Jinlong Xue
MiMo-V2-Flash Technical Report
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We present MiMo-V2-Flash, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model with 309B total parameters and 15B active parameters, designed for fast, strong reasoning and agentic capabilities. MiMo-V2-Flash adopts a hybrid attention architecture that interleaves Sliding Window Attention (SWA) with global attention, with a 128-token sliding window under a 5:1 hybrid ratio. The model is pre-trained on 27 trillion tokens with Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), employing a native 32k context length and subsequently extended to 256k. To efficiently scale post-training compute, MiMo-V2-Flash introduces a novel Multi-Teacher On-Policy Distillation (MOPD) paradigm. In this framework, domain-specialized teachers (e.g., trained via large-scale reinforcement learning) provide dense and token-level reward, enabling the student model to perfectly master teacher expertise. MiMo-V2-Flash rivals top-tier open-weight models such as DeepSeek-V3.2 and Kimi-K2, despite using only 1/2 and 1/3 of their total parameters, respectively. During inference, by repurposing MTP as a draft model for speculative decoding, MiMo-V2-Flash achieves up to 3.6 acceptance length and 2.6x decoding speedup with three MTP layers. We open-source both the model weights and the three-layer MTP weights to foster open research and community collaboration.
MiMo-Audio: Audio Language Models are Few-Shot Learners
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Existing audio language models typically rely on task-specific fine-tuning to accomplish particular audio tasks. In contrast, humans are able to generalize to new audio tasks with only a few examples or simple instructions. GPT-3 has shown that scaling next-token prediction pretraining enables strong generalization capabilities in text, and we believe this paradigm is equally applicable to the audio domain. By scaling MiMo-Audio's pretraining data to over one hundred million of hours, we observe the emergence of few-shot learning capabilities across a diverse set of audio tasks. We develop a systematic evaluation of these capabilities and find that MiMo-Audio-7B-Base achieves SOTA performance on both speech intelligence and audio understanding benchmarks among open-source models. Beyond standard metrics, MiMo-Audio-7B-Base generalizes to tasks absent from its training data, such as voice conversion, style transfer, and speech editing. MiMo-Audio-7B-Base also demonstrates powerful speech continuation capabilities, capable of generating highly realistic talk shows, recitations, livestreaming and debates. At the post-training stage, we curate a diverse instruction-tuning corpus and introduce thinking mechanisms into both audio understanding and generation. MiMo-Audio-7B-Instruct achieves open-source SOTA on audio understanding benchmarks (MMSU, MMAU, MMAR, MMAU-Pro), spoken dialogue benchmarks (Big Bench Audio, MultiChallenge Audio) and instruct-TTS evaluations, approaching or surpassing closed-source models. Model checkpoints and full evaluation suite are available at https://github.com/XiaomiMiMo/MiMo-Audio.
Improving Audio Codec-based Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech Synthesis with Multi-Modal Context and Large Language Model
Jun 06, 2024


Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) and development of audio codecs greatly propel the zero-shot TTS. They can synthesize personalized speech with only a 3-second speech of an unseen speaker as acoustic prompt. However, they only support short speech prompts and cannot leverage longer context information, as required in audiobook and conversational TTS scenarios. In this paper, we introduce a novel audio codec-based TTS model to adapt context features with multiple enhancements. Inspired by the success of Qformer, we propose a multi-modal context-enhanced Qformer (MMCE-Qformer) to utilize additional multi-modal context information. Besides, we adapt a pretrained LLM to leverage its understanding ability to predict semantic tokens, and use a SoundStorm to generate acoustic tokens thereby enhancing audio quality and speaker similarity. The extensive objective and subjective evaluations show that our proposed method outperforms baselines across various context TTS scenarios.
Retrieval Augmented Generation in Prompt-based Text-to-Speech Synthesis with Context-Aware Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining
Jun 06, 2024Abstract:Recent prompt-based text-to-speech (TTS) models can clone an unseen speaker using only a short speech prompt. They leverage a strong in-context ability to mimic the speech prompts, including speaker style, prosody, and emotion. Therefore, the selection of a speech prompt greatly influences the generated speech, akin to the importance of a prompt in large language models (LLMs). However, current prompt-based TTS models choose the speech prompt manually or simply at random. Hence, in this paper, we adapt retrieval augmented generation (RAG) from LLMs to prompt-based TTS. Unlike traditional RAG methods, we additionally consider contextual information during the retrieval process and present a Context-Aware Contrastive Language-Audio Pre-training (CA-CLAP) model to extract context-aware, style-related features. The objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate that our proposed RAG method outperforms baselines, and our CA-CLAP achieves better results than text-only retrieval methods.
Auffusion: Leveraging the Power of Diffusion and Large Language Models for Text-to-Audio Generation
Jan 02, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in diffusion models and large language models (LLMs) have significantly propelled the field of AIGC. Text-to-Audio (TTA), a burgeoning AIGC application designed to generate audio from natural language prompts, is attracting increasing attention. However, existing TTA studies often struggle with generation quality and text-audio alignment, especially for complex textual inputs. Drawing inspiration from state-of-the-art Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models, we introduce Auffusion, a TTA system adapting T2I model frameworks to TTA task, by effectively leveraging their inherent generative strengths and precise cross-modal alignment. Our objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate that Auffusion surpasses previous TTA approaches using limited data and computational resource. Furthermore, previous studies in T2I recognizes the significant impact of encoder choice on cross-modal alignment, like fine-grained details and object bindings, while similar evaluation is lacking in prior TTA works. Through comprehensive ablation studies and innovative cross-attention map visualizations, we provide insightful assessments of text-audio alignment in TTA. Our findings reveal Auffusion's superior capability in generating audios that accurately match textual descriptions, which further demonstrated in several related tasks, such as audio style transfer, inpainting and other manipulations. Our implementation and demos are available at https://auffusion.github.io.
Frame-level emotional state alignment method for speech emotion recognition
Dec 27, 2023Abstract:Speech emotion recognition (SER) systems aim to recognize human emotional state during human-computer interaction. Most existing SER systems are trained based on utterance-level labels. However, not all frames in an audio have affective states consistent with utterance-level label, which makes it difficult for the model to distinguish the true emotion of the audio and perform poorly. To address this problem, we propose a frame-level emotional state alignment method for SER. First, we fine-tune HuBERT model to obtain a SER system with task-adaptive pretraining (TAPT) method, and extract embeddings from its transformer layers to form frame-level pseudo-emotion labels with clustering. Then, the pseudo labels are used to pretrain HuBERT. Hence, the each frame output of HuBERT has corresponding emotional information. Finally, we fine-tune the above pretrained HuBERT for SER by adding an attention layer on the top of it, which can focus only on those frames that are emotionally more consistent with utterance-level label. The experimental results performed on IEMOCAP indicate that our proposed method performs better than state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods.
CONCSS: Contrastive-based Context Comprehension for Dialogue-appropriate Prosody in Conversational Speech Synthesis
Dec 16, 2023Abstract:Conversational speech synthesis (CSS) incorporates historical dialogue as supplementary information with the aim of generating speech that has dialogue-appropriate prosody. While previous methods have already delved into enhancing context comprehension, context representation still lacks effective representation capabilities and context-sensitive discriminability. In this paper, we introduce a contrastive learning-based CSS framework, CONCSS. Within this framework, we define an innovative pretext task specific to CSS that enables the model to perform self-supervised learning on unlabeled conversational datasets to boost the model's context understanding. Additionally, we introduce a sampling strategy for negative sample augmentation to enhance context vectors' discriminability. This is the first attempt to integrate contrastive learning into CSS. We conduct ablation studies on different contrastive learning strategies and comprehensive experiments in comparison with prior CSS systems. Results demonstrate that the synthesized speech from our proposed method exhibits more contextually appropriate and sensitive prosody.
Rhythm-controllable Attention with High Robustness for Long Sentence Speech Synthesis
Jun 05, 2023



Abstract:Regressive Text-to-Speech (TTS) system utilizes attention mechanism to generate alignment between text and acoustic feature sequence. Alignment determines synthesis robustness (e.g, the occurence of skipping, repeating, and collapse) and rhythm via duration control. However, current attention algorithms used in speech synthesis cannot control rhythm using external duration information to generate natural speech while ensuring robustness. In this study, we propose Rhythm-controllable Attention (RC-Attention) based on Tracotron2, which improves robustness and naturalness simultaneously. Proposed attention adopts a trainable scalar learned from four kinds of information to achieve rhythm control, which makes rhythm control more robust and natural, even when synthesized sentences are extremely longer than training corpus. We use word errors counting and AB preference test to measure robustness of proposed method and naturalness of synthesized speech, respectively. Results shows that RC-Attention has the lowest word error rate of nearly 0.6%, compared with 11.8% for baseline system. Moreover, nearly 60% subjects prefer to the speech synthesized with RC-Attention to that with Forward Attention, because the former has more natural rhythm.
M2-CTTS: End-to-End Multi-scale Multi-modal Conversational Text-to-Speech Synthesis
May 03, 2023


Abstract:Conversational text-to-speech (TTS) aims to synthesize speech with proper prosody of reply based on the historical conversation. However, it is still a challenge to comprehensively model the conversation, and a majority of conversational TTS systems only focus on extracting global information and omit local prosody features, which contain important fine-grained information like keywords and emphasis. Moreover, it is insufficient to only consider the textual features, and acoustic features also contain various prosody information. Hence, we propose M2-CTTS, an end-to-end multi-scale multi-modal conversational text-to-speech system, aiming to comprehensively utilize historical conversation and enhance prosodic expression. More specifically, we design a textual context module and an acoustic context module with both coarse-grained and fine-grained modeling. Experimental results demonstrate that our model mixed with fine-grained context information and additionally considering acoustic features achieves better prosody performance and naturalness in CMOS tests.
A Keypoint Based Enhancement Method for Audio Driven Free View Talking Head Synthesis
Oct 07, 2022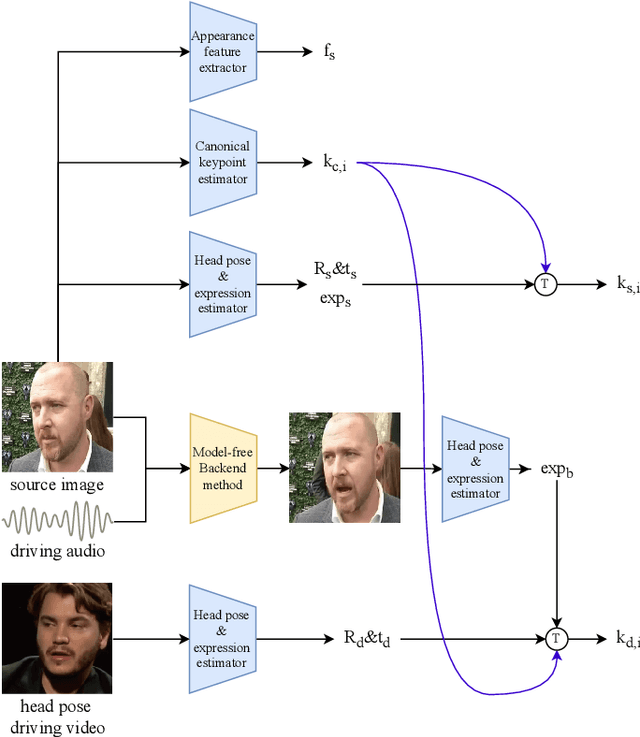
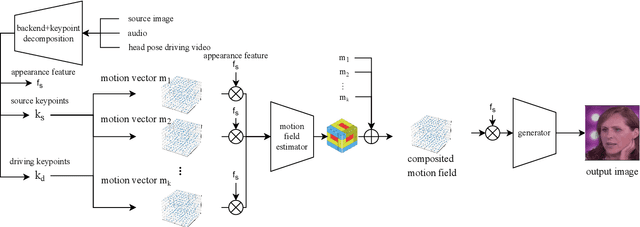


Abstract:Audio driven talking head synthesis is a challenging task that attracts increasing attention in recent years. Although existing methods based on 2D landmarks or 3D face models can synthesize accurate lip synchronization and rhythmic head pose for arbitrary identity, they still have limitations, such as the cut feeling in the mouth mapping and the lack of skin highlights. The morphed region is blurry compared to the surrounding face. A Keypoint Based Enhancement (KPBE) method is proposed for audio driven free view talking head synthesis to improve the naturalness of the generated video. Firstly, existing methods were used as the backend to synthesize intermediate results. Then we used keypoint decomposition to extract video synthesis controlling parameters from the backend output and the source image. After that, the controlling parameters were composited to the source keypoints and the driving keypoints. A motion field based method was used to generate the final image from the keypoint representation. With keypoint representation, we overcame the cut feeling in the mouth mapping and the lack of skin highlights. Experiments show that our proposed enhancement method improved the quality of talking-head videos in terms of mean opinion score.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge