Andrew Butcher
Adaptive patch foraging in deep reinforcement learning agents
Oct 14, 2022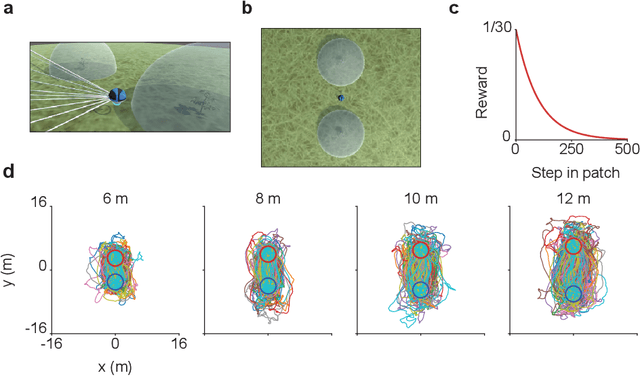
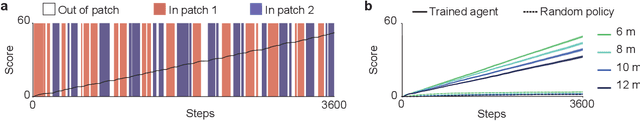
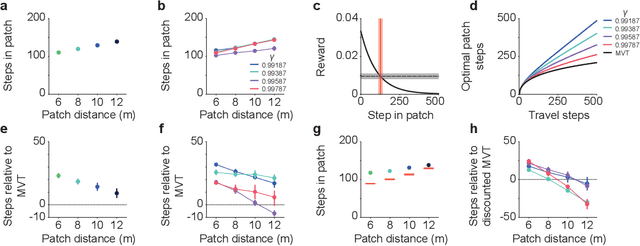
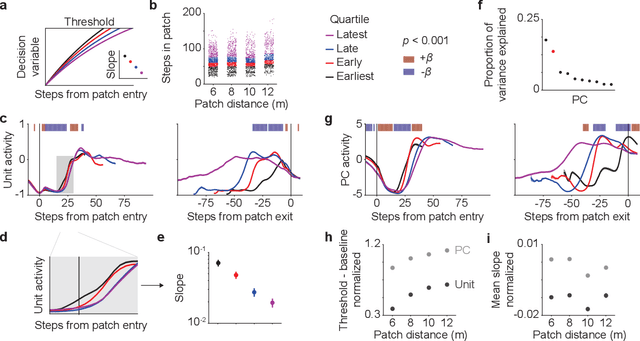
Abstract:Patch foraging is one of the most heavily studied behavioral optimization challenges in biology. However, despite its importance to biological intelligence, this behavioral optimization problem is understudied in artificial intelligence research. Patch foraging is especially amenable to study given that it has a known optimal solution, which may be difficult to discover given current techniques in deep reinforcement learning. Here, we investigate deep reinforcement learning agents in an ecological patch foraging task. For the first time, we show that machine learning agents can learn to patch forage adaptively in patterns similar to biological foragers, and approach optimal patch foraging behavior when accounting for temporal discounting. Finally, we show emergent internal dynamics in these agents that resemble single-cell recordings from foraging non-human primates, which complements experimental and theoretical work on the neural mechanisms of biological foraging. This work suggests that agents interacting in complex environments with ecologically valid pressures arrive at common solutions, suggesting the emergence of foundational computations behind adaptive, intelligent behavior in both biological and artificial agents.
The Frost Hollow Experiments: Pavlovian Signalling as a Path to Coordination and Communication Between Agents
Mar 17, 2022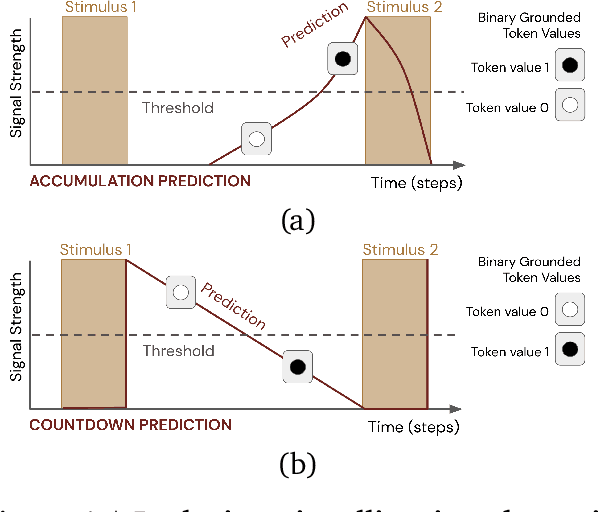
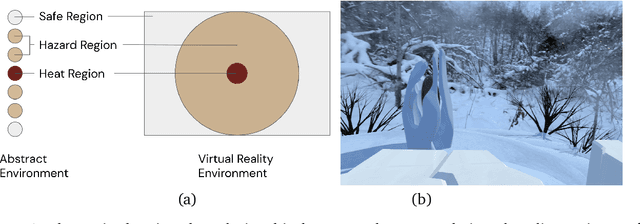
Abstract:Learned communication between agents is a powerful tool when approaching decision-making problems that are hard to overcome by any single agent in isolation. However, continual coordination and communication learning between machine agents or human-machine partnerships remains a challenging open problem. As a stepping stone toward solving the continual communication learning problem, in this paper we contribute a multi-faceted study into what we term Pavlovian signalling -- a process by which learned, temporally extended predictions made by one agent inform decision-making by another agent with different perceptual access to their shared environment. We seek to establish how different temporal processes and representational choices impact Pavlovian signalling between learning agents. To do so, we introduce a partially observable decision-making domain we call the Frost Hollow. In this domain a prediction learning agent and a reinforcement learning agent are coupled into a two-part decision-making system that seeks to acquire sparse reward while avoiding time-conditional hazards. We evaluate two domain variations: 1) machine prediction and control learning in a linear walk, and 2) a prediction learning machine interacting with a human participant in a virtual reality environment. Our results showcase the speed of learning for Pavlovian signalling, the impact that different temporal representations do (and do not) have on agent-agent coordination, and how temporal aliasing impacts agent-agent and human-agent interactions differently. As a main contribution, we establish Pavlovian signalling as a natural bridge between fixed signalling paradigms and fully adaptive communication learning. Our results therefore point to an actionable, constructivist path towards continual communication learning between reinforcement learning agents, with potential impact in a range of real-world settings.
Pavlovian Signalling with General Value Functions in Agent-Agent Temporal Decision Making
Jan 11, 2022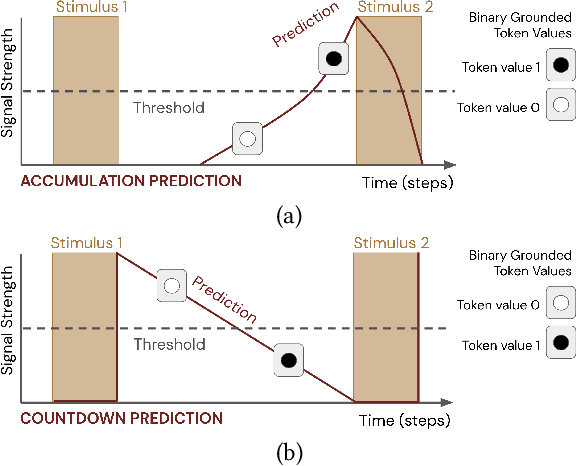
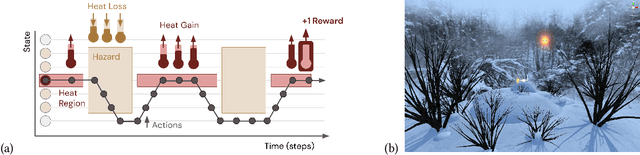
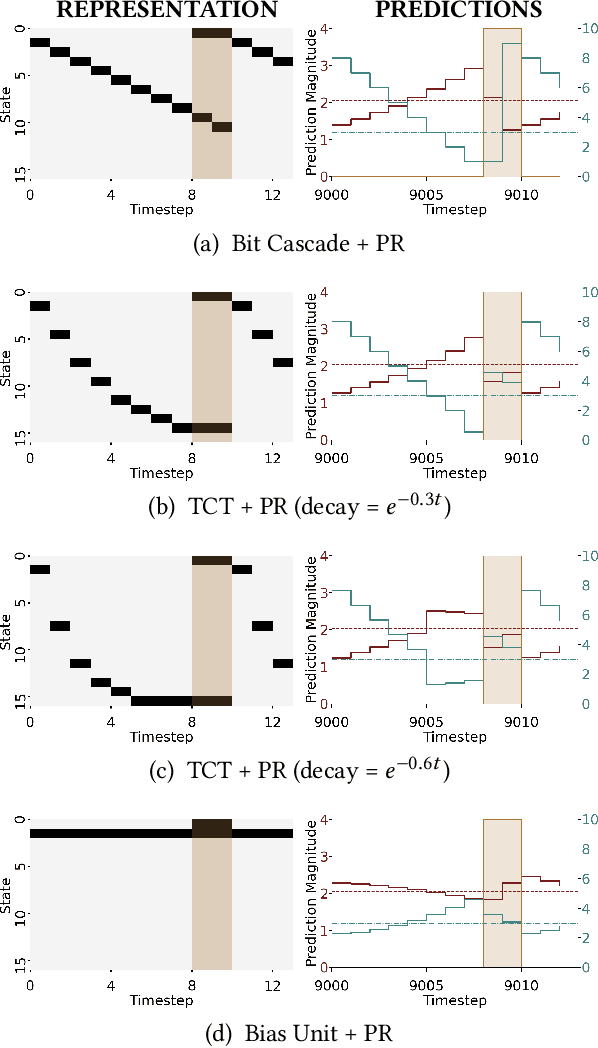
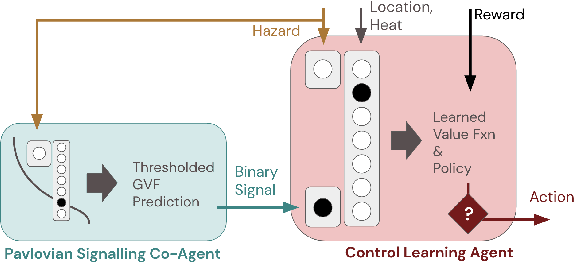
Abstract:In this paper, we contribute a multi-faceted study into Pavlovian signalling -- a process by which learned, temporally extended predictions made by one agent inform decision-making by another agent. Signalling is intimately connected to time and timing. In service of generating and receiving signals, humans and other animals are known to represent time, determine time since past events, predict the time until a future stimulus, and both recognize and generate patterns that unfold in time. We investigate how different temporal processes impact coordination and signalling between learning agents by introducing a partially observable decision-making domain we call the Frost Hollow. In this domain, a prediction learning agent and a reinforcement learning agent are coupled into a two-part decision-making system that works to acquire sparse reward while avoiding time-conditional hazards. We evaluate two domain variations: machine agents interacting in a seven-state linear walk, and human-machine interaction in a virtual-reality environment. Our results showcase the speed of learning for Pavlovian signalling, the impact that different temporal representations do (and do not) have on agent-agent coordination, and how temporal aliasing impacts agent-agent and human-agent interactions differently. As a main contribution, we establish Pavlovian signalling as a natural bridge between fixed signalling paradigms and fully adaptive communication learning between two agents. We further show how to computationally build this adaptive signalling process out of a fixed signalling process, characterized by fast continual prediction learning and minimal constraints on the nature of the agent receiving signals. Our results therefore suggest an actionable, constructivist path towards communication learning between reinforcement learning agents.
Assessing Human Interaction in Virtual Reality With Continually Learning Prediction Agents Based on Reinforcement Learning Algorithms: A Pilot Study
Dec 14, 2021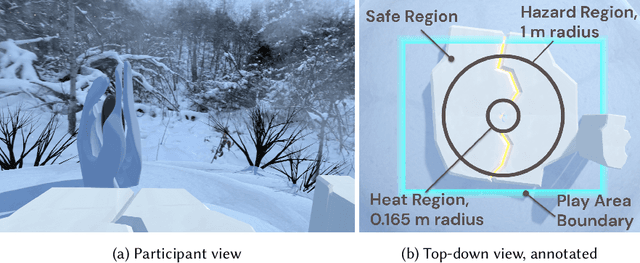
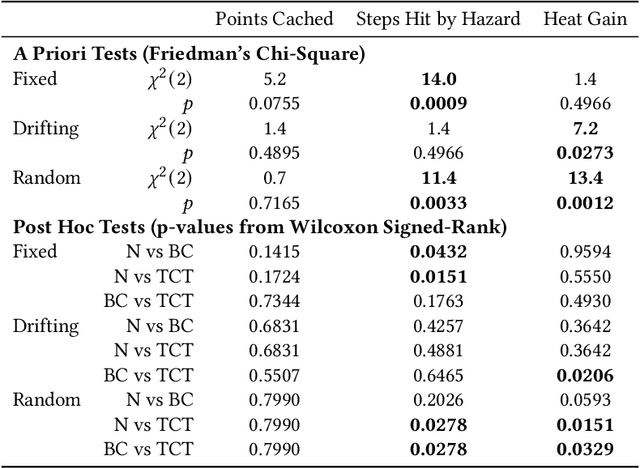
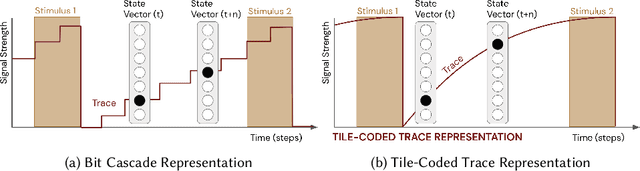
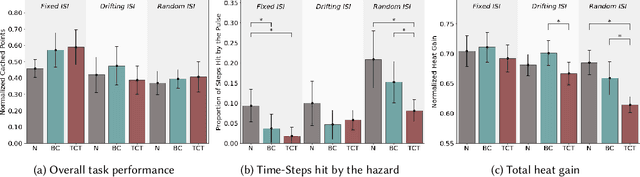
Abstract:Artificial intelligence systems increasingly involve continual learning to enable flexibility in general situations that are not encountered during system training. Human interaction with autonomous systems is broadly studied, but research has hitherto under-explored interactions that occur while the system is actively learning, and can noticeably change its behaviour in minutes. In this pilot study, we investigate how the interaction between a human and a continually learning prediction agent develops as the agent develops competency. Additionally, we compare two different agent architectures to assess how representational choices in agent design affect the human-agent interaction. We develop a virtual reality environment and a time-based prediction task wherein learned predictions from a reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm augment human predictions. We assess how a participant's performance and behaviour in this task differs across agent types, using both quantitative and qualitative analyses. Our findings suggest that human trust of the system may be influenced by early interactions with the agent, and that trust in turn affects strategic behaviour, but limitations of the pilot study rule out any conclusive statement. We identify trust as a key feature of interaction to focus on when considering RL-based technologies, and make several recommendations for modification to this study in preparation for a larger-scale investigation. A video summary of this paper can be found at https://youtu.be/oVYJdnBqTwQ .
Learned human-agent decision-making, communication and joint action in a virtual reality environment
May 07, 2019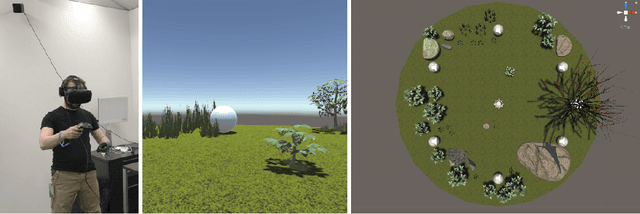
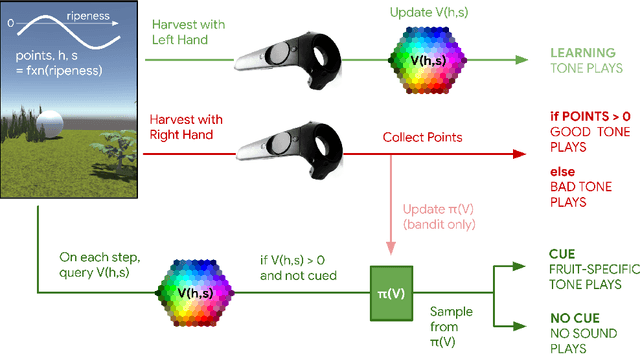
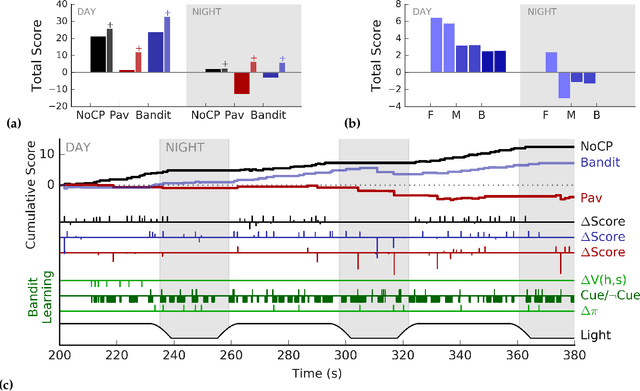
Abstract:Humans make decisions and act alongside other humans to pursue both short-term and long-term goals. As a result of ongoing progress in areas such as computing science and automation, humans now also interact with non-human agents of varying complexity as part of their day-to-day activities; substantial work is being done to integrate increasingly intelligent machine agents into human work and play. With increases in the cognitive, sensory, and motor capacity of these agents, intelligent machinery for human assistance can now reasonably be considered to engage in joint action with humans---i.e., two or more agents adapting their behaviour and their understanding of each other so as to progress in shared objectives or goals. The mechanisms, conditions, and opportunities for skillful joint action in human-machine partnerships is of great interest to multiple communities. Despite this, human-machine joint action is as yet under-explored, especially in cases where a human and an intelligent machine interact in a persistent way during the course of real-time, daily-life experience. In this work, we contribute a virtual reality environment wherein a human and an agent can adapt their predictions, their actions, and their communication so as to pursue a simple foraging task. In a case study with a single participant, we provide an example of human-agent coordination and decision-making involving prediction learning on the part of the human and the machine agent, and control learning on the part of the machine agent wherein audio communication signals are used to cue its human partner in service of acquiring shared reward. These comparisons suggest the utility of studying human-machine coordination in a virtual reality environment, and identify further research that will expand our understanding of persistent human-machine joint action.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge