Patrick M. Pilarski
University of Alberta Department of Computing Science and Alberta Machine Intelligence Institute
Primate-like perceptual decision making emerges through deep recurrent reinforcement learning
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Progress has led to a detailed understanding of the neural mechanisms that underlie decision making in primates. However, less is known about why such mechanisms are present in the first place. Theory suggests that primate decision making mechanisms, and their resultant behavioral abilities, emerged to maximize reward in the face of noisy, temporally evolving information. To test this theory, we trained an end-to-end deep recurrent neural network using reinforcement learning on a noisy perceptual discrimination task. Networks learned several key abilities of primate-like decision making including trading off speed for accuracy, and flexibly changing their mind in the face of new information. Internal dynamics of these networks suggest that these abilities were supported by similar decision mechanisms as those observed in primate neurophysiological studies. These results provide experimental support for key pressures that gave rise to the primate ability to make flexible decisions.
Continually Learned Pavlovian Signalling Without Forgetting for Human-in-the-Loop Robotic Control
May 16, 2023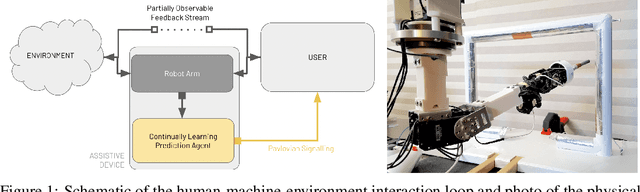
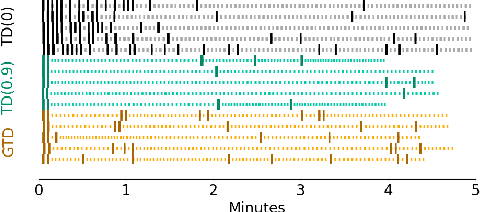
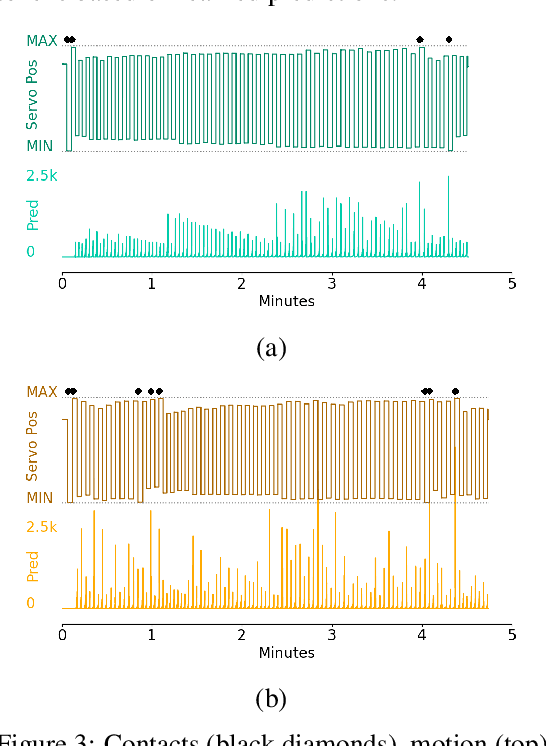
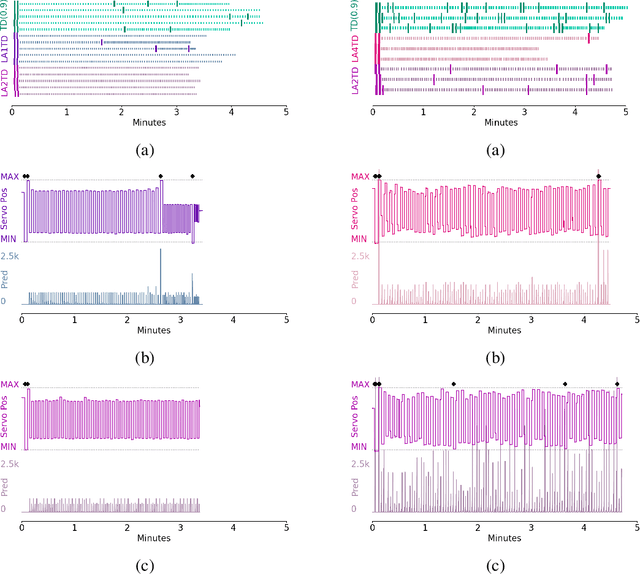
Abstract:Artificial limbs are sophisticated devices to assist people with tasks of daily living. Despite advanced robotic prostheses demonstrating similar motion capabilities to biological limbs, users report them difficult and non-intuitive to use. Providing more effective feedback from the device to the user has therefore become a topic of increased interest. In particular, prediction learning methods from the field of reinforcement learning -- specifically, an approach termed Pavlovian signalling -- have been proposed as one approach for better modulating feedback in prostheses since they can adapt during continuous use. One challenge identified in these learning methods is that they can forget previously learned predictions when a user begins to successfully act upon delivered feedback. The present work directly addresses this challenge, contributing new evidence on the impact of algorithmic choices, such as on- or off-policy methods and representation choices, on the Pavlovian signalling from a machine to a user during their control of a robotic arm. Two conditions of algorithmic differences were studied using different scenarios of controlling a robotic arm: an automated motion system and human participant piloting. Contrary to expectations, off-policy learning did not provide the expected solution to the forgetting problem. We instead identified beneficial properties of a look-ahead state representation that made existing approaches able to learn (and not forget) predictions in support of Pavlovian signalling. This work therefore contributes new insight into the challenges of providing learned predictive feedback from a prosthetic device, and demonstrates avenues for more dynamic signalling in future human-machine interactions.
Joint Action is a Framework for Understanding Partnerships Between Humans and Upper Limb Prostheses
Dec 28, 2022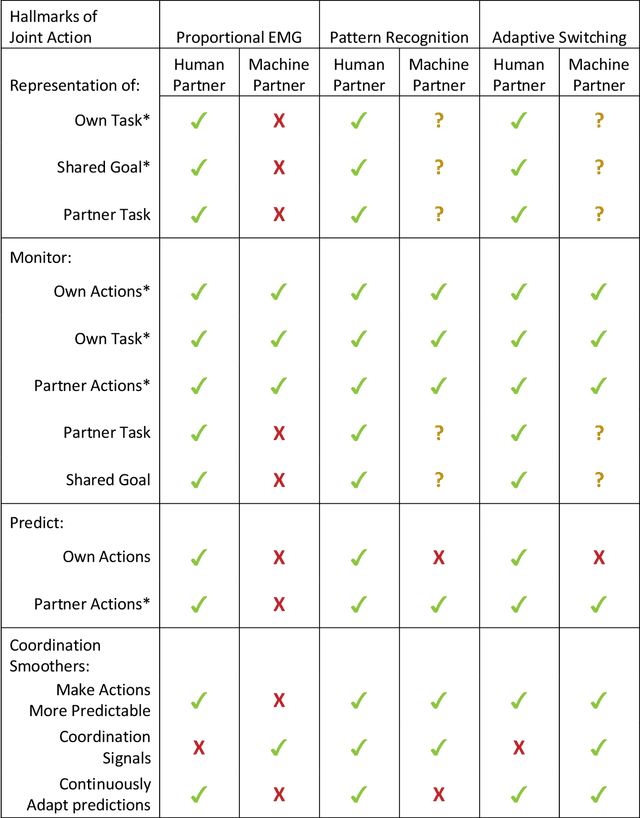
Abstract:Recent advances in upper limb prostheses have led to significant improvements in the number of movements provided by the robotic limb. However, the method for controlling multiple degrees of freedom via user-generated signals remains challenging. To address this issue, various machine learning controllers have been developed to better predict movement intent. As these controllers become more intelligent and take on more autonomy in the system, the traditional approach of representing the human-machine interface as a human controlling a tool becomes limiting. One possible approach to improve the understanding of these interfaces is to model them as collaborative, multi-agent systems through the lens of joint action. The field of joint action has been commonly applied to two human partners who are trying to work jointly together to achieve a task, such as singing or moving a table together, by effecting coordinated change in their shared environment. In this work, we compare different prosthesis controllers (proportional electromyography with sequential switching, pattern recognition, and adaptive switching) in terms of how they present the hallmarks of joint action. The results of the comparison lead to a new perspective for understanding how existing myoelectric systems relate to each other, along with recommendations for how to improve these systems by increasing the collaborative communication between each partner.
Five Properties of Specific Curiosity You Didn't Know Curious Machines Should Have
Dec 01, 2022Abstract:Curiosity for machine agents has been a focus of lively research activity. The study of human and animal curiosity, particularly specific curiosity, has unearthed several properties that would offer important benefits for machine learners, but that have not yet been well-explored in machine intelligence. In this work, we conduct a comprehensive, multidisciplinary survey of the field of animal and machine curiosity. As a principal contribution of this work, we use this survey as a foundation to introduce and define what we consider to be five of the most important properties of specific curiosity: 1) directedness towards inostensible referents, 2) cessation when satisfied, 3) voluntary exposure, 4) transience, and 5) coherent long-term learning. As a second main contribution of this work, we show how these properties may be implemented together in a proof-of-concept reinforcement learning agent: we demonstrate how the properties manifest in the behaviour of this agent in a simple non-episodic grid-world environment that includes curiosity-inducing locations and induced targets of curiosity. As we would hope, our example of a computational specific curiosity agent exhibits short-term directed behaviour while updating long-term preferences to adaptively seek out curiosity-inducing situations. This work, therefore, presents a landmark synthesis and translation of specific curiosity to the domain of machine learning and reinforcement learning and provides a novel view into how specific curiosity operates and in the future might be integrated into the behaviour of goal-seeking, decision-making computational agents in complex environments.
Adaptive patch foraging in deep reinforcement learning agents
Oct 14, 2022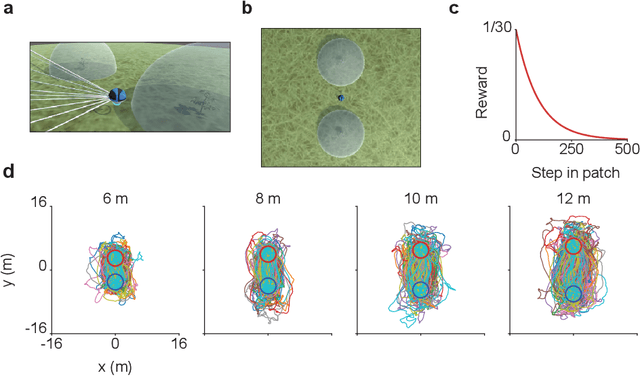
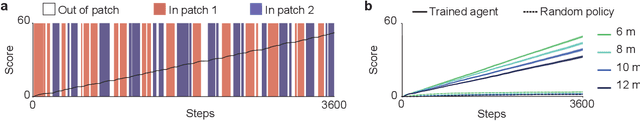
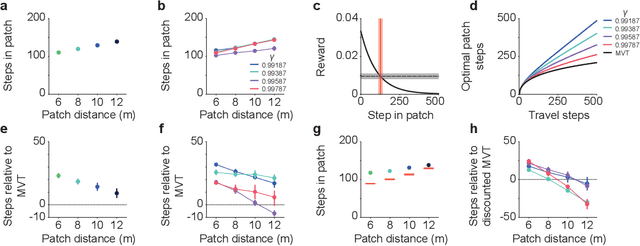
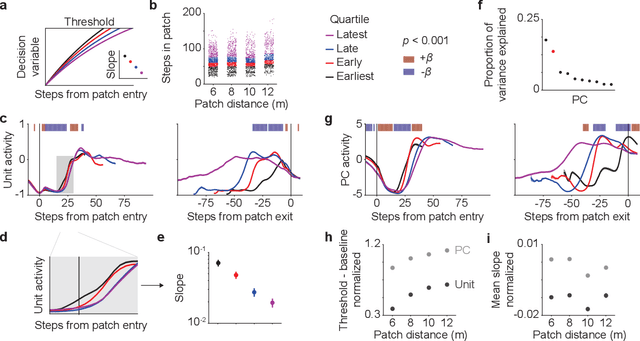
Abstract:Patch foraging is one of the most heavily studied behavioral optimization challenges in biology. However, despite its importance to biological intelligence, this behavioral optimization problem is understudied in artificial intelligence research. Patch foraging is especially amenable to study given that it has a known optimal solution, which may be difficult to discover given current techniques in deep reinforcement learning. Here, we investigate deep reinforcement learning agents in an ecological patch foraging task. For the first time, we show that machine learning agents can learn to patch forage adaptively in patterns similar to biological foragers, and approach optimal patch foraging behavior when accounting for temporal discounting. Finally, we show emergent internal dynamics in these agents that resemble single-cell recordings from foraging non-human primates, which complements experimental and theoretical work on the neural mechanisms of biological foraging. This work suggests that agents interacting in complex environments with ecologically valid pressures arrive at common solutions, suggesting the emergence of foundational computations behind adaptive, intelligent behavior in both biological and artificial agents.
The Alberta Plan for AI Research
Aug 23, 2022
Abstract:Herein we describe our approach to artificial intelligence research, which we call the Alberta Plan. The Alberta Plan is pursued within our research groups in Alberta and by others who are like minded throughout the world. We welcome all who would join us in this pursuit.
What Should I Know? Using Meta-gradient Descent for Predictive Feature Discovery in a Single Stream of Experience
Jun 13, 2022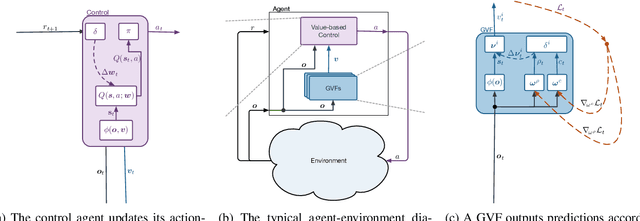
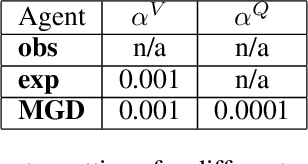
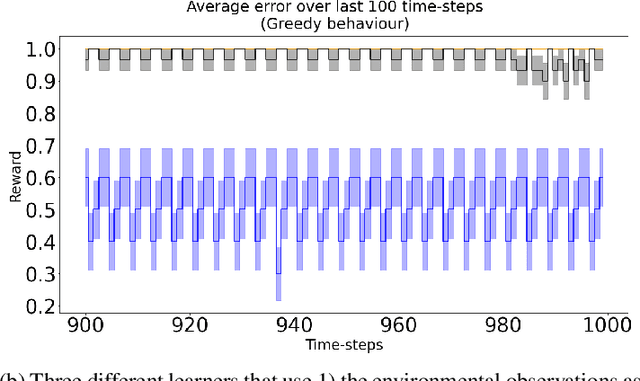
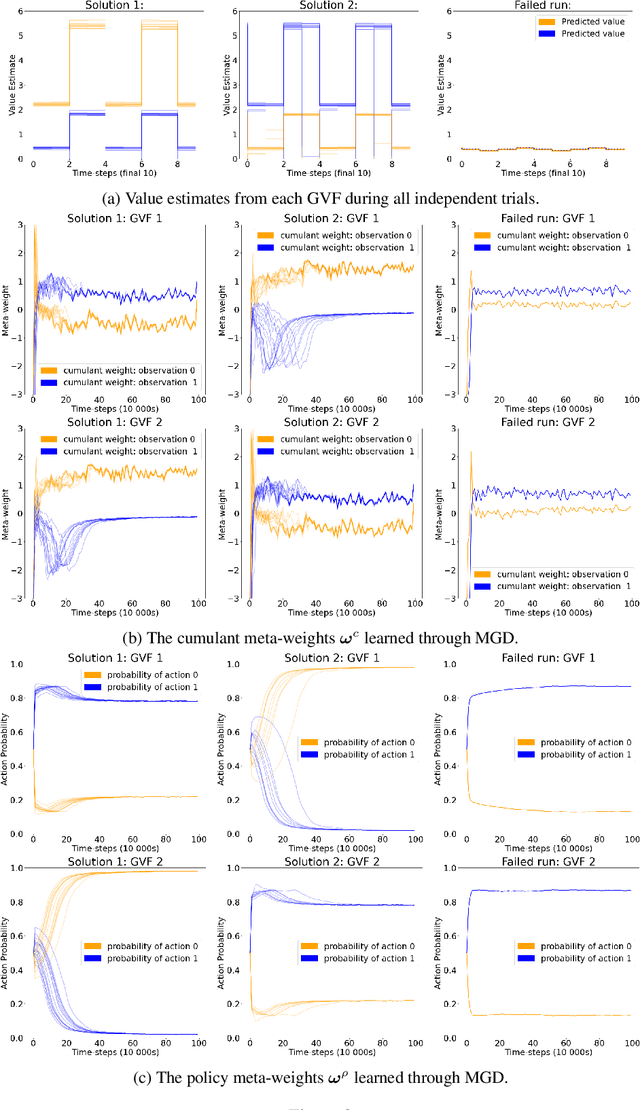
Abstract:In computational reinforcement learning, a growing body of work seeks to construct an agent's perception of the world through predictions of future sensations; predictions about environment observations are used as additional input features to enable better goal-directed decision-making. An open challenge in this line of work is determining from the infinitely many predictions that the agent could possibly make which predictions might best support decision-making. This challenge is especially apparent in continual learning problems where a single stream of experience is available to a singular agent. As a primary contribution, we introduce a meta-gradient descent process by which an agent learns 1) what predictions to make, 2) the estimates for its chosen predictions, and 3) how to use those estimates to generate policies that maximize future reward -- all during a single ongoing process of continual learning. In this manuscript we consider predictions expressed as General Value Functions: temporally extended estimates of the accumulation of a future signal. We demonstrate that through interaction with the environment an agent can independently select predictions that resolve partial-observability, resulting in performance similar to expertly specified GVFs. By learning, rather than manually specifying these predictions, we enable the agent to identify useful predictions in a self-supervised manner, taking a step towards truly autonomous systems.
Prototyping three key properties of specific curiosity in computational reinforcement learning
May 20, 2022

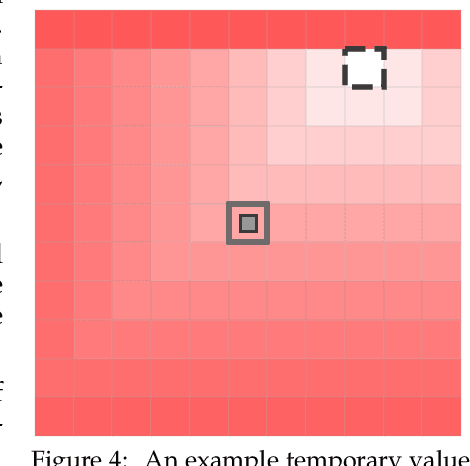
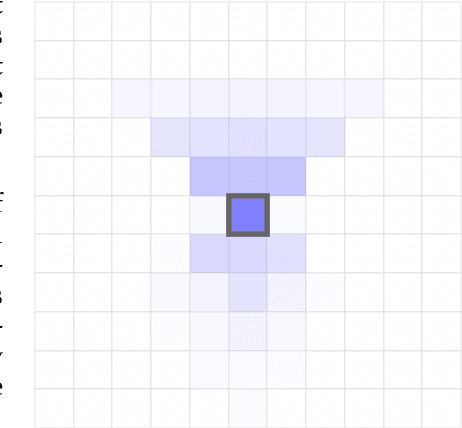
Abstract:Curiosity for machine agents has been a focus of intense research. The study of human and animal curiosity, particularly specific curiosity, has unearthed several properties that would offer important benefits for machine learners, but that have not yet been well-explored in machine intelligence. In this work, we introduce three of the most immediate of these properties -- directedness, cessation when satisfied, and voluntary exposure -- and show how they may be implemented together in a proof-of-concept reinforcement learning agent; further, we demonstrate how the properties manifest in the behaviour of this agent in a simple non-episodic grid-world environment that includes curiosity-inducing locations and induced targets of curiosity. As we would hope, the agent exhibits short-term directed behaviour while updating long-term preferences to adaptively seek out curiosity-inducing situations. This work therefore presents a novel view into how specific curiosity operates and in the future might be integrated into the behaviour of goal-seeking, decision-making agents in complex environments.
A Brief Guide to Designing and Evaluating Human-Centered Interactive Machine Learning
Apr 20, 2022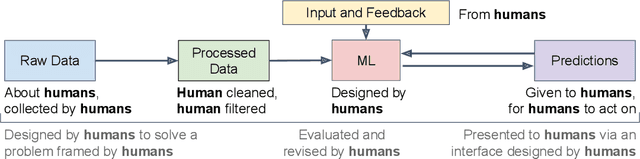
Abstract:Interactive machine learning (IML) is a field of research that explores how to leverage both human and computational abilities in decision making systems. IML represents a collaboration between multiple complementary human and machine intelligent systems working as a team, each with their own unique abilities and limitations. This teamwork might mean that both systems take actions at the same time, or in sequence. Two major open research questions in the field of IML are: "How should we design systems that can learn to make better decisions over time with human interaction?" and "How should we evaluate the design and deployment of such systems?" A lack of appropriate consideration for the humans involved can lead to problematic system behaviour, and issues of fairness, accountability, and transparency. Thus, our goal with this work is to present a human-centred guide to designing and evaluating IML systems while mitigating risks. This guide is intended to be used by machine learning practitioners who are responsible for the health, safety, and well-being of interacting humans. An obligation of responsibility for public interaction means acting with integrity, honesty, fairness, and abiding by applicable legal statutes. With these values and principles in mind, we as a machine learning research community can better achieve goals of augmenting human skills and abilities. This practical guide therefore aims to support many of the responsible decisions necessary throughout the iterative design, development, and dissemination of IML systems.
The Frost Hollow Experiments: Pavlovian Signalling as a Path to Coordination and Communication Between Agents
Mar 17, 2022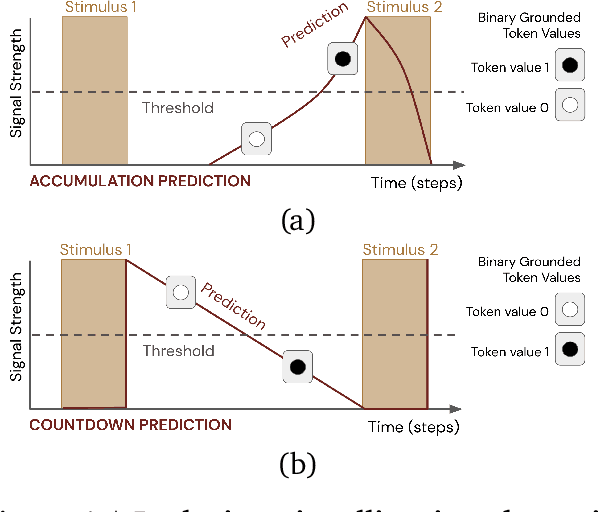
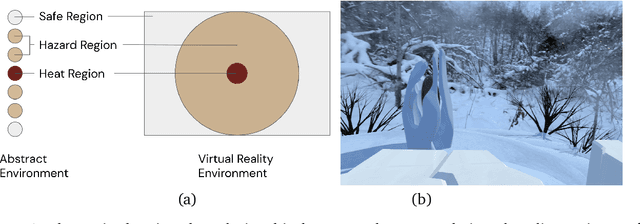
Abstract:Learned communication between agents is a powerful tool when approaching decision-making problems that are hard to overcome by any single agent in isolation. However, continual coordination and communication learning between machine agents or human-machine partnerships remains a challenging open problem. As a stepping stone toward solving the continual communication learning problem, in this paper we contribute a multi-faceted study into what we term Pavlovian signalling -- a process by which learned, temporally extended predictions made by one agent inform decision-making by another agent with different perceptual access to their shared environment. We seek to establish how different temporal processes and representational choices impact Pavlovian signalling between learning agents. To do so, we introduce a partially observable decision-making domain we call the Frost Hollow. In this domain a prediction learning agent and a reinforcement learning agent are coupled into a two-part decision-making system that seeks to acquire sparse reward while avoiding time-conditional hazards. We evaluate two domain variations: 1) machine prediction and control learning in a linear walk, and 2) a prediction learning machine interacting with a human participant in a virtual reality environment. Our results showcase the speed of learning for Pavlovian signalling, the impact that different temporal representations do (and do not) have on agent-agent coordination, and how temporal aliasing impacts agent-agent and human-agent interactions differently. As a main contribution, we establish Pavlovian signalling as a natural bridge between fixed signalling paradigms and fully adaptive communication learning. Our results therefore point to an actionable, constructivist path towards continual communication learning between reinforcement learning agents, with potential impact in a range of real-world settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge