-SGD (IDP-SGD). Because IDP-SGD provides privacy guarantees tailored to the preferences of individual users and their data points, we find it empirically improves privacy-utility trade-offs.
NL-Augmenter: A Framework for Task-Sensitive Natural Language Augmentation
Dec 06, 2021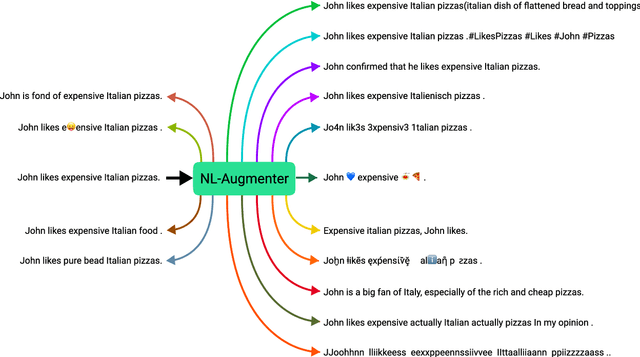
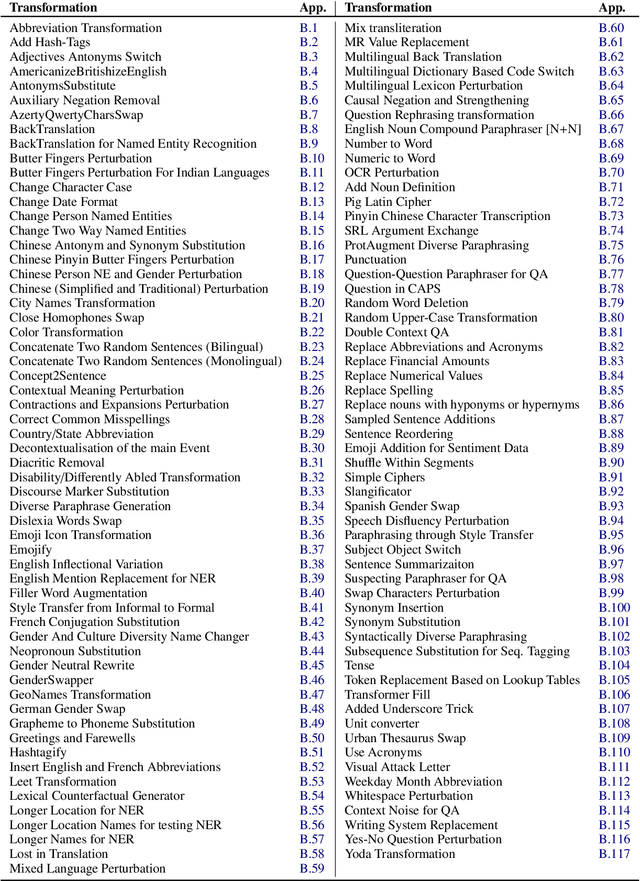
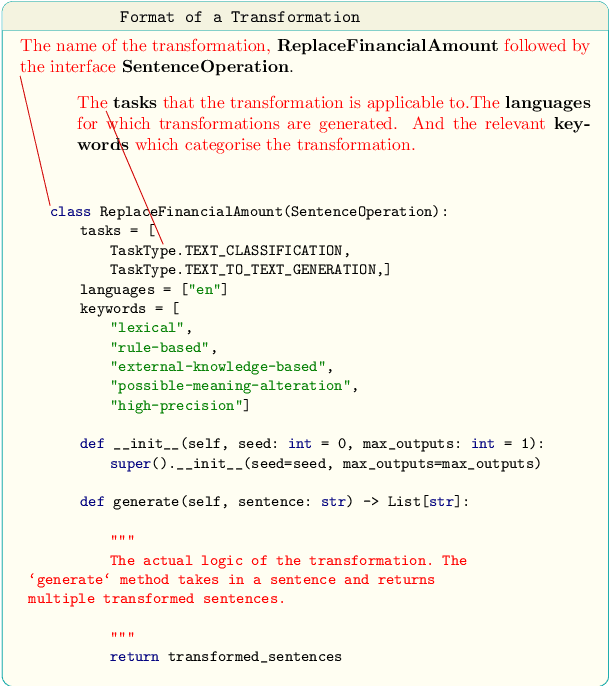
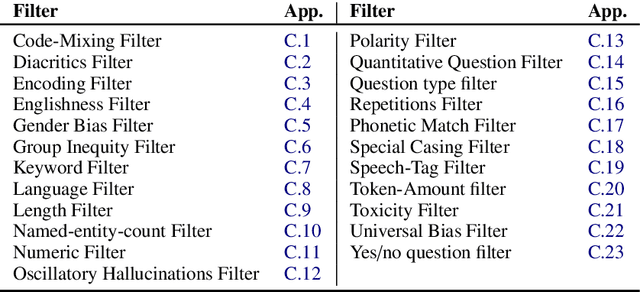
Abstract:Data augmentation is an important component in the robustness evaluation of models in natural language processing (NLP) and in enhancing the diversity of the data they are trained on. In this paper, we present NL-Augmenter, a new participatory Python-based natural language augmentation framework which supports the creation of both transformations (modifications to the data) and filters (data splits according to specific features). We describe the framework and an initial set of 117 transformations and 23 filters for a variety of natural language tasks. We demonstrate the efficacy of NL-Augmenter by using several of its transformations to analyze the robustness of popular natural language models. The infrastructure, datacards and robustness analysis results are available publicly on the NL-Augmenter repository (\url{https://github.com/GEM-benchmark/NL-Augmenter}).
Creolizing the Web
Feb 24, 2021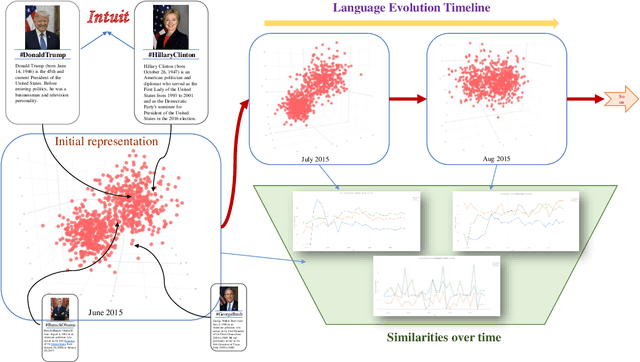
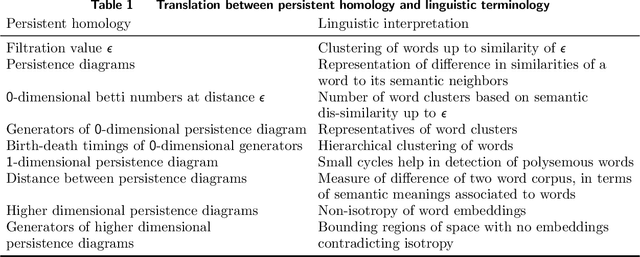
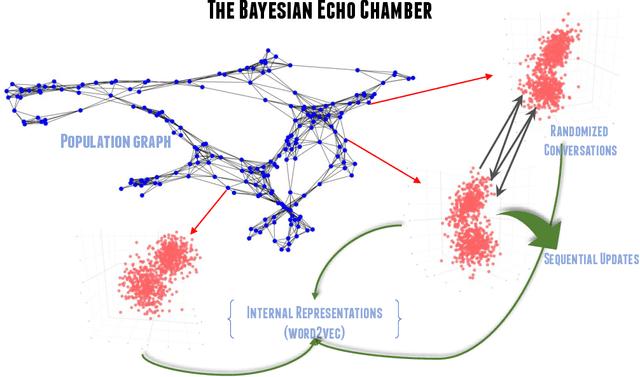
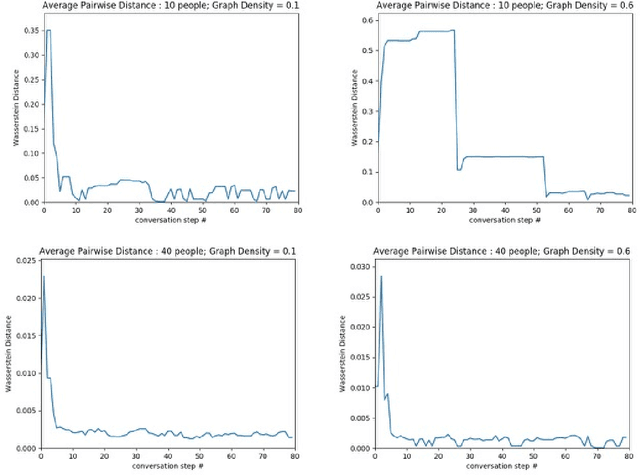
Abstract:The evolution of language has been a hotly debated subject with contradicting hypotheses and unreliable claims. Drawing from signalling games, dynamic population mechanics, machine learning and algebraic topology, we present a method for detecting evolutionary patterns in a sociological model of language evolution. We develop a minimalistic model that provides a rigorous base for any generalized evolutionary model for language based on communication between individuals. We also discuss theoretical guarantees of this model, ranging from stability of language representations to fast convergence of language by temporal communication and language drift in an interactive setting. Further we present empirical results and their interpretations on a real world dataset from \rdt to identify communities and echo chambers for opinions, thus placing obstructions to reliable communication among communities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge