The Frost Hollow Experiments: Pavlovian Signalling as a Path to Coordination and Communication Between Agents
Paper and Code
Mar 17, 2022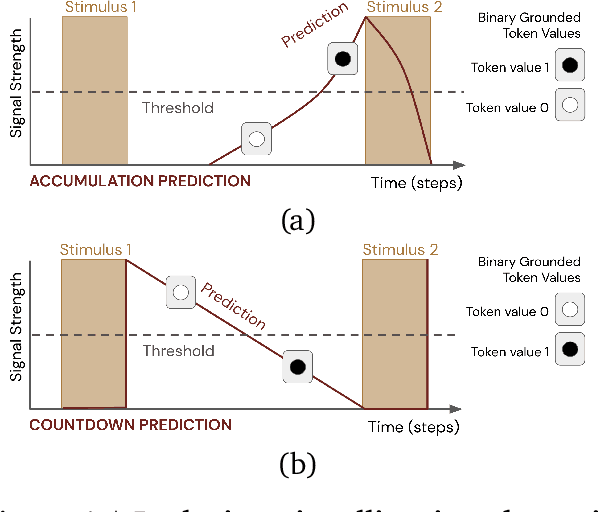
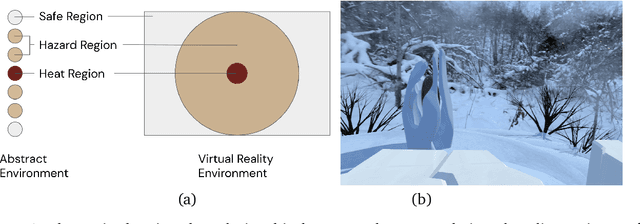
Learned communication between agents is a powerful tool when approaching decision-making problems that are hard to overcome by any single agent in isolation. However, continual coordination and communication learning between machine agents or human-machine partnerships remains a challenging open problem. As a stepping stone toward solving the continual communication learning problem, in this paper we contribute a multi-faceted study into what we term Pavlovian signalling -- a process by which learned, temporally extended predictions made by one agent inform decision-making by another agent with different perceptual access to their shared environment. We seek to establish how different temporal processes and representational choices impact Pavlovian signalling between learning agents. To do so, we introduce a partially observable decision-making domain we call the Frost Hollow. In this domain a prediction learning agent and a reinforcement learning agent are coupled into a two-part decision-making system that seeks to acquire sparse reward while avoiding time-conditional hazards. We evaluate two domain variations: 1) machine prediction and control learning in a linear walk, and 2) a prediction learning machine interacting with a human participant in a virtual reality environment. Our results showcase the speed of learning for Pavlovian signalling, the impact that different temporal representations do (and do not) have on agent-agent coordination, and how temporal aliasing impacts agent-agent and human-agent interactions differently. As a main contribution, we establish Pavlovian signalling as a natural bridge between fixed signalling paradigms and fully adaptive communication learning. Our results therefore point to an actionable, constructivist path towards continual communication learning between reinforcement learning agents, with potential impact in a range of real-world settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge