Mubashir Noman
EoCD: Encoder only Remote Sensing Change Detection
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Being a cornerstone of temporal analysis, change detection has been playing a pivotal role in modern earth observation. Existing change detection methods rely on the Siamese encoder to individually extract temporal features followed by temporal fusion. Subsequently, these methods design sophisticated decoders to improve the change detection performance without taking into consideration the complexity of the model. These aforementioned issues intensify the overall computational cost as well as the network's complexity which is undesirable. Alternatively, few methods utilize the early fusion scheme to combine the temporal images. These methods prevent the extra overhead of Siamese encoder, however, they also rely on sophisticated decoders for better performance. In addition, these methods demonstrate inferior performance as compared to late fusion based methods. To bridge these gaps, we introduce encoder only change detection (EoCD) that is a simple and effective method for the change detection task. The proposed method performs the early fusion of the temporal data and replaces the decoder with a parameter-free multiscale feature fusion module thereby significantly reducing the overall complexity of the model. EoCD demonstrate the optimal balance between the change detection performance and the prediction speed across a variety of encoder architectures. Additionally, EoCD demonstrate that the performance of the model is predominantly dependent on the encoder network, making the decoder an additional component. Extensive experimentation on four challenging change detection datasets reveals the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Distillation-based Layer Dropping (DLD): Effective End-to-end Framework for Dynamic Speech Networks
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Edge devices operate in constrained and varying resource settings, requiring dynamic architectures that can adapt to limitations of the available resources. To meet such demands, layer dropping ($\mathcal{LD}$) approach is typically used to transform static models into dynamic ones by skipping parts of the network along with reducing overall computational complexity. However, existing $\mathcal{LD}$ methods greatly impact the dynamic model's performance for low and high dropping cases, deteriorating the performance-computation trade-off. To this end, we propose a distillation-based layer dropping (DLD) framework that effectively combines the capabilities of knowledge distillation and $\mathcal{LD}$ in an end-to-end fashion, thereby achieving state-of-the-art performance for dynamic speech networks. Comprehensive experimentation utilizing well-known speech recognition methods, including conformer and WavLM, on three public benchmarks demonstrates the effectiveness of our framework, reducing the word error rate by $9.32\%$ and $2.25\%$ for high and no dropping cases with $33.3\%$ reduction in training time.
Face-Voice Association with Inductive Bias for Maximum Class Separation
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Face-voice association is widely studied in multimodal learning and is approached representing faces and voices with embeddings that are close for a same person and well separated from those of others. Previous work achieved this with loss functions. Recent advancements in classification have shown that the discriminative ability of embeddings can be strengthened by imposing maximum class separation as inductive bias. This technique has never been used in the domain of face-voice association, and this work aims at filling this gap. More specifically, we develop a method for face-voice association that imposes maximum class separation among multimodal representations of different speakers as an inductive bias. Through quantitative experiments we demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, showing that it achieves SOTA performance on two task formulation of face-voice association. Furthermore, we carry out an ablation study to show that imposing inductive bias is most effective when combined with losses for inter-class orthogonality. To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first that applies and demonstrates the effectiveness of maximum class separation as an inductive bias in multimodal learning; it hence paves the way to establish a new paradigm.
HyRet-Change: A hybrid retentive network for remote sensing change detection
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Recently convolution and transformer-based change detection (CD) methods provide promising performance. However, it remains unclear how the local and global dependencies interact to effectively alleviate the pseudo changes. Moreover, directly utilizing standard self-attention presents intrinsic limitations including governing global feature representations limit to capture subtle changes, quadratic complexity, and restricted training parallelism. To address these limitations, we propose a Siamese-based framework, called HyRet-Change, which can seamlessly integrate the merits of convolution and retention mechanisms at multi-scale features to preserve critical information and enhance adaptability in complex scenes. Specifically, we introduce a novel feature difference module to exploit both convolutions and multi-head retention mechanisms in a parallel manner to capture complementary information. Furthermore, we propose an adaptive local-global interactive context awareness mechanism that enables mutual learning and enhances discrimination capability through information exchange. We perform experiments on three challenging CD datasets and achieve state-of-the-art performance compared to existing methods. Our source code is publicly available at https://github.com/mustansarfiaz/HyRect-Change.
* Accepted at IEEE IGARSS 2025
InceptionMamba: Efficient Multi-Stage Feature Enhancement with Selective State Space Model for Microscopic Medical Image Segmentation
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Accurate microscopic medical image segmentation plays a crucial role in diagnosing various cancerous cells and identifying tumors. Driven by advancements in deep learning, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transformer-based models have been extensively studied to enhance receptive fields and improve medical image segmentation task. However, they often struggle to capture complex cellular and tissue structures in challenging scenarios such as background clutter and object overlap. Moreover, their reliance on the availability of large datasets for improved performance, along with the high computational cost, limit their practicality. To address these issues, we propose an efficient framework for the segmentation task, named InceptionMamba, which encodes multi-stage rich features and offers both performance and computational efficiency. Specifically, we exploit semantic cues to capture both low-frequency and high-frequency regions to enrich the multi-stage features to handle the blurred region boundaries (e.g., cell boundaries). These enriched features are input to a hybrid model that combines an Inception depth-wise convolution with a Mamba block, to maintain high efficiency and capture inherent variations in the scales and shapes of the regions of interest. These enriched features along with low-resolution features are fused to get the final segmentation mask. Our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on two challenging microscopic segmentation datasets (SegPC21 and GlaS) and two skin lesion segmentation datasets (ISIC2017 and ISIC2018), while reducing computational cost by about 5 times compared to the previous best performing method.
PAEFF: Precise Alignment and Enhanced Gated Feature Fusion for Face-Voice Association
May 22, 2025Abstract:We study the task of learning association between faces and voices, which is gaining interest in the multimodal community lately. These methods suffer from the deliberate crafting of negative mining procedures as well as the reliance on the distant margin parameter. These issues are addressed by learning a joint embedding space in which orthogonality constraints are applied to the fused embeddings of faces and voices. However, embedding spaces of faces and voices possess different characteristics and require spaces to be aligned before fusing them. To this end, we propose a method that accurately aligns the embedding spaces and fuses them with an enhanced gated fusion thereby improving the performance of face-voice association. Extensive experiments on the VoxCeleb dataset reveals the merits of the proposed approach.
An Effective Training Framework for Light-Weight Automatic Speech Recognition Models
May 22, 2025Abstract:Recent advancement in deep learning encouraged developing large automatic speech recognition (ASR) models that achieve promising results while ignoring computational and memory constraints. However, deploying such models on low resource devices is impractical despite of their favorable performance. Existing approaches (pruning, distillation, layer skip etc.) transform the large models into smaller ones at the cost of significant performance degradation or require prolonged training of smaller models for better performance. To address these issues, we introduce an efficacious two-step representation learning based approach capable of producing several small sized models from a single large model ensuring considerably better performance in limited number of epochs. Comprehensive experimentation on ASR benchmarks reveals the efficacy of our approach, achieving three-fold training speed-up and up to 12.54% word error rate improvement.
COSNet: A Novel Semantic Segmentation Network using Enhanced Boundaries in Cluttered Scenes
Oct 31, 2024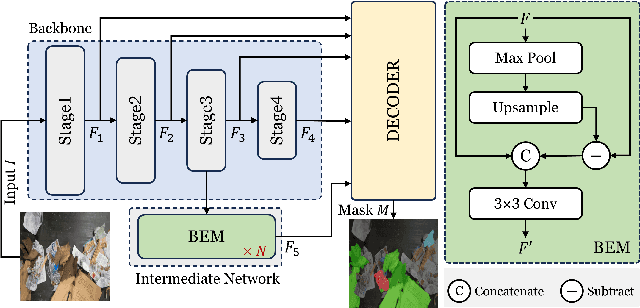


Abstract:Automated waste recycling aims to efficiently separate the recyclable objects from the waste by employing vision-based systems. However, the presence of varying shaped objects having different material types makes it a challenging problem, especially in cluttered environments. Existing segmentation methods perform reasonably on many semantic segmentation datasets by employing multi-contextual representations, however, their performance is degraded when utilized for waste object segmentation in cluttered scenarios. In addition, plastic objects further increase the complexity of the problem due to their translucent nature. To address these limitations, we introduce an efficacious segmentation network, named COSNet, that uses boundary cues along with multi-contextual information to accurately segment the objects in cluttered scenes. COSNet introduces novel components including feature sharpening block (FSB) and boundary enhancement module (BEM) for enhancing the features and highlighting the boundary information of irregular waste objects in cluttered environment. Extensive experiments on three challenging datasets including ZeroWaste-f, SpectralWaste, and ADE20K demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Our COSNet achieves a significant gain of 1.8% on ZeroWaste-f and 2.1% on SpectralWaste datasets respectively in terms of mIoU metric.
CDChat: A Large Multimodal Model for Remote Sensing Change Description
Sep 24, 2024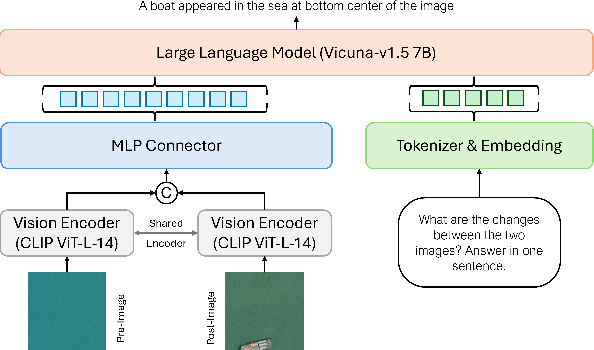
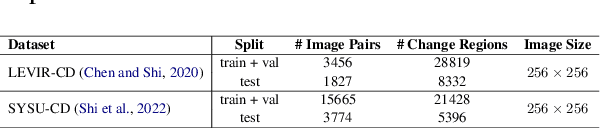
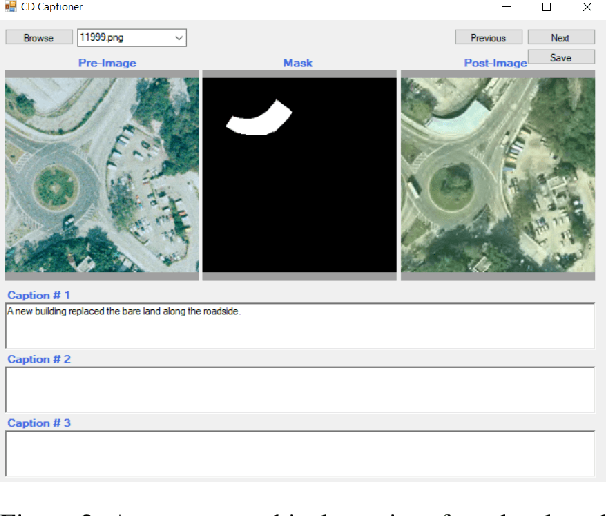
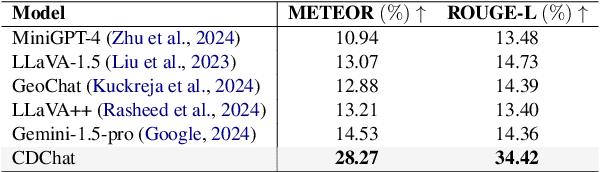
Abstract:Large multimodal models (LMMs) have shown encouraging performance in the natural image domain using visual instruction tuning. However, these LMMs struggle to describe the content of remote sensing images for tasks such as image or region grounding, classification, etc. Recently, GeoChat make an effort to describe the contents of the RS images. Although, GeoChat achieves promising performance for various RS tasks, it struggles to describe the changes between bi-temporal RS images which is a key RS task. This necessitates the development of an LMM that can describe the changes between the bi-temporal RS images. However, there is insufficiency of datasets that can be utilized to tune LMMs. In order to achieve this, we introduce a change description instruction dataset that can be utilized to finetune an LMM and provide better change descriptions for RS images. Furthermore, we show that the LLaVA-1.5 model, with slight modifications, can be finetuned on the change description instruction dataset and achieve favorably better performance.
FANet: Feature Amplification Network for Semantic Segmentation in Cluttered Background
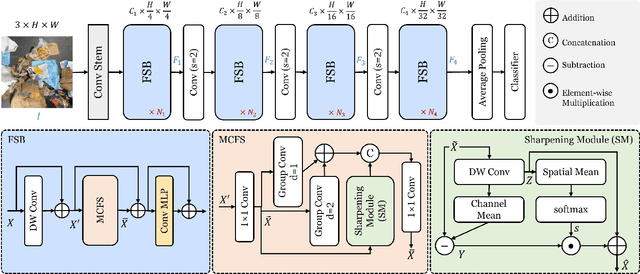
Jul 12, 2024Abstract:Existing deep learning approaches leave out the semantic cues that are crucial in semantic segmentation present in complex scenarios including cluttered backgrounds and translucent objects, etc. To handle these challenges, we propose a feature amplification network (FANet) as a backbone network that incorporates semantic information using a novel feature enhancement module at multi-stages. To achieve this, we propose an adaptive feature enhancement (AFE) block that benefits from both a spatial context module (SCM) and a feature refinement module (FRM) in a parallel fashion. SCM aims to exploit larger kernel leverages for the increased receptive field to handle scale variations in the scene. Whereas our novel FRM is responsible for generating semantic cues that can capture both low-frequency and high-frequency regions for better segmentation tasks. We perform experiments over challenging real-world ZeroWaste-f dataset which contains background-cluttered and translucent objects. Our experimental results demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance compared to existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge