Peter Liu
Hamming Attention Distillation: Binarizing Keys and Queries for Efficient Long-Context Transformers
Feb 03, 2025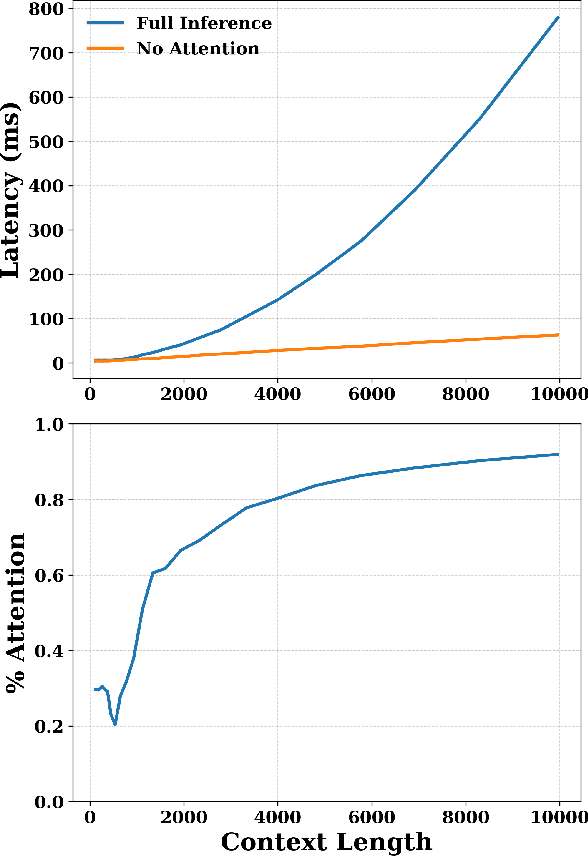
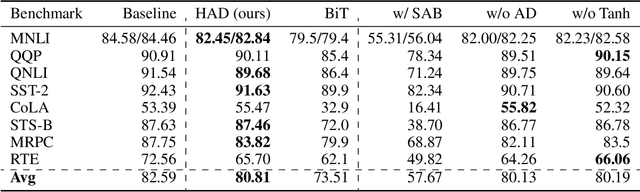
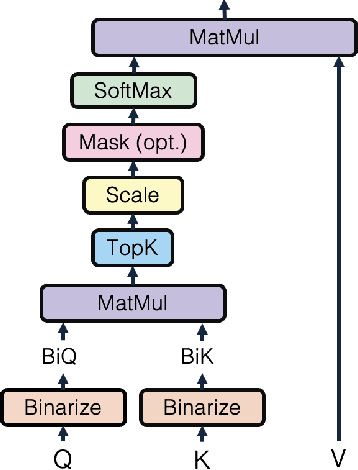
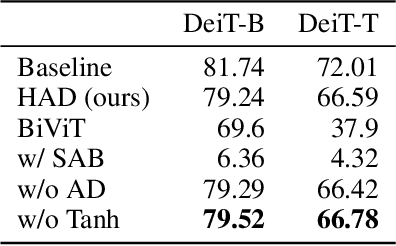
Abstract:Pre-trained transformer models with extended context windows are notoriously expensive to run at scale, often limiting real-world deployment due to their high computational and memory requirements. In this paper, we introduce Hamming Attention Distillation (HAD), a novel framework that binarizes keys and queries in the attention mechanism to achieve significant efficiency gains. By converting keys and queries into {-1, +1} vectors and replacing dot-product operations with efficient Hamming distance computations, our method drastically reduces computational overhead. Additionally, we incorporate attention matrix sparsification to prune low-impact activations, which further reduces the cost of processing long-context sequences. \par Despite these aggressive compression strategies, our distilled approach preserves a high degree of representational power, leading to substantially improved accuracy compared to prior transformer binarization methods. We evaluate HAD on a range of tasks and models, including the GLUE benchmark, ImageNet, and QuALITY, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance among binarized Transformers while drastically reducing the computational costs of long-context inference. \par We implement HAD in custom hardware simulations, demonstrating superior performance characteristics compared to a custom hardware implementation of standard attention. HAD achieves just $\mathbf{1.78}\%$ performance losses on GLUE compared to $9.08\%$ in state-of-the-art binarization work, and $\mathbf{2.5}\%$ performance losses on ImageNet compared to $12.14\%$, all while targeting custom hardware with a $\mathbf{79}\%$ area reduction and $\mathbf{87}\%$ power reduction compared to its standard attention counterpart.
Gemma 2: Improving Open Language Models at a Practical Size
Aug 02, 2024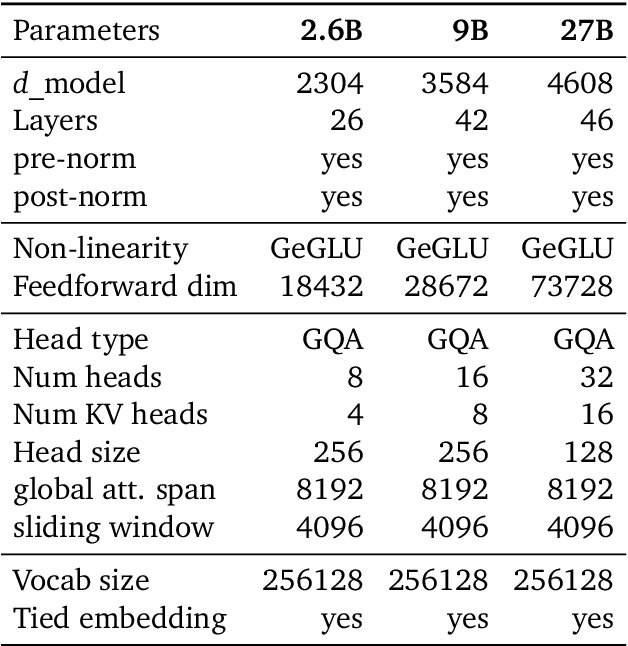
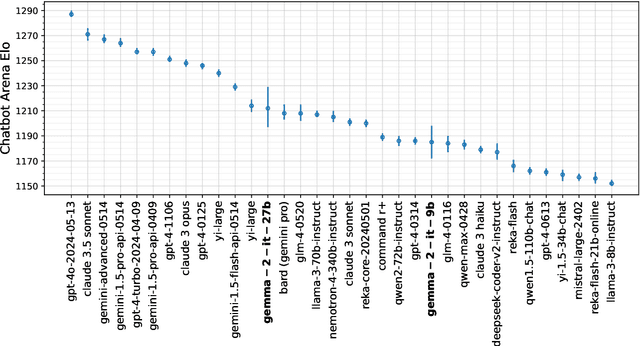
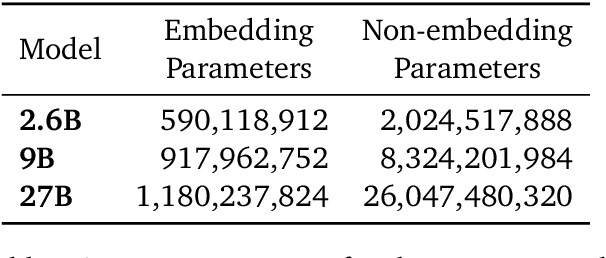
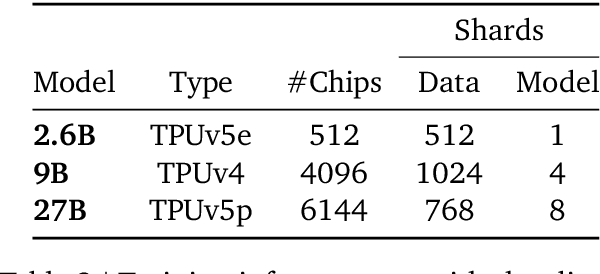
Abstract:In this work, we introduce Gemma 2, a new addition to the Gemma family of lightweight, state-of-the-art open models, ranging in scale from 2 billion to 27 billion parameters. In this new version, we apply several known technical modifications to the Transformer architecture, such as interleaving local-global attentions (Beltagy et al., 2020a) and group-query attention (Ainslie et al., 2023). We also train the 2B and 9B models with knowledge distillation (Hinton et al., 2015) instead of next token prediction. The resulting models deliver the best performance for their size, and even offer competitive alternatives to models that are 2-3 times bigger. We release all our models to the community.
A Multi-attribute Controllable Generative Model for Histopathology Image Synthesis
Nov 10, 2021



Abstract:Generative models have been applied in the medical imaging domain for various image recognition and synthesis tasks. However, a more controllable and interpretable image synthesis model is still lacking yet necessary for important applications such as assisting in medical training. In this work, we leverage the efficient self-attention and contrastive learning modules and build upon state-of-the-art generative adversarial networks (GANs) to achieve an attribute-aware image synthesis model, termed AttributeGAN, which can generate high-quality histopathology images based on multi-attribute inputs. In comparison to existing single-attribute conditional generative models, our proposed model better reflects input attributes and enables smoother interpolation among attribute values. We conduct experiments on a histopathology dataset containing stained H&E images of urothelial carcinoma and demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed model via comprehensive quantitative and qualitative comparisons with state-of-the-art models as well as different variants of our model. Code is available at https://github.com/karenyyy/MICCAI2021AttributeGAN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge