Niluthpol Chowdhury Mithun
DUDA: Distilled Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Lightweight Semantic Segmentation
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) is essential for enabling semantic segmentation in new domains without requiring costly pixel-wise annotations. State-of-the-art (SOTA) UDA methods primarily use self-training with architecturally identical teacher and student networks, relying on Exponential Moving Average (EMA) updates. However, these approaches face substantial performance degradation with lightweight models due to inherent architectural inflexibility leading to low-quality pseudo-labels. To address this, we propose Distilled Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (DUDA), a novel framework that combines EMA-based self-training with knowledge distillation (KD). Our method employs an auxiliary student network to bridge the architectural gap between heavyweight and lightweight models for EMA-based updates, resulting in improved pseudo-label quality. DUDA employs a strategic fusion of UDA and KD, incorporating innovative elements such as gradual distillation from large to small networks, inconsistency loss prioritizing poorly adapted classes, and learning with multiple teachers. Extensive experiments across four UDA benchmarks demonstrate DUDA's superiority in achieving SOTA performance with lightweight models, often surpassing the performance of heavyweight models from other approaches.
Diffusion-Guided Gaussian Splatting for Large-Scale Unconstrained 3D Reconstruction and Novel View Synthesis
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) and Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have achieved impressive results in real-time 3D reconstruction and novel view synthesis. However, these methods struggle in large-scale, unconstrained environments where sparse and uneven input coverage, transient occlusions, appearance variability, and inconsistent camera settings lead to degraded quality. We propose GS-Diff, a novel 3DGS framework guided by a multi-view diffusion model to address these limitations. By generating pseudo-observations conditioned on multi-view inputs, our method transforms under-constrained 3D reconstruction problems into well-posed ones, enabling robust optimization even with sparse data. GS-Diff further integrates several enhancements, including appearance embedding, monocular depth priors, dynamic object modeling, anisotropy regularization, and advanced rasterization techniques, to tackle geometric and photometric challenges in real-world settings. Experiments on four benchmarks demonstrate that GS-Diff consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by significant margins.
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation with Pseudo Label Self-Refinement
Oct 25, 2023



Abstract:Deep learning-based solutions for semantic segmentation suffer from significant performance degradation when tested on data with different characteristics than what was used during the training. Adapting the models using annotated data from the new domain is not always practical. Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) approaches are crucial in deploying these models in the actual operating conditions. Recent state-of-the-art (SOTA) UDA methods employ a teacher-student self-training approach, where a teacher model is used to generate pseudo-labels for the new data which in turn guide the training process of the student model. Though this approach has seen a lot of success, it suffers from the issue of noisy pseudo-labels being propagated in the training process. To address this issue, we propose an auxiliary pseudo-label refinement network (PRN) for online refining of the pseudo labels and also localizing the pixels whose predicted labels are likely to be noisy. Being able to improve the quality of pseudo labels and select highly reliable ones, PRN helps self-training of segmentation models to be robust against pseudo label noise propagation during different stages of adaptation. We evaluate our approach on benchmark datasets with three different domain shifts, and our approach consistently performs significantly better than the previous state-of-the-art methods.
C-SFDA: A Curriculum Learning Aided Self-Training Framework for Efficient Source Free Domain Adaptation
Mar 30, 2023



Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) approaches focus on adapting models trained on a labeled source domain to an unlabeled target domain. UDA methods have a strong assumption that the source data is accessible during adaptation, which may not be feasible in many real-world scenarios due to privacy concerns and resource constraints of devices. In this regard, source-free domain adaptation (SFDA) excels as access to source data is no longer required during adaptation. Recent state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on SFDA mostly focus on pseudo-label refinement based self-training which generally suffers from two issues: i) inevitable occurrence of noisy pseudo-labels that could lead to early training time memorization, ii) refinement process requires maintaining a memory bank which creates a significant burden in resource constraint scenarios. To address these concerns, we propose C-SFDA, a curriculum learning aided self-training framework for SFDA that adapts efficiently and reliably to changes across domains based on selective pseudo-labeling. Specifically, we employ a curriculum learning scheme to promote learning from a restricted amount of pseudo labels selected based on their reliabilities. This simple yet effective step successfully prevents label noise propagation during different stages of adaptation and eliminates the need for costly memory-bank based label refinement. Our extensive experimental evaluations on both image recognition and semantic segmentation tasks confirm the effectiveness of our method. C-SFDA is readily applicable to online test-time domain adaptation and also outperforms previous SOTA methods in this task.
Cross-View Visual Geo-Localization for Outdoor Augmented Reality
Mar 28, 2023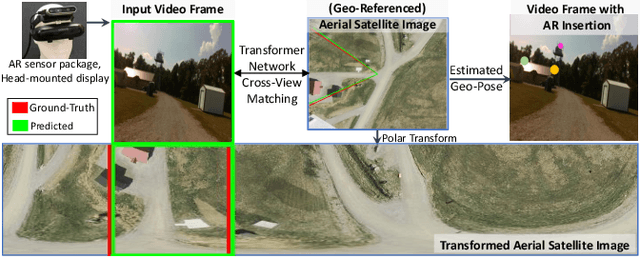



Abstract:Precise estimation of global orientation and location is critical to ensure a compelling outdoor Augmented Reality (AR) experience. We address the problem of geo-pose estimation by cross-view matching of query ground images to a geo-referenced aerial satellite image database. Recently, neural network-based methods have shown state-of-the-art performance in cross-view matching. However, most of the prior works focus only on location estimation, ignoring orientation, which cannot meet the requirements in outdoor AR applications. We propose a new transformer neural network-based model and a modified triplet ranking loss for joint location and orientation estimation. Experiments on several benchmark cross-view geo-localization datasets show that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance. Furthermore, we present an approach to extend the single image query-based geo-localization approach by utilizing temporal information from a navigation pipeline for robust continuous geo-localization. Experimentation on several large-scale real-world video sequences demonstrates that our approach enables high-precision and stable AR insertion.
GraphMapper: Efficient Visual Navigation by Scene Graph Generation
May 17, 2022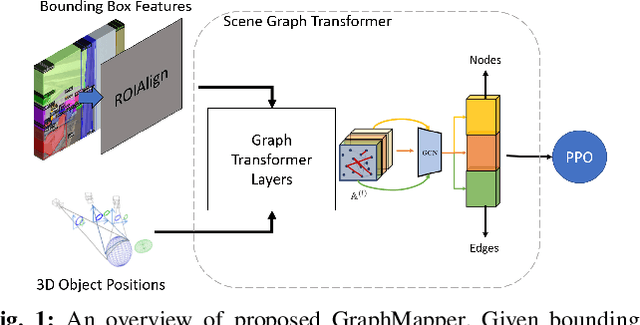
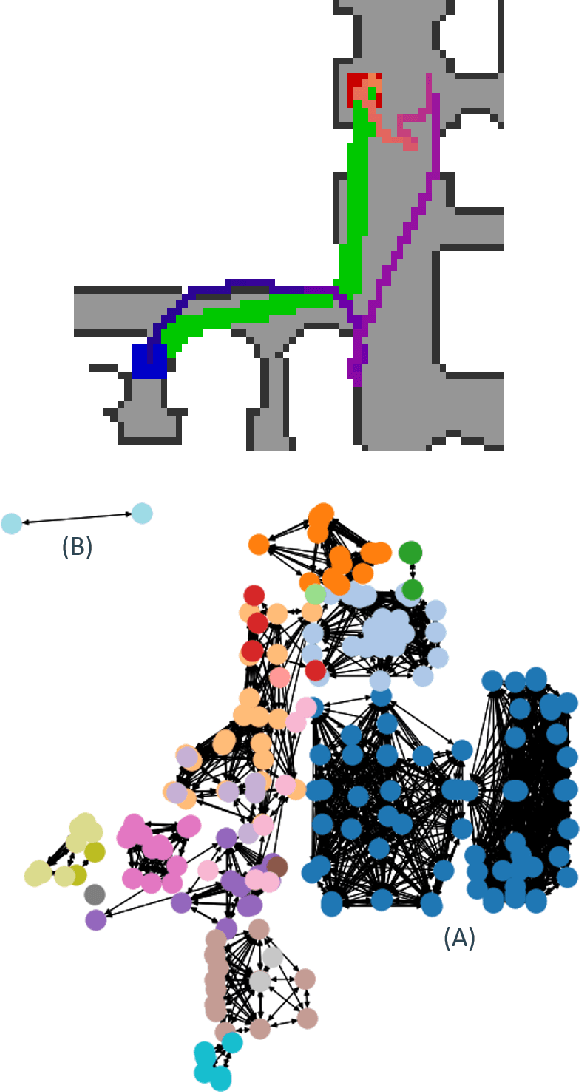
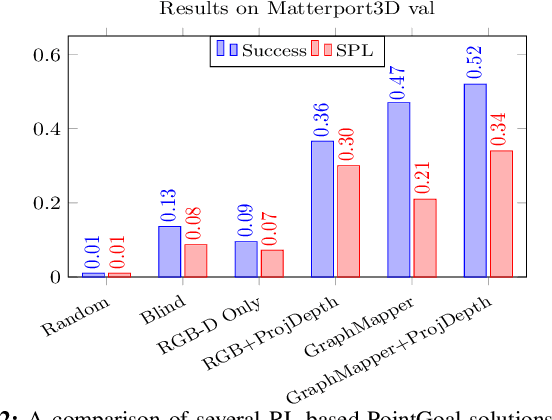
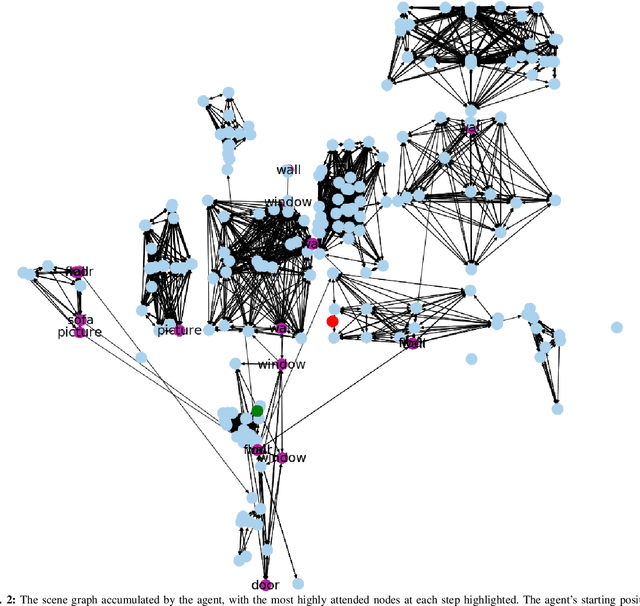
Abstract:Understanding the geometric relationships between objects in a scene is a core capability in enabling both humans and autonomous agents to navigate in new environments. A sparse, unified representation of the scene topology will allow agents to act efficiently to move through their environment, communicate the environment state with others, and utilize the representation for diverse downstream tasks. To this end, we propose a method to train an autonomous agent to learn to accumulate a 3D scene graph representation of its environment by simultaneously learning to navigate through said environment. We demonstrate that our approach, GraphMapper, enables the learning of effective navigation policies through fewer interactions with the environment than vision-based systems alone. Further, we show that GraphMapper can act as a modular scene encoder to operate alongside existing Learning-based solutions to not only increase navigational efficiency but also generate intermediate scene representations that are useful for other future tasks.
SASRA: Semantically-aware Spatio-temporal Reasoning Agent for Vision-and-Language Navigation in Continuous Environments
Aug 26, 2021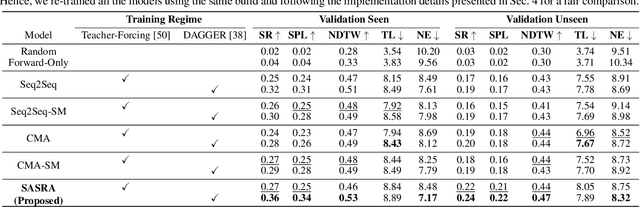
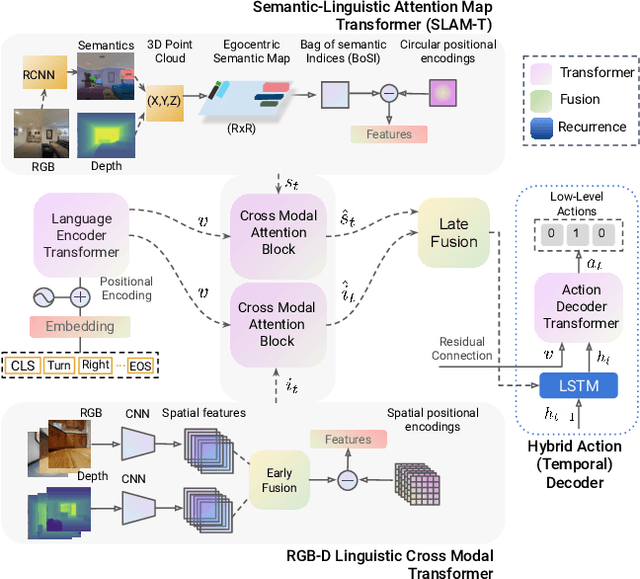
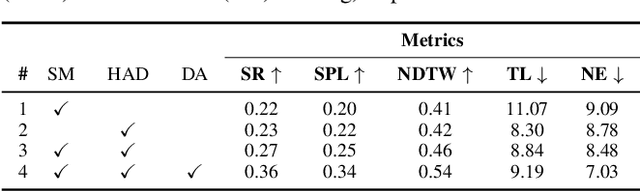
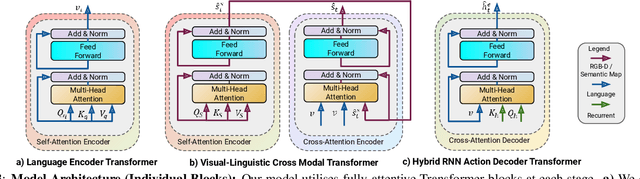
Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach for the Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) task in continuous 3D environments, which requires an autonomous agent to follow natural language instructions in unseen environments. Existing end-to-end learning-based VLN methods struggle at this task as they focus mostly on utilizing raw visual observations and lack the semantic spatio-temporal reasoning capabilities which is crucial in generalizing to new environments. In this regard, we present a hybrid transformer-recurrence model which focuses on combining classical semantic mapping techniques with a learning-based method. Our method creates a temporal semantic memory by building a top-down local ego-centric semantic map and performs cross-modal grounding to align map and language modalities to enable effective learning of VLN policy. Empirical results in a photo-realistic long-horizon simulation environment show that the proposed approach outperforms a variety of state-of-the-art methods and baselines with over 22% relative improvement in SPL in prior unseen environments.
RGB2LIDAR: Towards Solving Large-Scale Cross-Modal Visual Localization
Sep 12, 2020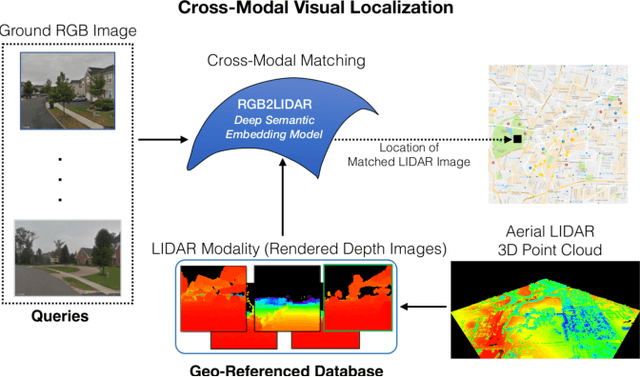
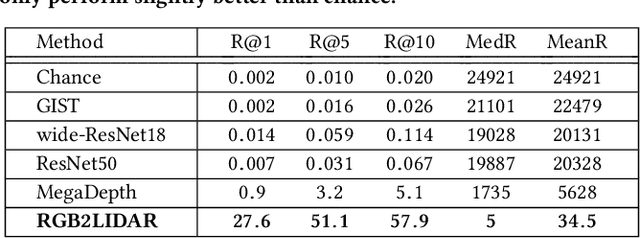

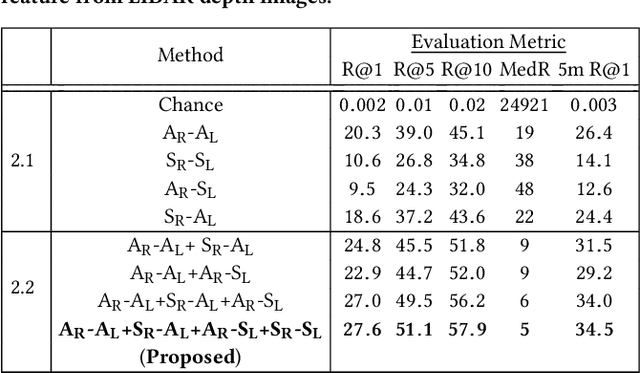
Abstract:We study an important, yet largely unexplored problem of large-scale cross-modal visual localization by matching ground RGB images to a geo-referenced aerial LIDAR 3D point cloud (rendered as depth images). Prior works were demonstrated on small datasets and did not lend themselves to scaling up for large-scale applications. To enable large-scale evaluation, we introduce a new dataset containing over 550K pairs (covering 143 km^2 area) of RGB and aerial LIDAR depth images. We propose a novel joint embedding based method that effectively combines the appearance and semantic cues from both modalities to handle drastic cross-modal variations. Experiments on the proposed dataset show that our model achieves a strong result of a median rank of 5 in matching across a large test set of 50K location pairs collected from a 14km^2 area. This represents a significant advancement over prior works in performance and scale. We conclude with qualitative results to highlight the challenging nature of this task and the benefits of the proposed model. Our work provides a foundation for further research in cross-modal visual localization.
Text-based Localization of Moments in a Video Corpus
Aug 20, 2020
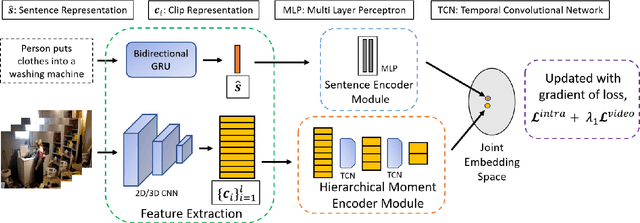
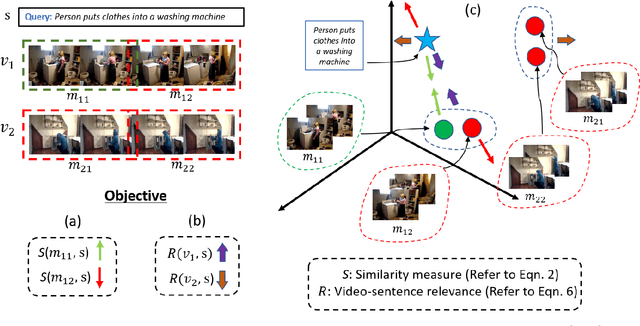

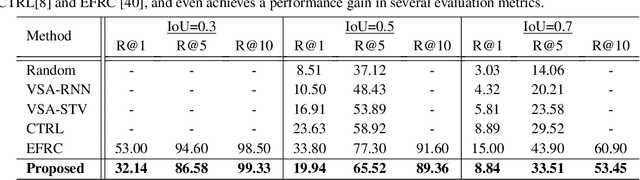
Abstract:Prior works on text-based video moment localization focus on temporally grounding the textual query in an untrimmed video. These works assume that the relevant video is already known and attempt to localize the moment on that relevant video only. Different from such works, we relax this assumption and address the task of localizing moments in a corpus of videos for a given sentence query. This task poses a unique challenge as the system is required to perform: (i) retrieval of the relevant video where only a segment of the video corresponds with the queried sentence, and (ii) temporal localization of moment in the relevant video based on sentence query. Towards overcoming this challenge, we propose Hierarchical Moment Alignment Network (HMAN) which learns an effective joint embedding space for moments and sentences. In addition to learning subtle differences between intra-video moments, HMAN focuses on distinguishing inter-video global semantic concepts based on sentence queries. Qualitative and quantitative results on three benchmark text-based video moment retrieval datasets - Charades-STA, DiDeMo, and ActivityNet Captions - demonstrate that our method achieves promising performance on the proposed task of temporal localization of moments in a corpus of videos.
Weakly Supervised Video Moment Retrieval From Text Queries
Apr 05, 2019
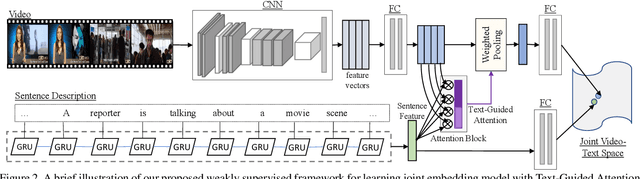
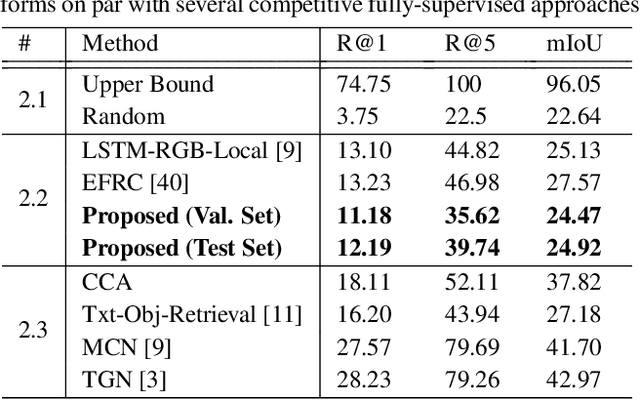
Abstract:There have been a few recent methods proposed in text to video moment retrieval using natural language queries, but requiring full supervision during training. However, acquiring a large number of training videos with temporal boundary annotations for each text description is extremely time-consuming and often not scalable. In order to cope with this issue, in this work, we introduce the problem of learning from weak labels for the task of text to video moment retrieval. The weak nature of the supervision is because, during training, we only have access to the video-text pairs rather than the temporal extent of the video to which different text descriptions relate. We propose a joint visual-semantic embedding based framework that learns the notion of relevant segments from video using only video-level sentence descriptions. Specifically, our main idea is to utilize latent alignment between video frames and sentence descriptions using Text-Guided Attention (TGA). TGA is then used during the test phase to retrieve relevant moments. Experiments on two benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method achieves comparable performance to state-of-the-art fully supervised approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge