Forecasting local behavior of multi-agent system and its application to forest fire model
Paper and Code
Oct 28, 2022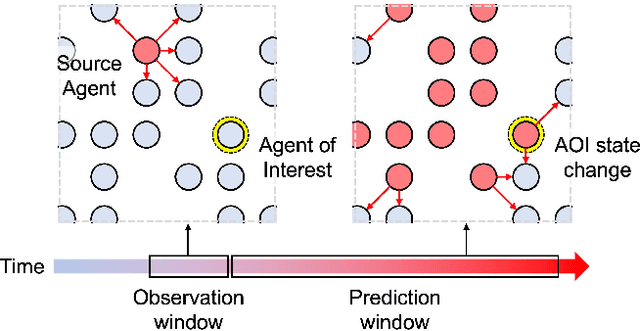
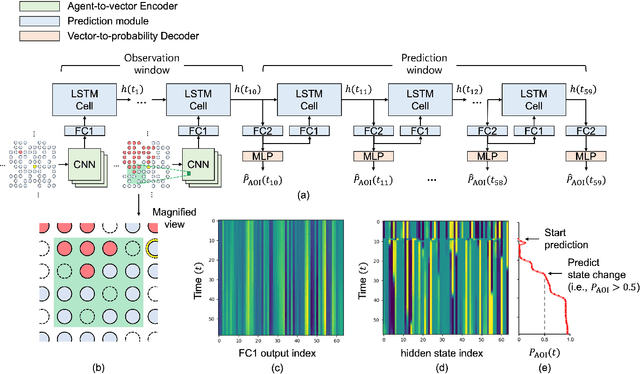
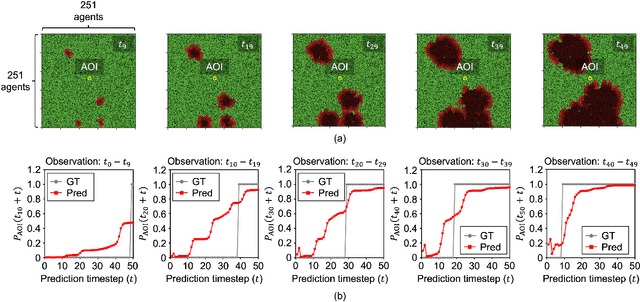
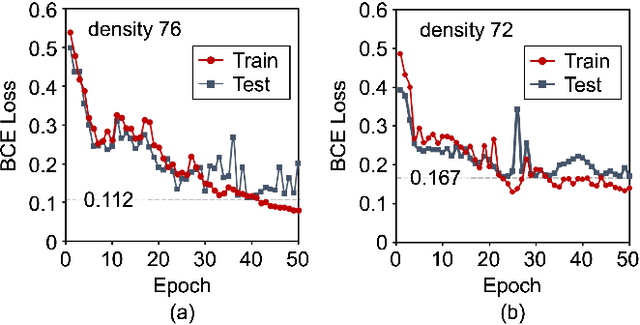
In this paper, we study a CNN-LSTM model to forecast the state of a specific agent in a large multi-agent system. The proposed model consists of a CNN encoder to represent the system into a low-dimensional vector, a LSTM module to learn the agent dynamics in the vector space, and a MLP decoder to predict the future state of an agent. A forest fire model is considered as an example where we need to predict when a specific tree agent will be burning. We observe that the proposed model achieves higher AUC with less computation than a frame-based model and significantly saves computational costs such as the activation than ConvLSTM.
* submitted to IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and
Signal Processing (ICASSP)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge