Qifei Li
KPLM-STA: Physically-Accurate Shadow Synthesis for Human Relighting via Keypoint-Based Light Modeling
Nov 11, 2025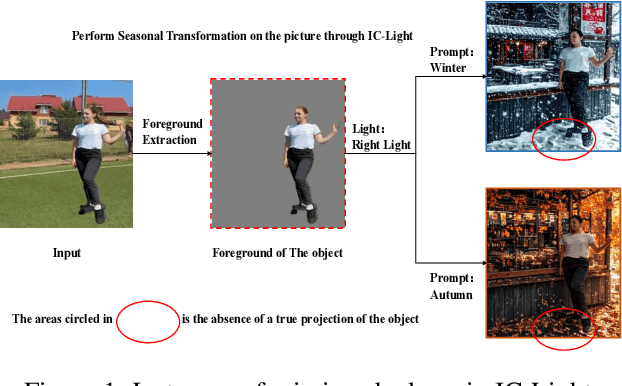
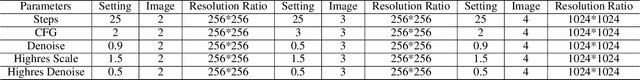

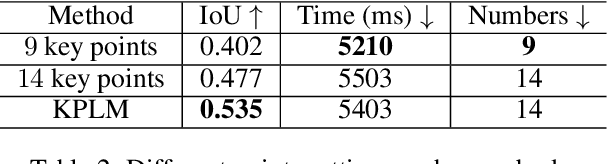
Abstract:Image composition aims to seamlessly integrate a foreground object into a background, where generating realistic and geometrically accurate shadows remains a persistent challenge. While recent diffusion-based methods have outperformed GAN-based approaches, existing techniques, such as the diffusion-based relighting framework IC-Light, still fall short in producing shadows with both high appearance realism and geometric precision, especially in composite images. To address these limitations, we propose a novel shadow generation framework based on a Keypoints Linear Model (KPLM) and a Shadow Triangle Algorithm (STA). KPLM models articulated human bodies using nine keypoints and one bounding block, enabling physically plausible shadow projection and dynamic shading across joints, thereby enhancing visual realism. STA further improves geometric accuracy by computing shadow angles, lengths, and spatial positions through explicit geometric formulations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on shadow realism benchmarks, particularly under complex human poses, and generalizes effectively to multi-directional relighting scenarios such as those supported by IC-Light.
LoD: Loss-difference OOD Detection by Intentionally Label-Noisifying Unlabeled Wild Data
May 19, 2025Abstract:Using unlabeled wild data containing both in-distribution (ID) and out-of-distribution (OOD) data to improve the safety and reliability of models has recently received increasing attention. Existing methods either design customized losses for labeled ID and unlabeled wild data then perform joint optimization, or first filter out OOD data from the latter then learn an OOD detector. While achieving varying degrees of success, two potential issues remain: (i) Labeled ID data typically dominates the learning of models, inevitably making models tend to fit OOD data as IDs; (ii) The selection of thresholds for identifying OOD data in unlabeled wild data usually faces dilemma due to the unavailability of pure OOD samples. To address these issues, we propose a novel loss-difference OOD detection framework (LoD) by \textit{intentionally label-noisifying} unlabeled wild data. Such operations not only enable labeled ID data and OOD data in unlabeled wild data to jointly dominate the models' learning but also ensure the distinguishability of the losses between ID and OOD samples in unlabeled wild data, allowing the classic clustering technique (e.g., K-means) to filter these OOD samples without requiring thresholds any longer. We also provide theoretical foundation for LoD's viability, and extensive experiments verify its superiority.
Enhancing Modal Fusion by Alignment and Label Matching for Multimodal Emotion Recognition
Aug 18, 2024Abstract:To address the limitation in multimodal emotion recognition (MER) performance arising from inter-modal information fusion, we propose a novel MER framework based on multitask learning where fusion occurs after alignment, called Foal-Net. The framework is designed to enhance the effectiveness of modality fusion and includes two auxiliary tasks: audio-video emotion alignment (AVEL) and cross-modal emotion label matching (MEM). First, AVEL achieves alignment of emotional information in audio-video representations through contrastive learning. Then, a modal fusion network integrates the aligned features. Meanwhile, MEM assesses whether the emotions of the current sample pair are the same, providing assistance for modal information fusion and guiding the model to focus more on emotional information. The experimental results conducted on IEMOCAP corpus show that Foal-Net outperforms the state-of-the-art methods and emotion alignment is necessary before modal fusion.
Frame-level emotional state alignment method for speech emotion recognition
Dec 27, 2023Abstract:Speech emotion recognition (SER) systems aim to recognize human emotional state during human-computer interaction. Most existing SER systems are trained based on utterance-level labels. However, not all frames in an audio have affective states consistent with utterance-level label, which makes it difficult for the model to distinguish the true emotion of the audio and perform poorly. To address this problem, we propose a frame-level emotional state alignment method for SER. First, we fine-tune HuBERT model to obtain a SER system with task-adaptive pretraining (TAPT) method, and extract embeddings from its transformer layers to form frame-level pseudo-emotion labels with clustering. Then, the pseudo labels are used to pretrain HuBERT. Hence, the each frame output of HuBERT has corresponding emotional information. Finally, we fine-tune the above pretrained HuBERT for SER by adding an attention layer on the top of it, which can focus only on those frames that are emotionally more consistent with utterance-level label. The experimental results performed on IEMOCAP indicate that our proposed method performs better than state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods.
CONCSS: Contrastive-based Context Comprehension for Dialogue-appropriate Prosody in Conversational Speech Synthesis
Dec 16, 2023Abstract:Conversational speech synthesis (CSS) incorporates historical dialogue as supplementary information with the aim of generating speech that has dialogue-appropriate prosody. While previous methods have already delved into enhancing context comprehension, context representation still lacks effective representation capabilities and context-sensitive discriminability. In this paper, we introduce a contrastive learning-based CSS framework, CONCSS. Within this framework, we define an innovative pretext task specific to CSS that enables the model to perform self-supervised learning on unlabeled conversational datasets to boost the model's context understanding. Additionally, we introduce a sampling strategy for negative sample augmentation to enhance context vectors' discriminability. This is the first attempt to integrate contrastive learning into CSS. We conduct ablation studies on different contrastive learning strategies and comprehensive experiments in comparison with prior CSS systems. Results demonstrate that the synthesized speech from our proposed method exhibits more contextually appropriate and sensitive prosody.
Learning to Predict Persona Information forDialogue Personalization without Explicit Persona Description
Nov 30, 2021



Abstract:Personalizing dialogue agents is important for dialogue systems to generate more specific, consistent, and engaging responses. However, most current dialogue personalization approaches rely on explicit persona descriptions during inference, which severely restricts its application. In this paper, we propose a novel approach that learns to predict persona information based on the dialogue history to personalize the dialogue agent without relying on any explicit persona descriptions during inference. Experimental results on the PersonaChat dataset show that the proposed method can improve the consistency of generated responses when conditioning on the predicted profile of the dialogue agent (i.e. "self persona"), and improve the engagingness of the generated responses when conditioning on the predicted persona of the dialogue partner (i.e. "their persona"). We also find that a trained persona prediction model can be successfully transferred to other datasets and help generate more relevant responses.
Learning from Perturbations: Diverse and Informative Dialogue Generation with Inverse Adversarial Training
May 31, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we propose Inverse Adversarial Training (IAT) algorithm for training neural dialogue systems to avoid generic responses and model dialogue history better. In contrast to standard adversarial training algorithms, IAT encourages the model to be sensitive to the perturbation in the dialogue history and therefore learning from perturbations. By giving higher rewards for responses whose output probability reduces more significantly when dialogue history is perturbed, the model is encouraged to generate more diverse and consistent responses. By penalizing the model when generating the same response given perturbed dialogue history, the model is forced to better capture dialogue history and generate more informative responses. Experimental results on two benchmark datasets show that our approach can better model dialogue history and generate more diverse and consistent responses. In addition, we point out a problem of the widely used maximum mutual information (MMI) based methods for improving the diversity of dialogue response generation models and demonstrate it empirically.
DebiasedRec: Bias-aware User Modeling and Click Prediction for Personalized News Recommendation
Apr 15, 2021



Abstract:News recommendation is critical for personalized news access. Existing news recommendation methods usually infer users' personal interest based on their historical clicked news, and train the news recommendation models by predicting future news clicks. A core assumption behind these methods is that news click behaviors can indicate user interest. However, in practical scenarios, beyond the relevance between user interest and news content, the news click behaviors may also be affected by other factors, such as the bias of news presentation in the online platform. For example, news with higher positions and larger sizes are usually more likely to be clicked. The bias of clicked news may bring noises to user interest modeling and model training, which may hurt the performance of the news recommendation model. In this paper, we propose a bias-aware personalized news recommendation method named DebiasRec, which can handle the bias information for more accurate user interest inference and model training. The core of our method includes a bias representation module, a bias-aware user modeling module, and a bias-aware click prediction module. The bias representation module is used to model different kinds of news bias and their interactions to capture their joint effect on click behaviors. The bias-aware user modeling module aims to infer users' debiased interest from the clicked news articles by using their bias information to calibrate the interest model. The bias-aware click prediction module is used to train a debiased news recommendation model from the biased click behaviors, where the click score is decomposed into a preference score indicating user's interest in the news content and a news bias score inferred from its different bias features. Experiments on two real-world datasets show that our method can effectively improve the performance of news recommendation.
Connecting the Dots Between Fact Verification and Fake News Detection
Oct 11, 2020



Abstract:Fact verification models have enjoyed a fast advancement in the last two years with the development of pre-trained language models like BERT and the release of large scale datasets such as FEVER. However, the challenging problem of fake news detection has not benefited from the improvement of fact verification models, which is closely related to fake news detection. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective approach to connect the dots between fact verification and fake news detection. Our approach first employs a text summarization model pre-trained on news corpora to summarize the long news article into a short claim. Then we use a fact verification model pre-trained on the FEVER dataset to detect whether the input news article is real or fake. Our approach makes use of the recent success of fact verification models and enables zero-shot fake news detection, alleviating the need of large-scale training data to train fake news detection models. Experimental results on FakenewsNet, a benchmark dataset for fake news detection, demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge