Muhammad Arslan Manzoor
PAEFF: Precise Alignment and Enhanced Gated Feature Fusion for Face-Voice Association
May 22, 2025Abstract:We study the task of learning association between faces and voices, which is gaining interest in the multimodal community lately. These methods suffer from the deliberate crafting of negative mining procedures as well as the reliance on the distant margin parameter. These issues are addressed by learning a joint embedding space in which orthogonality constraints are applied to the fused embeddings of faces and voices. However, embedding spaces of faces and voices possess different characteristics and require spaces to be aligned before fusing them. To this end, we propose a method that accurately aligns the embedding spaces and fuses them with an enhanced gated fusion thereby improving the performance of face-voice association. Extensive experiments on the VoxCeleb dataset reveals the merits of the proposed approach.
UrduFactCheck: An Agentic Fact-Checking Framework for Urdu with Evidence Boosting and Benchmarking
May 21, 2025Abstract:The rapid use of large language models (LLMs) has raised critical concerns regarding the factual reliability of their outputs, especially in low-resource languages such as Urdu. Existing automated fact-checking solutions overwhelmingly focus on English, leaving a significant gap for the 200+ million Urdu speakers worldwide. In this work, we introduce UrduFactCheck, the first comprehensive, modular fact-checking framework specifically tailored for Urdu. Our system features a dynamic, multi-strategy evidence retrieval pipeline that combines monolingual and translation-based approaches to address the scarcity of high-quality Urdu evidence. We curate and release two new hand-annotated benchmarks: UrduFactBench for claim verification and UrduFactQA for evaluating LLM factuality. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UrduFactCheck, particularly its translation-augmented variants, consistently outperforms baselines and open-source alternatives on multiple metrics. We further benchmark twelve state-of-the-art (SOTA) LLMs on factual question answering in Urdu, highlighting persistent gaps between proprietary and open-source models. UrduFactCheck's code and datasets are open-sourced and publicly available at https://github.com/mbzuai-nlp/UrduFactCheck.
A Decade of Deep Learning: A Survey on The Magnificent Seven
Dec 13, 2024Abstract:Deep learning has fundamentally reshaped the landscape of artificial intelligence over the past decade, enabling remarkable achievements across diverse domains. At the heart of these developments lie multi-layered neural network architectures that excel at automatic feature extraction, leading to significant improvements in machine learning tasks. To demystify these advances and offer accessible guidance, we present a comprehensive overview of the most influential deep learning algorithms selected through a broad-based survey of the field. Our discussion centers on pivotal architectures, including Residual Networks, Transformers, Generative Adversarial Networks, Variational Autoencoders, Graph Neural Networks, Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training, and Diffusion models. We detail their historical context, highlight their mathematical foundations and algorithmic principles, and examine subsequent variants, extensions, and practical considerations such as training methodologies, normalization techniques, and learning rate schedules. Beyond historical and technical insights, we also address their applications, challenges, and potential research directions. This survey aims to serve as a practical manual for both newcomers seeking an entry point into cutting-edge deep learning methods and experienced researchers transitioning into this rapidly evolving domain.
MGM: Global Understanding of Audience Overlap Graphs for Predicting the Factuality and the Bias of News Media
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:In the current era of rapidly growing digital data, evaluating the political bias and factuality of news outlets has become more important for seeking reliable information online. In this work, we study the classification problem of profiling news media from the lens of political bias and factuality. Traditional profiling methods, such as Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs) and Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have shown promising results, but they face notable challenges. PLMs focus solely on textual features, causing them to overlook the complex relationships between entities, while GNNs often struggle with media graphs containing disconnected components and insufficient labels. To address these limitations, we propose MediaGraphMind (MGM), an effective solution within a variational Expectation-Maximization (EM) framework. Instead of relying on limited neighboring nodes, MGM leverages features, structural patterns, and label information from globally similar nodes. Such a framework not only enables GNNs to capture long-range dependencies for learning expressive node representations but also enhances PLMs by integrating structural information and therefore improving the performance of both models. The extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework and achieve new state-of-the-art results. Further, we share our repository1 which contains the dataset, code, and documentation
Can Machines Resonate with Humans? Evaluating the Emotional and Empathic Comprehension of LMs
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Empathy plays a pivotal role in fostering prosocial behavior, often triggered by the sharing of personal experiences through narratives. However, modeling empathy using NLP approaches remains challenging due to its deep interconnection with human interaction dynamics. Previous approaches, which involve fine-tuning language models (LMs) on human-annotated empathic datasets, have had limited success. In our pursuit of improving empathy understanding in LMs, we propose several strategies, including contrastive learning with masked LMs and supervised fine-tuning with Large Language Models (LLMs). While these methods show improvements over previous methods, the overall results remain unsatisfactory. To better understand this trend, we performed an analysis which reveals a low agreement among annotators. This lack of consensus hinders training and highlights the subjective nature of the task. We also explore the cultural impact on annotations. To study this, we meticulously collected story pairs in Urdu language and find that subjectivity in interpreting empathy among annotators appears to be independent of cultural background. The insights from our systematic exploration of LMs' understanding of empathy suggest that there is considerable room for exploration in both task formulation and modeling.
Factuality of Large Language Models in the Year 2024
Feb 09, 2024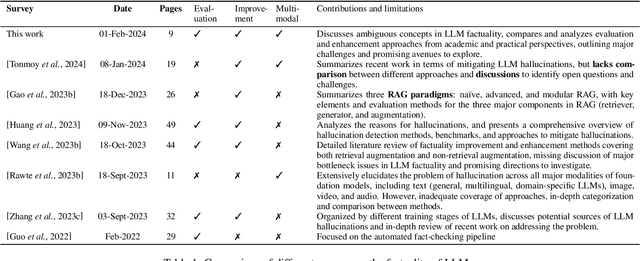
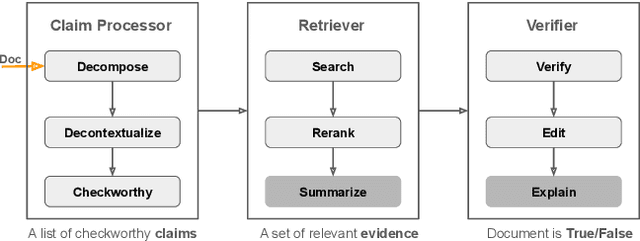
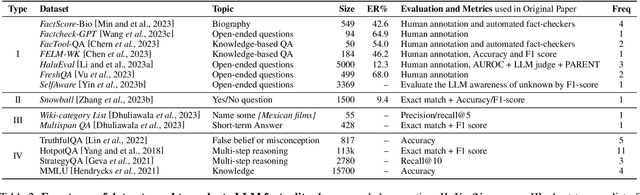
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), especially when instruction-tuned for chat, have become part of our daily lives, freeing people from the process of searching, extracting, and integrating information from multiple sources by offering a straightforward answer to a variety of questions in a single place. Unfortunately, in many cases, LLM responses are factually incorrect, which limits their applicability in real-world scenarios. As a result, research on evaluating and improving the factuality of LLMs has attracted a lot of research attention recently. In this survey, we critically analyze existing work with the aim to identify the major challenges and their associated causes, pointing out to potential solutions for improving the factuality of LLMs, and analyzing the obstacles to automated factuality evaluation for open-ended text generation. We further offer an outlook on where future research should go.
Multimodality Representation Learning: A Survey on Evolution, Pretraining and Its Applications
Feb 01, 2023Abstract:Multimodality Representation Learning, as a technique of learning to embed information from different modalities and their correlations, has achieved remarkable success on a variety of applications, such as Visual Question Answering (VQA), Natural Language for Visual Reasoning (NLVR), and Vision Language Retrieval (VLR). Among these applications, cross-modal interaction and complementary information from different modalities are crucial for advanced models to perform any multimodal task, e.g., understand, recognize, retrieve, or generate optimally. Researchers have proposed diverse methods to address these tasks. The different variants of transformer-based architectures performed extraordinarily on multiple modalities. This survey presents the comprehensive literature on the evolution and enhancement of deep learning multimodal architectures to deal with textual, visual and audio features for diverse cross-modal and modern multimodal tasks. This study summarizes the (i) recent task-specific deep learning methodologies, (ii) the pretraining types and multimodal pretraining objectives, (iii) from state-of-the-art pretrained multimodal approaches to unifying architectures, and (iv) multimodal task categories and possible future improvements that can be devised for better multimodal learning. Moreover, we prepare a dataset section for new researchers that covers most of the benchmarks for pretraining and finetuning. Finally, major challenges, gaps, and potential research topics are explored. A constantly-updated paperlist related to our survey is maintained at https://github.com/marslanm/multimodality-representation-learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge