Oscar Leong
Feature, Alignment, and Supervision in Category Learning: A Comparative Approach with Children and Neural Networks
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Understanding how humans and machines learn from sparse data is central to cognitive science and machine learning. Using a species-fair design, we compare children and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) in a few-shot semi-supervised category learning task. Both learners are exposed to novel object categories under identical conditions. Learners receive mixtures of labeled and unlabeled exemplars while we vary supervision (1/3/6 labels), target feature (size, shape, pattern), and perceptual alignment (high/low). We find that children generalize rapidly from minimal labels but show strong feature-specific biases and sensitivity to alignment. CNNs show a different interaction profile: added supervision improves performance, but both alignment and feature structure moderate the impact additional supervision has on learning. These results show that human-model comparisons must be drawn under the right conditions, emphasizing interactions among supervision, feature structure, and alignment rather than overall accuracy.
What Makes a Good Example? Modeling Exemplar Selection with Neural Network Representations
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Teaching requires distilling a rich category distribution into a small set of informative exemplars. Although prior work shows that humans consider both representativeness and diversity when teaching, the computational principles underlying these tradeoffs remain unclear. We address this gap by modeling human exemplar selection using neural network feature representations and principled subset selection criteria. Novel visual categories were embedded along a one-dimensional morph continuum using pretrained vision models, and selection strategies varied in their emphasis on prototypicality, joint representativeness, and diversity. Adult participants selected one to three exemplars to teach a learner. Model-human comparisons revealed that strategies based on joint representativeness, or its combination with diversity, best captured human judgments, whereas purely prototypical or diversity-based strategies performed worse. Moreover, transformer-based representations consistently aligned more closely with human behavior than convolutional networks. These results highlight the potential utility of dataset distillation methods in machine learning as computational models for teaching.
Riemannian AmbientFlow: Towards Simultaneous Manifold Learning and Generative Modeling from Corrupted Data
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Modern generative modeling methods have demonstrated strong performance in learning complex data distributions from clean samples. In many scientific and imaging applications, however, clean samples are unavailable, and only noisy or linearly corrupted measurements can be observed. Moreover, latent structures, such as manifold geometries, present in the data are important to extract for further downstream scientific analysis. In this work, we introduce Riemannian AmbientFlow, a framework for simultaneously learning a probabilistic generative model and the underlying, nonlinear data manifold directly from corrupted observations. Building on the variational inference framework of AmbientFlow, our approach incorporates data-driven Riemannian geometry induced by normalizing flows, enabling the extraction of manifold structure through pullback metrics and Riemannian Autoencoders. We establish theoretical guarantees showing that, under appropriate geometric regularization and measurement conditions, the learned model recovers the underlying data distribution up to a controllable error and yields a smooth, bi-Lipschitz manifold parametrization. We further show that the resulting smooth decoder can serve as a principled generative prior for inverse problems with recovery guarantees. We empirically validate our approach on low-dimensional synthetic manifolds and on MNIST.
Learning Regularization Functionals for Inverse Problems: A Comparative Study
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:In recent years, a variety of learned regularization frameworks for solving inverse problems in imaging have emerged. These offer flexible modeling together with mathematical insights. The proposed methods differ in their architectural design and training strategies, making direct comparison challenging due to non-modular implementations. We address this gap by collecting and unifying the available code into a common framework. This unified view allows us to systematically compare the approaches and highlight their strengths and limitations, providing valuable insights into their future potential. We also provide concise descriptions of each method, complemented by practical guidelines.
Restoration Score Distillation: From Corrupted Diffusion Pretraining to One-Step High-Quality Generation
May 19, 2025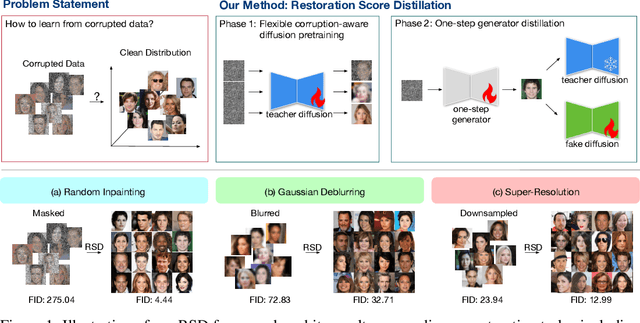

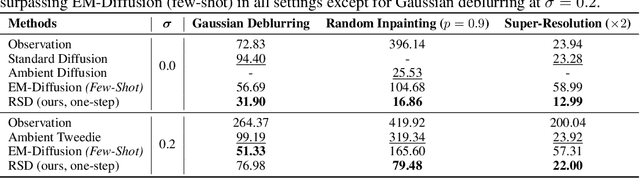
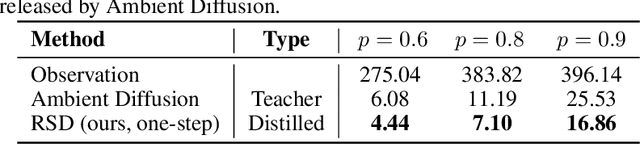
Abstract:Learning generative models from corrupted data is a fundamental yet persistently challenging task across scientific disciplines, particularly when access to clean data is limited or expensive. Denoising Score Distillation (DSD) \cite{chen2025denoising} recently introduced a novel and surprisingly effective strategy that leverages score distillation to train high-fidelity generative models directly from noisy observations. Building upon this foundation, we propose \textit{Restoration Score Distillation} (RSD), a principled generalization of DSD that accommodates a broader range of corruption types, such as blurred, incomplete, or low-resolution images. RSD operates by first pretraining a teacher diffusion model solely on corrupted data and subsequently distilling it into a single-step generator that produces high-quality reconstructions. Empirically, RSD consistently surpasses its teacher model across diverse restoration tasks on both natural and scientific datasets. Moreover, beyond standard diffusion objectives, the RSD framework is compatible with several corruption-aware training techniques such as Ambient Tweedie, Ambient Diffusion, and its Fourier-space variant, enabling flexible integration with recent advances in diffusion modeling. Theoretically, we demonstrate that in a linear regime, RSD recovers the eigenspace of the clean data covariance matrix from linear measurements, thereby serving as an implicit regularizer. This interpretation recasts score distillation not only as a sampling acceleration technique but as a principled approach to enhancing generative performance in severely degraded data regimes.
Denoising Score Distillation: From Noisy Diffusion Pretraining to One-Step High-Quality Generation
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in generating high-resolution, realistic images across diverse natural distributions. However, their performance heavily relies on high-quality training data, making it challenging to learn meaningful distributions from corrupted samples. This limitation restricts their applicability in scientific domains where clean data is scarce or costly to obtain. In this work, we introduce denoising score distillation (DSD), a surprisingly effective and novel approach for training high-quality generative models from low-quality data. DSD first pretrains a diffusion model exclusively on noisy, corrupted samples and then distills it into a one-step generator capable of producing refined, clean outputs. While score distillation is traditionally viewed as a method to accelerate diffusion models, we show that it can also significantly enhance sample quality, particularly when starting from a degraded teacher model. Across varying noise levels and datasets, DSD consistently improves generative performancewe summarize our empirical evidence in Fig. 1. Furthermore, we provide theoretical insights showing that, in a linear model setting, DSD identifies the eigenspace of the clean data distributions covariance matrix, implicitly regularizing the generator. This perspective reframes score distillation as not only a tool for efficiency but also a mechanism for improving generative models, particularly in low-quality data settings.
The Star Geometry of Critic-Based Regularizer Learning
Aug 29, 2024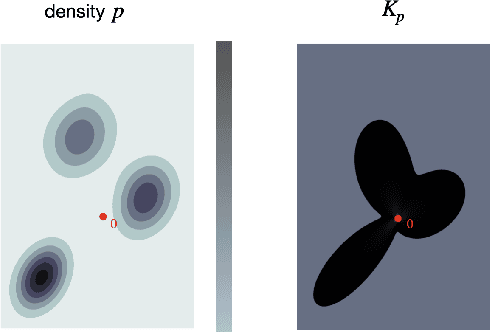
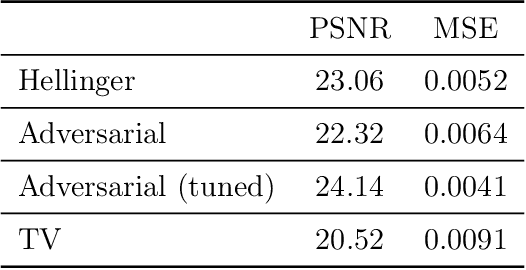
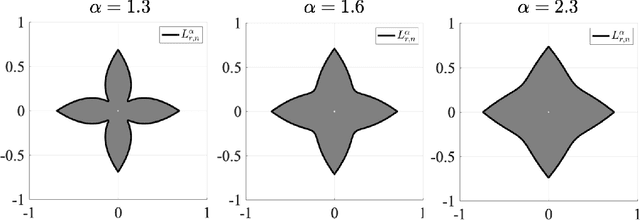
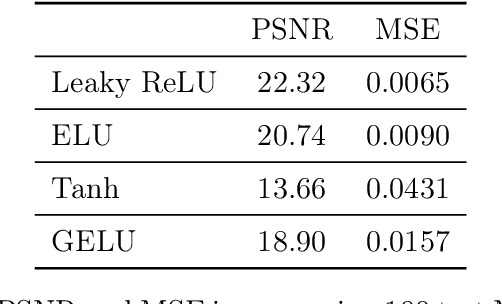
Abstract:Variational regularization is a classical technique to solve statistical inference tasks and inverse problems, with modern data-driven approaches parameterizing regularizers via deep neural networks showcasing impressive empirical performance. Recent works along these lines learn task-dependent regularizers. This is done by integrating information about the measurements and ground-truth data in an unsupervised, critic-based loss function, where the regularizer attributes low values to likely data and high values to unlikely data. However, there is little theory about the structure of regularizers learned via this process and how it relates to the two data distributions. To make progress on this challenge, we initiate a study of optimizing critic-based loss functions to learn regularizers over a particular family of regularizers: gauges (or Minkowski functionals) of star-shaped bodies. This family contains regularizers that are commonly employed in practice and shares properties with regularizers parameterized by deep neural networks. We specifically investigate critic-based losses derived from variational representations of statistical distances between probability measures. By leveraging tools from star geometry and dual Brunn-Minkowski theory, we illustrate how these losses can be interpreted as dual mixed volumes that depend on the data distribution. This allows us to derive exact expressions for the optimal regularizer in certain cases. Finally, we identify which neural network architectures give rise to such star body gauges and when do such regularizers have favorable properties for optimization. More broadly, this work highlights how the tools of star geometry can aid in understanding the geometry of unsupervised regularizer learning.
Flow Priors for Linear Inverse Problems via Iterative Corrupted Trajectory Matching
May 29, 2024Abstract:Generative models based on flow matching have attracted significant attention for their simplicity and superior performance in high-resolution image synthesis. By leveraging the instantaneous change-of-variables formula, one can directly compute image likelihoods from a learned flow, making them enticing candidates as priors for downstream tasks such as inverse problems. In particular, a natural approach would be to incorporate such image probabilities in a maximum-a-posteriori (MAP) estimation problem. A major obstacle, however, lies in the slow computation of the log-likelihood, as it requires backpropagating through an ODE solver, which can be prohibitively slow for high-dimensional problems. In this work, we propose an iterative algorithm to approximate the MAP estimator efficiently to solve a variety of linear inverse problems. Our algorithm is mathematically justified by the observation that the MAP objective can be approximated by a sum of $N$ ``local MAP'' objectives, where $N$ is the number of function evaluations. By leveraging Tweedie's formula, we show that we can perform gradient steps to sequentially optimize these objectives. We validate our approach for various linear inverse problems, such as super-resolution, deblurring, inpainting, and compressed sensing, and demonstrate that we can outperform other methods based on flow matching.
Score-Based Diffusion Models for Photoacoustic Tomography Image Reconstruction
Mar 30, 2024



Abstract:Photoacoustic tomography (PAT) is a rapidly-evolving medical imaging modality that combines optical absorption contrast with ultrasound imaging depth. One challenge in PAT is image reconstruction with inadequate acoustic signals due to limited sensor coverage or due to the density of the transducer array. Such cases call for solving an ill-posed inverse reconstruction problem. In this work, we use score-based diffusion models to solve the inverse problem of reconstructing an image from limited PAT measurements. The proposed approach allows us to incorporate an expressive prior learned by a diffusion model on simulated vessel structures while still being robust to varying transducer sparsity conditions.
* 5 pages
Ill-Posed Image Reconstruction Without an Image Prior
Apr 12, 2023Abstract:We consider solving ill-posed imaging inverse problems without access to an image prior or ground-truth examples. An overarching challenge in these inverse problems is that an infinite number of images, including many that are implausible, are consistent with the observed measurements. Thus, image priors are required to reduce the space of possible solutions to more desireable reconstructions. However, in many applications it is difficult or potentially impossible to obtain example images to construct an image prior. Hence inaccurate priors are often used, which inevitably result in biased solutions. Rather than solving an inverse problem using priors that encode the spatial structure of any one image, we propose to solve a set of inverse problems jointly by incorporating prior constraints on the collective structure of the underlying images. The key assumption of our work is that the underlying images we aim to reconstruct share common, low-dimensional structure. We show that such a set of inverse problems can be solved simultaneously without the use of a spatial image prior by instead inferring a shared image generator with a low-dimensional latent space. The parameters of the generator and latent embeddings are found by maximizing a proxy for the Evidence Lower Bound (ELBO). Once identified, the generator and latent embeddings can be combined to provide reconstructed images for each inverse problem. The framework we propose can handle general forward model corruptions, and we show that measurements derived from only a small number of ground-truth images ($\leqslant 150$) are sufficient for "prior-free" image reconstruction. We demonstrate our approach on a variety of convex and non-convex inverse problems, ranging from denoising, phase retrieval, and black hole video reconstruction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge