Beomseok Kang
Token Sparse Attention: Efficient Long-Context Inference with Interleaved Token Selection
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:The quadratic complexity of attention remains the central bottleneck in long-context inference for large language models. Prior acceleration methods either sparsify the attention map with structured patterns or permanently evict tokens at specific layers, which can retain irrelevant tokens or rely on irreversible early decisions despite the layer-/head-wise dynamics of token importance. In this paper, we propose Token Sparse Attention, a lightweight and dynamic token-level sparsification mechanism that compresses per-head $Q$, $K$, $V$ to a reduced token set during attention and then decompresses the output back to the original sequence, enabling token information to be reconsidered in subsequent layers. Furthermore, Token Sparse Attention exposes a new design point at the intersection of token selection and sparse attention. Our approach is fully compatible with dense attention implementations, including Flash Attention, and can be seamlessly composed with existing sparse attention kernels. Experimental results show that Token Sparse Attention consistently improves accuracy-latency trade-off, achieving up to $\times$3.23 attention speedup at 128K context with less than 1% accuracy degradation. These results demonstrate that dynamic and interleaved token-level sparsification is a complementary and effective strategy for scalable long-context inference.
LiteStage: Latency-aware Layer Skipping for Multi-stage Reasoning
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Multi-stage reasoning has emerged as an effective strategy for enhancing the reasoning capability of small language models by decomposing complex problems into sequential sub-stages. However, this comes at the cost of increased latency. We observe that existing adaptive acceleration techniques, such as layer skipping, struggle to balance efficiency and accuracy in this setting due to two key challenges: (1) stage-wise variation in skip sensitivity, and (2) the generation of redundant output tokens. To address these, we propose LiteStage, a latency-aware layer skipping framework for multi-stage reasoning. LiteStage combines a stage-wise offline search that allocates optimal layer budgets with an online confidence-based generation early exit to suppress unnecessary decoding. Experiments on three benchmarks, e.g., OBQA, CSQA, and StrategyQA, show that LiteStage achieves up to 1.70x speedup with less than 4.0% accuracy loss, outperforming prior training-free layer skipping methods.
Retrospective Sparse Attention for Efficient Long-Context Generation
Aug 12, 2025
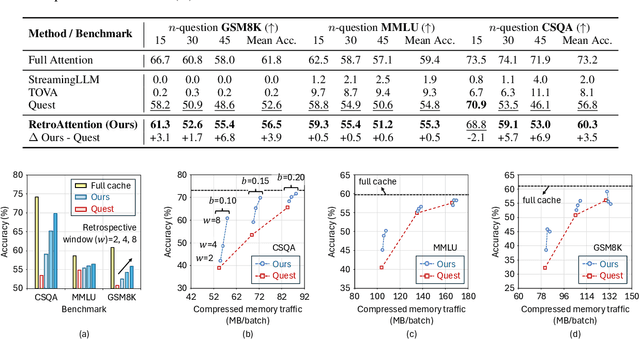

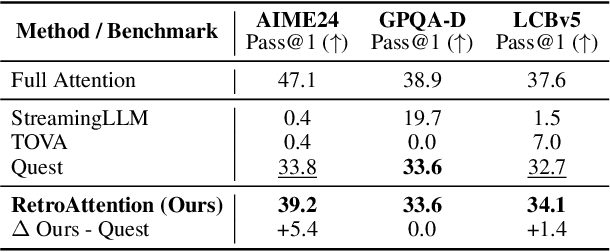
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in long-context tasks such as reasoning, code generation, and multi-turn dialogue. However, inference over extended contexts is bottlenecked by the Key-Value (KV) cache, whose memory footprint grows linearly with sequence length and dominates latency at each decoding step. While recent KV cache compression methods identify and load important tokens, they focus predominantly on input contexts and fail to address the cumulative attention errors that arise during long decoding. In this paper, we introduce RetroAttention, a novel KV cache update technique that retrospectively revises past attention outputs using newly arrived KV entries from subsequent decoding steps. By maintaining a lightweight output cache, RetroAttention enables past queries to efficiently access more relevant context, while incurring minimal latency overhead. This breaks the fixed-attention-output paradigm and allows continual correction of prior approximations. Extensive experiments on long-generation benchmarks show that RetroAttention consistently outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) KV compression methods, increasing effective KV exposure by up to 1.6$\times$ and accuracy by up to 21.9\%.
DUDA: Distilled Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Lightweight Semantic Segmentation
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) is essential for enabling semantic segmentation in new domains without requiring costly pixel-wise annotations. State-of-the-art (SOTA) UDA methods primarily use self-training with architecturally identical teacher and student networks, relying on Exponential Moving Average (EMA) updates. However, these approaches face substantial performance degradation with lightweight models due to inherent architectural inflexibility leading to low-quality pseudo-labels. To address this, we propose Distilled Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (DUDA), a novel framework that combines EMA-based self-training with knowledge distillation (KD). Our method employs an auxiliary student network to bridge the architectural gap between heavyweight and lightweight models for EMA-based updates, resulting in improved pseudo-label quality. DUDA employs a strategic fusion of UDA and KD, incorporating innovative elements such as gradual distillation from large to small networks, inconsistency loss prioritizing poorly adapted classes, and learning with multiple teachers. Extensive experiments across four UDA benchmarks demonstrate DUDA's superiority in achieving SOTA performance with lightweight models, often surpassing the performance of heavyweight models from other approaches.
Dynamic Graph Structure Estimation for Learning Multivariate Point Process using Spiking Neural Networks
Apr 01, 2025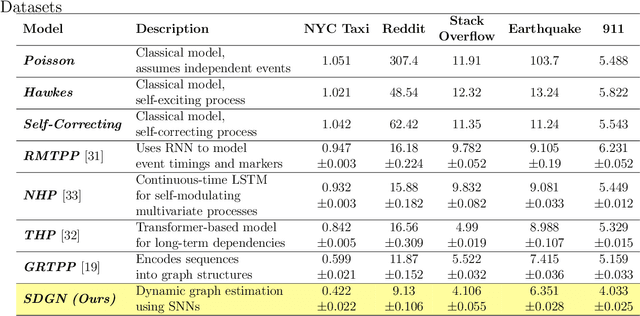
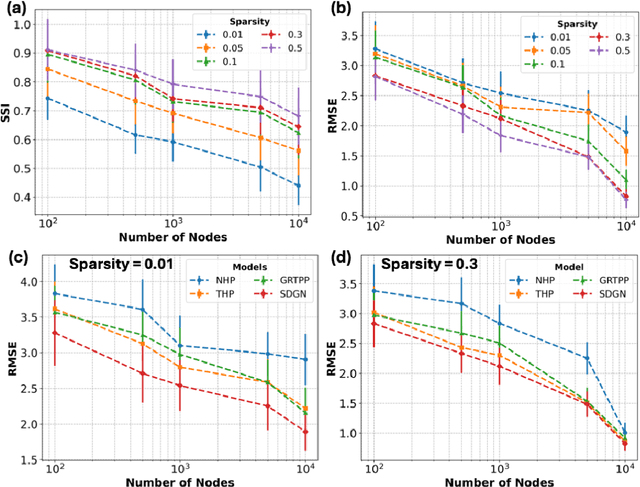
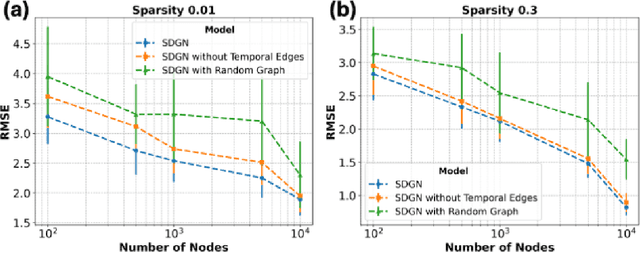
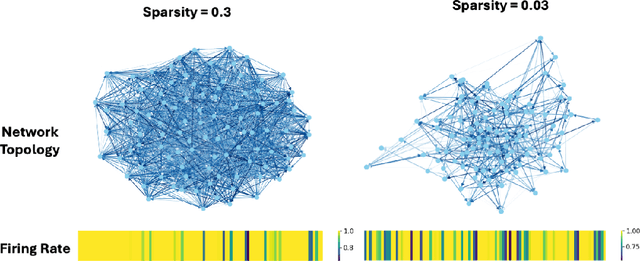
Abstract:Modeling and predicting temporal point processes (TPPs) is critical in domains such as neuroscience, epidemiology, finance, and social sciences. We introduce the Spiking Dynamic Graph Network (SDGN), a novel framework that leverages the temporal processing capabilities of spiking neural networks (SNNs) and spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) to dynamically estimate underlying spatio-temporal functional graphs. Unlike existing methods that rely on predefined or static graph structures, SDGN adapts to any dataset by learning dynamic spatio-temporal dependencies directly from the event data, enhancing generalizability and robustness. While SDGN offers significant improvements over prior methods, we acknowledge its limitations in handling dense graphs and certain non-Gaussian dependencies, providing opportunities for future refinement. Our evaluations, conducted on both synthetic and real-world datasets including NYC Taxi, 911, Reddit, and Stack Overflow, demonstrate that SDGN achieves superior predictive accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency. Furthermore, we include ablation studies to highlight the contributions of its core components.
Online Relational Inference for Evolving Multi-agent Interacting Systems
Nov 03, 2024



Abstract:We introduce a novel framework, Online Relational Inference (ORI), designed to efficiently identify hidden interaction graphs in evolving multi-agent interacting systems using streaming data. Unlike traditional offline methods that rely on a fixed training set, ORI employs online backpropagation, updating the model with each new data point, thereby allowing it to adapt to changing environments in real-time. A key innovation is the use of an adjacency matrix as a trainable parameter, optimized through a new adaptive learning rate technique called AdaRelation, which adjusts based on the historical sensitivity of the decoder to changes in the interaction graph. Additionally, a data augmentation method named Trajectory Mirror (TM) is introduced to improve generalization by exposing the model to varied trajectory patterns. Experimental results on both synthetic datasets and real-world data (CMU MoCap for human motion) demonstrate that ORI significantly improves the accuracy and adaptability of relational inference in dynamic settings compared to existing methods. This approach is model-agnostic, enabling seamless integration with various neural relational inference (NRI) architectures, and offers a robust solution for real-time applications in complex, evolving systems.
Learning Locally Interacting Discrete Dynamical Systems: Towards Data-Efficient and Scalable Prediction
Apr 09, 2024



Abstract:Locally interacting dynamical systems, such as epidemic spread, rumor propagation through crowd, and forest fire, exhibit complex global dynamics originated from local, relatively simple, and often stochastic interactions between dynamic elements. Their temporal evolution is often driven by transitions between a finite number of discrete states. Despite significant advancements in predictive modeling through deep learning, such interactions among many elements have rarely explored as a specific domain for predictive modeling. We present Attentive Recurrent Neural Cellular Automata (AR-NCA), to effectively discover unknown local state transition rules by associating the temporal information between neighboring cells in a permutation-invariant manner. AR-NCA exhibits the superior generalizability across various system configurations (i.e., spatial distribution of states), data efficiency and robustness in extremely data-limited scenarios even in the presence of stochastic interactions, and scalability through spatial dimension-independent prediction.
Sparse Spiking Neural Network: Exploiting Heterogeneity in Timescales for Pruning Recurrent SNN
Mar 06, 2024Abstract:Recurrent Spiking Neural Networks (RSNNs) have emerged as a computationally efficient and brain-inspired learning model. The design of sparse RSNNs with fewer neurons and synapses helps reduce the computational complexity of RSNNs. Traditionally, sparse SNNs are obtained by first training a dense and complex SNN for a target task, and, then, pruning neurons with low activity (activity-based pruning) while maintaining task performance. In contrast, this paper presents a task-agnostic methodology for designing sparse RSNNs by pruning a large randomly initialized model. We introduce a novel Lyapunov Noise Pruning (LNP) algorithm that uses graph sparsification methods and utilizes Lyapunov exponents to design a stable sparse RSNN from a randomly initialized RSNN. We show that the LNP can leverage diversity in neuronal timescales to design a sparse Heterogeneous RSNN (HRSNN). Further, we show that the same sparse HRSNN model can be trained for different tasks, such as image classification and temporal prediction. We experimentally show that, in spite of being task-agnostic, LNP increases computational efficiency (fewer neurons and synapses) and prediction performance of RSNNs compared to traditional activity-based pruning of trained dense models.
* Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2024
Studying the Impact of Stochasticity on the Evaluation of Deep Neural Networks for Forest-Fire Prediction
Feb 23, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents the first systematic study of the evaluation of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) for discrete dynamical systems under stochastic assumptions, with a focus on wildfire prediction. We develop a framework to study the impact of stochasticity on two classes of evaluation metrics: classification-based metrics, which assess fidelity to observed ground truth (GT), and proper scoring rules, which test fidelity-to-statistic. Our findings reveal that evaluating for fidelity-to-statistic is a reliable alternative in highly stochastic scenarios. We extend our analysis to real-world wildfire data, highlighting limitations in traditional wildfire prediction evaluation methods, and suggest interpretable stochasticity-compatible alternatives.
Unsupervised 3D Object Learning through Neuron Activity aware Plasticity
Feb 22, 2023Abstract:We present an unsupervised deep learning model for 3D object classification. Conventional Hebbian learning, a well-known unsupervised model, suffers from loss of local features leading to reduced performance for tasks with complex geometric objects. We present a deep network with a novel Neuron Activity Aware (NeAW) Hebbian learning rule that dynamically switches the neurons to be governed by Hebbian learning or anti-Hebbian learning, depending on its activity. We analytically show that NeAW Hebbian learning relieves the bias in neuron activity, allowing more neurons to attend to the representation of the 3D objects. Empirical results show that the NeAW Hebbian learning outperforms other variants of Hebbian learning and shows higher accuracy over fully supervised models when training data is limited.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge