Ronak Pradeep
Michael Pokorny
NeuCLIRTech: Chinese Monolingual and Cross-Language Information Retrieval Evaluation in a Challenging Domain
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Measuring advances in retrieval requires test collections with relevance judgments that can faithfully distinguish systems. This paper presents NeuCLIRTech, an evaluation collection for cross-language retrieval over technical information. The collection consists of technical documents written natively in Chinese and those same documents machine translated into English. It includes 110 queries with relevance judgments. The collection supports two retrieval scenarios: monolingual retrieval in Chinese, and cross-language retrieval with English as the query language. NeuCLIRTech combines the TREC NeuCLIR track topics of 2023 and 2024. The 110 queries with 35,962 document judgments provide strong statistical discriminatory power when trying to distinguish retrieval approaches. A fusion baseline of strong neural retrieval systems is included so that developers of reranking algorithms are not reliant on BM25 as their first stage retriever. The dataset and artifacts are released on Huggingface Datasets
NeuCLIRBench: A Modern Evaluation Collection for Monolingual, Cross-Language, and Multilingual Information Retrieval
Nov 18, 2025
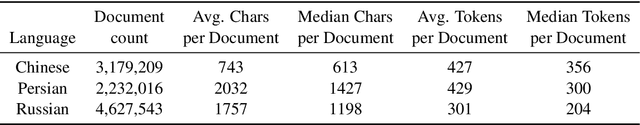
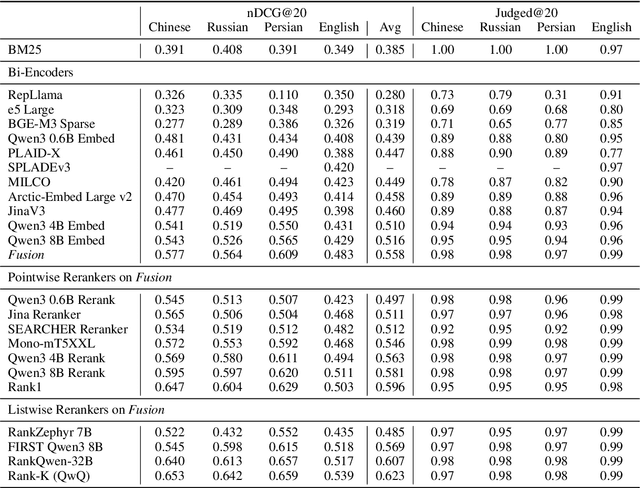
Abstract:To measure advances in retrieval, test collections with relevance judgments that can faithfully distinguish systems are required. This paper presents NeuCLIRBench, an evaluation collection for cross-language and multilingual retrieval. The collection consists of documents written natively in Chinese, Persian, and Russian, as well as those same documents machine translated into English. The collection supports several retrieval scenarios including: monolingual retrieval in English, Chinese, Persian, or Russian; cross-language retrieval with English as the query language and one of the other three languages as the document language; and multilingual retrieval, again with English as the query language and relevant documents in all three languages. NeuCLIRBench combines the TREC NeuCLIR track topics of 2022, 2023, and 2024. The 250,128 judgments across approximately 150 queries for the monolingual and cross-language tasks and 100 queries for multilingual retrieval provide strong statistical discriminatory power to distinguish retrieval approaches. A fusion baseline of strong neural retrieval systems is included with the collection so that developers of reranking algorithms are no longer reliant on BM25 as their first-stage retriever. NeuCLIRBench is publicly available.
RankLLM: A Python Package for Reranking with LLMs
May 25, 2025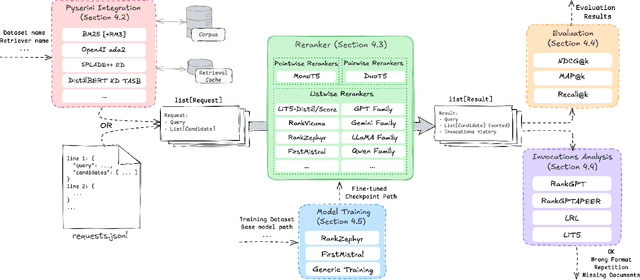
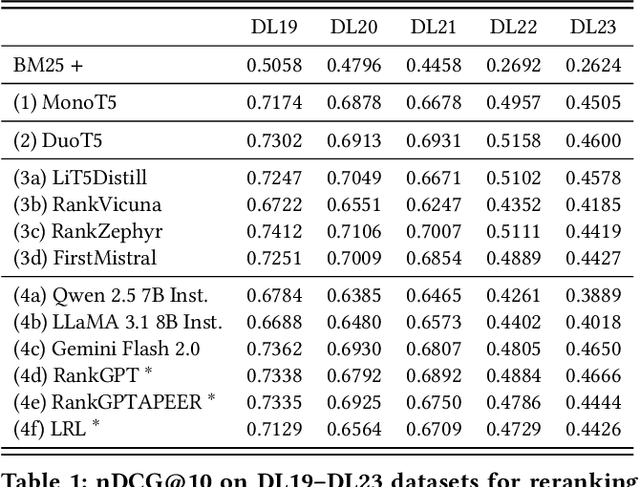
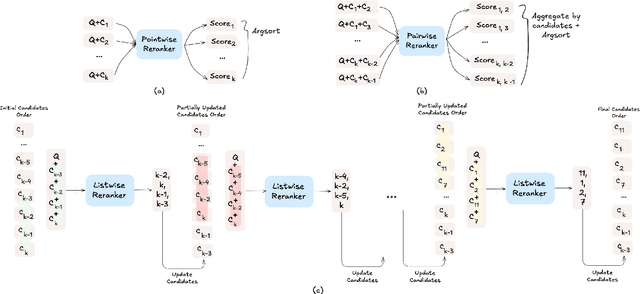
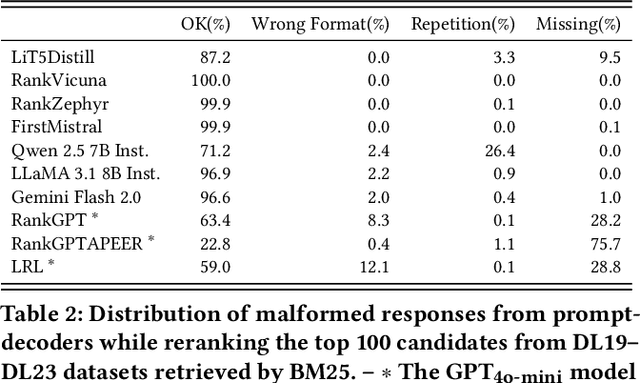
Abstract:The adoption of large language models (LLMs) as rerankers in multi-stage retrieval systems has gained significant traction in academia and industry. These models refine a candidate list of retrieved documents, often through carefully designed prompts, and are typically used in applications built on retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). This paper introduces RankLLM, an open-source Python package for reranking that is modular, highly configurable, and supports both proprietary and open-source LLMs in customized reranking workflows. To improve usability, RankLLM features optional integration with Pyserini for retrieval and provides integrated evaluation for multi-stage pipelines. Additionally, RankLLM includes a module for detailed analysis of input prompts and LLM responses, addressing reliability concerns with LLM APIs and non-deterministic behavior in Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models. This paper presents the architecture of RankLLM, along with a detailed step-by-step guide and sample code. We reproduce results from RankGPT, LRL, RankVicuna, RankZephyr, and other recent models. RankLLM integrates with common inference frameworks and a wide range of LLMs. This compatibility allows for quick reproduction of reported results, helping to speed up both research and real-world applications. The complete repository is available at rankllm.ai, and the package can be installed via PyPI.
Chatbot Arena Meets Nuggets: Towards Explanations and Diagnostics in the Evaluation of LLM Responses
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Battles, or side-by-side comparisons in so called arenas that elicit human preferences, have emerged as a popular approach to assessing the output quality of LLMs. Recently, this idea has been extended to retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems. While undoubtedly representing an advance in evaluation, battles have at least two drawbacks, particularly in the context of complex information-seeking queries: they are neither explanatory nor diagnostic. Recently, the nugget evaluation methodology has emerged as a promising approach to evaluate the quality of RAG answers. Nuggets decompose long-form LLM-generated answers into atomic facts, highlighting important pieces of information necessary in a "good" response. In this work, we apply our AutoNuggetizer framework to analyze data from roughly 7K Search Arena battles provided by LMArena in a fully automatic manner. Our results show a significant correlation between nugget scores and human preferences, showcasing promise in our approach to explainable and diagnostic system evaluations.
The Great Nugget Recall: Automating Fact Extraction and RAG Evaluation with Large Language Models
Apr 21, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced the capabilities of information access systems, especially with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). Nevertheless, the evaluation of RAG systems remains a barrier to continued progress, a challenge we tackle in this work by proposing an automatic evaluation framework that is validated against human annotations. We believe that the nugget evaluation methodology provides a solid foundation for evaluating RAG systems. This approach, originally developed for the TREC Question Answering (QA) Track in 2003, evaluates systems based on atomic facts that should be present in good answers. Our efforts focus on "refactoring" this methodology, where we describe the AutoNuggetizer framework that specifically applies LLMs to both automatically create nuggets and automatically assign nuggets to system answers. In the context of the TREC 2024 RAG Track, we calibrate a fully automatic approach against strategies where nuggets are created manually or semi-manually by human assessors and then assigned manually to system answers. Based on results from a community-wide evaluation, we observe strong agreement at the run level between scores derived from fully automatic nugget evaluation and human-based variants. The agreement is stronger when individual framework components such as nugget assignment are automated independently. This suggests that our evaluation framework provides tradeoffs between effort and quality that can be used to guide the development of future RAG systems. However, further research is necessary to refine our approach, particularly in establishing robust per-topic agreement to diagnose system failures effectively.
Support Evaluation for the TREC 2024 RAG Track: Comparing Human versus LLM Judges
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) enables large language models (LLMs) to generate answers with citations from source documents containing "ground truth", thereby reducing system hallucinations. A crucial factor in RAG evaluation is "support", whether the information in the cited documents supports the answer. To this end, we conducted a large-scale comparative study of 45 participant submissions on 36 topics to the TREC 2024 RAG Track, comparing an automatic LLM judge (GPT-4o) against human judges for support assessment. We considered two conditions: (1) fully manual assessments from scratch and (2) manual assessments with post-editing of LLM predictions. Our results indicate that for 56% of the manual from-scratch assessments, human and GPT-4o predictions match perfectly (on a three-level scale), increasing to 72% in the manual with post-editing condition. Furthermore, by carefully analyzing the disagreements in an unbiased study, we found that an independent human judge correlates better with GPT-4o than a human judge, suggesting that LLM judges can be a reliable alternative for support assessment. To conclude, we provide a qualitative analysis of human and GPT-4o errors to help guide future iterations of support assessment.
Humanity's Last Exam
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Benchmarks are important tools for tracking the rapid advancements in large language model (LLM) capabilities. However, benchmarks are not keeping pace in difficulty: LLMs now achieve over 90\% accuracy on popular benchmarks like MMLU, limiting informed measurement of state-of-the-art LLM capabilities. In response, we introduce Humanity's Last Exam (HLE), a multi-modal benchmark at the frontier of human knowledge, designed to be the final closed-ended academic benchmark of its kind with broad subject coverage. HLE consists of 3,000 questions across dozens of subjects, including mathematics, humanities, and the natural sciences. HLE is developed globally by subject-matter experts and consists of multiple-choice and short-answer questions suitable for automated grading. Each question has a known solution that is unambiguous and easily verifiable, but cannot be quickly answered via internet retrieval. State-of-the-art LLMs demonstrate low accuracy and calibration on HLE, highlighting a significant gap between current LLM capabilities and the expert human frontier on closed-ended academic questions. To inform research and policymaking upon a clear understanding of model capabilities, we publicly release HLE at https://lastexam.ai.
Initial Nugget Evaluation Results for the TREC 2024 RAG Track with the AutoNuggetizer Framework
Nov 14, 2024

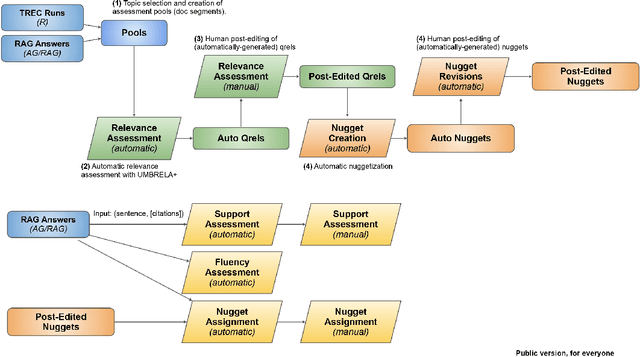

Abstract:This report provides an initial look at partial results from the TREC 2024 Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Track. We have identified RAG evaluation as a barrier to continued progress in information access (and more broadly, natural language processing and artificial intelligence), and it is our hope that we can contribute to tackling the many challenges in this space. The central hypothesis we explore in this work is that the nugget evaluation methodology, originally developed for the TREC Question Answering Track in 2003, provides a solid foundation for evaluating RAG systems. As such, our efforts have focused on "refactoring" this methodology, specifically applying large language models to both automatically create nuggets and to automatically assign nuggets to system answers. We call this the AutoNuggetizer framework. Within the TREC setup, we are able to calibrate our fully automatic process against a manual process whereby nuggets are created by human assessors semi-manually and then assigned manually to system answers. Based on initial results across 21 topics from 45 runs, we observe a strong correlation between scores derived from a fully automatic nugget evaluation and a (mostly) manual nugget evaluation by human assessors. This suggests that our fully automatic evaluation process can be used to guide future iterations of RAG systems.
A Large-Scale Study of Relevance Assessments with Large Language Models: An Initial Look
Nov 13, 2024Abstract:The application of large language models to provide relevance assessments presents exciting opportunities to advance information retrieval, natural language processing, and beyond, but to date many unknowns remain. This paper reports on the results of a large-scale evaluation (the TREC 2024 RAG Track) where four different relevance assessment approaches were deployed in situ: the "standard" fully manual process that NIST has implemented for decades and three different alternatives that take advantage of LLMs to different extents using the open-source UMBRELA tool. This setup allows us to correlate system rankings induced by the different approaches to characterize tradeoffs between cost and quality. We find that in terms of nDCG@20, nDCG@100, and Recall@100, system rankings induced by automatically generated relevance assessments from UMBRELA correlate highly with those induced by fully manual assessments across a diverse set of 77 runs from 19 teams. Our results suggest that automatically generated UMBRELA judgments can replace fully manual judgments to accurately capture run-level effectiveness. Surprisingly, we find that LLM assistance does not appear to increase correlation with fully manual assessments, suggesting that costs associated with human-in-the-loop processes do not bring obvious tangible benefits. Overall, human assessors appear to be stricter than UMBRELA in applying relevance criteria. Our work validates the use of LLMs in academic TREC-style evaluations and provides the foundation for future studies.
An Early FIRST Reproduction and Improvements to Single-Token Decoding for Fast Listwise Reranking
Nov 08, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances have demonstrated that large language models (LLMs) excel as listwise rerankers, but their high computational demands remain a barrier to widespread adoption. Further, the traditional language modeling (LM) objective is not ideally suited for reranking tasks. FIRST is a novel approach that addresses these challenges by integrating a learning-to-rank objective and leveraging the logits of only the first generated token, thereby significantly reducing inference latency compared to traditional LLM rerankers. In this study, we extend the evaluation of FIRST to the TREC Deep Learning datasets (DL19-22), validating its robustness across diverse domains. We investigate the influence of different first-stage retrievers on FIRST rerankers, observing diminishing returns and patterns consistent with traditional LLM rerankers. Through applying the FIRST objective to a broader range of backbone models, we achieve effectiveness surpassing the original implementation. Our experiments confirm that fast reranking with single-token logits does not compromise out-of-domain reranking quality. To better quantify the computational savings in the original study, we measure and compare latency to find a 21%-42% gain across various models and benchmarks. Moreover, while LM training implicitly improves zero-shot single-token reranking, our experiments also raise questions about whether LM pre-training may hinder subsequent fine-tuning with the FIRST objective. These findings pave the way for more efficient and effective listwise reranking in future applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge