Pierre Godard
Controlling Utterance Length in NMT-based Word Segmentation with Attention
Oct 18, 2019
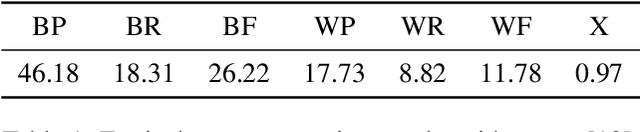


Abstract:One of the basic tasks of computational language documentation (CLD) is to identify word boundaries in an unsegmented phonemic stream. While several unsupervised monolingual word segmentation algorithms exist in the literature, they are challenged in real-world CLD settings by the small amount of available data. A possible remedy is to take advantage of glosses or translation in a foreign, well-resourced, language, which often exist for such data. In this paper, we explore and compare ways to exploit neural machine translation models to perform unsupervised boundary detection with bilingual information, notably introducing a new loss function for jointly learning alignment and segmentation. We experiment with an actual under-resourced language, Mboshi, and show that these techniques can effectively control the output segmentation length.
Unsupervised Word Segmentation from Speech with Attention
Jun 18, 2018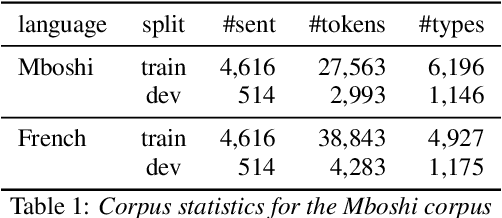

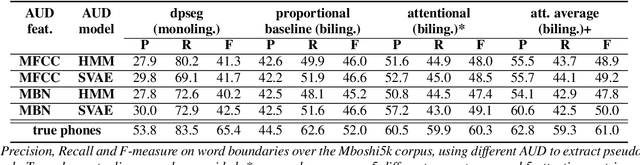
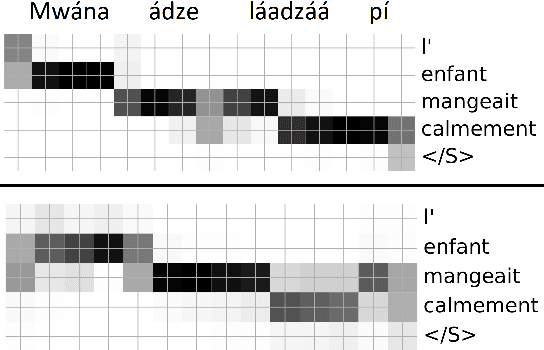
Abstract:We present a first attempt to perform attentional word segmentation directly from the speech signal, with the final goal to automatically identify lexical units in a low-resource, unwritten language (UL). Our methodology assumes a pairing between recordings in the UL with translations in a well-resourced language. It uses Acoustic Unit Discovery (AUD) to convert speech into a sequence of pseudo-phones that is segmented using neural soft-alignments produced by a neural machine translation model. Evaluation uses an actual Bantu UL, Mboshi; comparisons to monolingual and bilingual baselines illustrate the potential of attentional word segmentation for language documentation.
XNMT: The eXtensible Neural Machine Translation Toolkit
Mar 01, 2018
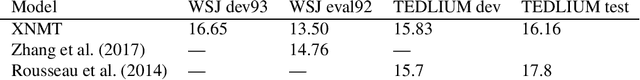

Abstract:This paper describes XNMT, the eXtensible Neural Machine Translation toolkit. XNMT distin- guishes itself from other open-source NMT toolkits by its focus on modular code design, with the purpose of enabling fast iteration in research and replicable, reliable results. In this paper we describe the design of XNMT and its experiment configuration system, and demonstrate its utility on the tasks of machine translation, speech recognition, and multi-tasked machine translation/parsing. XNMT is available open-source at https://github.com/neulab/xnmt
Bayesian Models for Unit Discovery on a Very Low Resource Language
Feb 20, 2018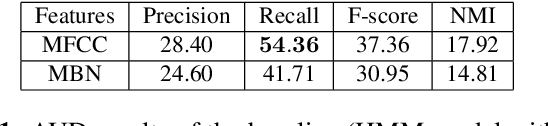
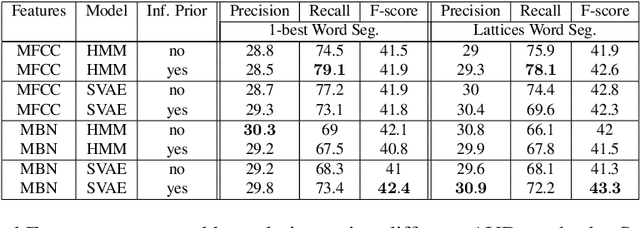
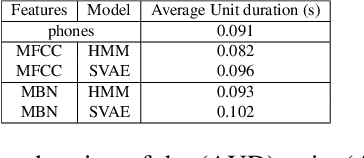
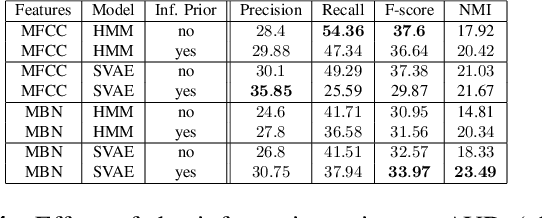
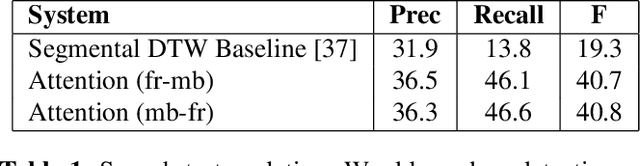
Abstract:Developing speech technologies for low-resource languages has become a very active research field over the last decade. Among others, Bayesian models have shown some promising results on artificial examples but still lack of in situ experiments. Our work applies state-of-the-art Bayesian models to unsupervised Acoustic Unit Discovery (AUD) in a real low-resource language scenario. We also show that Bayesian models can naturally integrate information from other resourceful languages by means of informative prior leading to more consistent discovered units. Finally, discovered acoustic units are used, either as the 1-best sequence or as a lattice, to perform word segmentation. Word segmentation results show that this Bayesian approach clearly outperforms a Segmental-DTW baseline on the same corpus.
Linguistic unit discovery from multi-modal inputs in unwritten languages: Summary of the "Speaking Rosetta" JSALT 2017 Workshop
Feb 14, 2018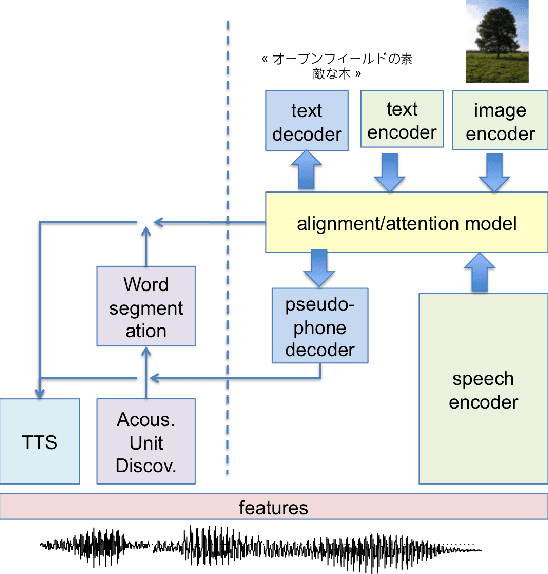
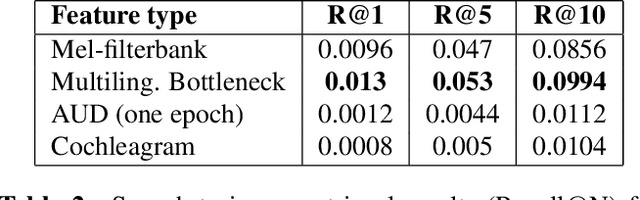
Abstract:We summarize the accomplishments of a multi-disciplinary workshop exploring the computational and scientific issues surrounding the discovery of linguistic units (subwords and words) in a language without orthography. We study the replacement of orthographic transcriptions by images and/or translated text in a well-resourced language to help unsupervised discovery from raw speech.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge