Michele Caprio
Bayesian Conformal Prediction as a Decision Risk Problem
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Bayesian posterior predictive densities as non-conformity scores and Bayesian quadrature are used to estimate and minimise the expected prediction set size. Operating within a split conformal framework, BCP provides valid coverage guarantees and demonstrates reliable empirical coverage under model misspecification. Across regression and classification tasks, including distribution-shifted settings such as ImageNet-A, BCP yields prediction sets of comparable size to split conformal prediction, while exhibiting substantially lower run-to-run variability in set size. In sparse regression with nominal coverage of 80 percent, BCP achieves 81 percent empirical coverage under a misspecified prior, whereas Bayesian credible intervals under-cover at 49 percent.
Quantifying Epistemic Predictive Uncertainty in Conformal Prediction
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We study the problem of quantifying epistemic predictive uncertainty (EPU) -- that is, uncertainty faced at prediction time due to the existence of multiple plausible predictive models -- within the framework of conformal prediction (CP). To expose the implicit model multiplicity underlying CP, we build on recent results showing that, under a mild assumption, any full CP procedure induces a set of closed and convex predictive distributions, commonly referred to as a credal set. Importantly, the conformal prediction region (CPR) coincides exactly with the set of labels to which all distributions in the induced credal set assign probability at least $1-α$. As our first contribution, we prove that this characterisation also holds in split CP. Building on this connection, we then propose a computationally efficient and analytically tractable uncertainty measure, based on \emph{Maximum Mean Imprecision}, to quantify the EPU by measuring the degree of conflicting information within the induced credal set. Experiments on active learning and selective classification demonstrate that the quantified EPU provides substantially more informative and fine-grained uncertainty assessments than reliance on CPR size alone. More broadly, this work highlights the potential of CP serving as a principled basis for decision-making under epistemic uncertainty.
Bulk-Calibrated Credal Ambiguity Sets: Fast, Tractable Decision Making under Out-of-Sample Contamination
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Distributionally robust optimisation (DRO) minimises the worst-case expected loss over an ambiguity set that can capture distributional shifts in out-of-sample environments. While Huber (linear-vacuous) contamination is a classical minimal-assumption model for an $\varepsilon$-fraction of arbitrary perturbations, including it in an ambiguity set can make the worst-case risk infinite and the DRO objective vacuous unless one imposes strong boundedness or support assumptions. We address these challenges by introducing bulk-calibrated credal ambiguity sets: we learn a high-mass bulk set from data while considering contamination inside the bulk and bounding the remaining tail contribution separately. This leads to a closed-form, finite $\mathrm{mean}+\sup$ robust objective and tractable linear or second-order cone programs for common losses and bulk geometries. Through this framework, we highlight and exploit the equivalence between the imprecise probability (IP) notion of upper expectation and the worst-case risk, demonstrating how IP credal sets translate into DRO objectives with interpretable tolerance levels. Experiments on heavy-tailed inventory control, geographically shifted house-price regression, and demographically shifted text classification show competitive robustness-accuracy trade-offs and efficient optimisation times, using Bayesian, frequentist, or empirical reference distributions.
When Do Credal Sets Stabilize? Fixed-Point Theorems for Credal Set Updates
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Many machine learning algorithms rely on iterative updates of uncertainty representations, ranging from variational inference and expectation-maximization, to reinforcement learning, continual learning, and multi-agent learning. In the presence of imprecision and ambiguity, credal sets -- closed, convex sets of probability distributions -- have emerged as a popular framework for representing imprecise probabilistic beliefs. Under such imprecision, many learning problems in imprecise probabilistic machine learning (IPML) may be viewed as processes involving successive applications of update rules on credal sets. This naturally raises the question of whether this iterative process converges to stable fixed points -- or, more generally, under what conditions on the updating mechanism such fixed points exist, and whether they can be attained. We provide the first analysis of this problem and illustrate our findings using Credal Bayesian Deep Learning as a concrete example. Our work demonstrates that incorporating imprecision into the learning process not only enriches the representation of uncertainty, but also reveals structural conditions under which stability emerges, thereby offering new insights into the dynamics of iterative learning under imprecision.
HumanoidVerse: A Versatile Humanoid for Vision-Language Guided Multi-Object Rearrangement
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:We introduce HumanoidVerse, a novel framework for vision-language guided humanoid control that enables a single physically simulated robot to perform long-horizon, multi-object rearrangement tasks across diverse scenes. Unlike prior methods that operate in fixed settings with single-object interactions, our approach supports consecutive manipulation of multiple objects, guided only by natural language instructions and egocentric camera RGB observations. HumanoidVerse is trained via a multi-stage curriculum using a dual-teacher distillation pipeline, enabling fluid transitions between sub-tasks without requiring environment resets. To support this, we construct a large-scale dataset comprising 350 multi-object tasks spanning four room layouts. Extensive experiments in the Isaac Gym simulator demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms prior state-of-the-art in both task success rate and spatial precision, and generalizes well to unseen environments and instructions. Our work represents a key step toward robust, general-purpose humanoid agents capable of executing complex, sequential tasks under real-world sensory constraints. The video visualization results can be found on the project page: https://haozhuo-zhang.github.io/HumanoidVerse-project-page/.
Epistemic Errors of Imperfect Multitask Learners When Distributions Shift
May 29, 2025Abstract:When data are noisy, a statistical learner's goal is to resolve epistemic uncertainty about the data it will encounter at test-time, i.e., to identify the distribution of test (target) data. Many real-world learning settings introduce sources of epistemic uncertainty that can not be resolved on the basis of training (source) data alone: The source data may arise from multiple tasks (multitask learning), the target data may differ systematically from the source data tasks (distribution shift), and/or the learner may not arrive at an accurate characterization of the source data (imperfect learning). We introduce a principled definition of epistemic error, and provide a generic, decompositional epistemic error bound. Our error bound is the first to (i) consider epistemic error specifically, (ii) accommodate all the sources of epistemic uncertainty above, and (iii) separately attribute the error to each of multiple aspects of the learning procedure and environment. As corollaries of the generic result, we provide (i) epistemic error bounds specialized to the settings of Bayesian transfer learning and distribution shift within $\epsilon$-neighborhoods, and (ii) a set of corresponding generalization bounds. Finally, we provide a novel definition of negative transfer, and validate its insights in a synthetic experimental setting.
Integral Imprecise Probability Metrics
May 22, 2025Abstract:Quantifying differences between probability distributions is fundamental to statistics and machine learning, primarily for comparing statistical uncertainty. In contrast, epistemic uncertainty (EU) -- due to incomplete knowledge -- requires richer representations than those offered by classical probability. Imprecise probability (IP) theory offers such models, capturing ambiguity and partial belief. This has driven growing interest in imprecise probabilistic machine learning (IPML), where inference and decision-making rely on broader uncertainty models -- highlighting the need for metrics beyond classical probability. This work introduces the Integral Imprecise Probability Metric (IIPM) framework, a Choquet integral-based generalisation of classical Integral Probability Metric (IPM) to the setting of capacities -- a broad class of IP models encompassing many existing ones, including lower probabilities, probability intervals, belief functions, and more. Theoretically, we establish conditions under which IIPM serves as a valid metric and metrises a form of weak convergence of capacities. Practically, IIPM not only enables comparison across different IP models but also supports the quantification of epistemic uncertainty within a single IP model. In particular, by comparing an IP model with its conjugate, IIPM gives rise to a new class of EU measures -- Maximum Mean Imprecision -- which satisfy key axiomatic properties proposed in the Uncertainty Quantification literature. We validate MMI through selective classification experiments, demonstrating strong empirical performance against established EU measures, and outperforming them when classical methods struggle to scale to a large number of classes. Our work advances both theory and practice in IPML, offering a principled framework for comparing and quantifying epistemic uncertainty under imprecision.
TAR: Teacher-Aligned Representations via Contrastive Learning for Quadrupedal Locomotion
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Quadrupedal locomotion via Reinforcement Learning (RL) is commonly addressed using the teacher-student paradigm, where a privileged teacher guides a proprioceptive student policy. However, key challenges such as representation misalignment between the privileged teacher and the proprioceptive-only student, covariate shift due to behavioral cloning, and lack of deployable adaptation lead to poor generalization in real-world scenarios. We propose Teacher-Aligned Representations via Contrastive Learning (TAR), a framework that leverages privileged information with self-supervised contrastive learning to bridge this gap. By aligning representations to a privileged teacher in simulation via contrastive objectives, our student policy learns structured latent spaces and exhibits robust generalization to Out-of-Distribution (OOD) scenarios, surpassing the fully privileged "Teacher". Results showed accelerated training by 2x compared to state-of-the-art baselines to achieve peak performance. OOD scenarios showed better generalization by 40 percent on average compared to existing methods. Additionally, TAR transitions seamlessly into learning during deployment without requiring privileged states, setting a new benchmark in sample-efficient, adaptive locomotion and enabling continual fine-tuning in real-world scenarios. Open-source code and videos are available at https://ammousa.github.io/TARLoco/.
Conformal Prediction Regions are Imprecise Highest Density Regions
Feb 10, 2025


Abstract:Recently, Cella and Martin proved how, under an assumption called consonance, a credal set (i.e. a closed and convex set of probabilities) can be derived from the conformal transducer associated with transductive conformal prediction. We show that the Imprecise Highest Density Region (IHDR) associated with such a credal set corresponds to the classical Conformal Prediction Region. In proving this result, we relate the set of probability density/mass functions (pdf/pmf's) associated with the elements of the credal set to the imprecise probabilistic concept of a cloud. As a result, we establish new relationships between Conformal Prediction and Imprecise Probability (IP) theories. A byproduct of our presentation is the discovery that consonant plausibility functions are monoid homomorphisms, a new algebraic property of an IP tool.
Conformalized Credal Regions for Classification with Ambiguous Ground Truth
Nov 07, 2024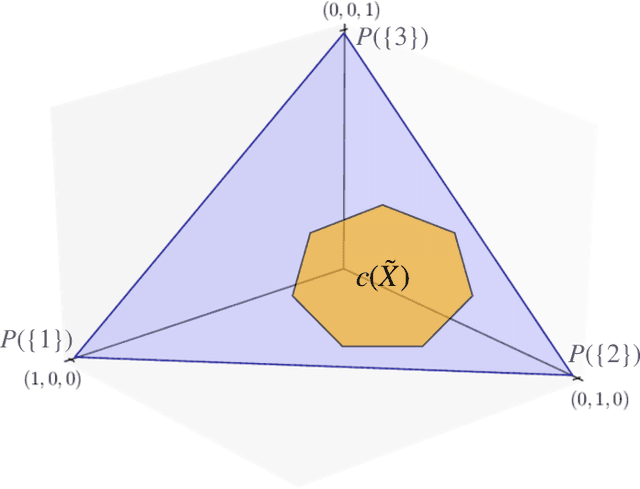
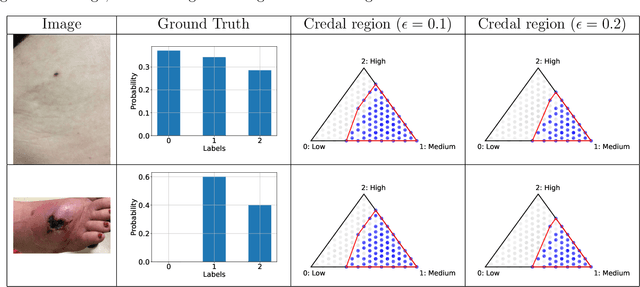
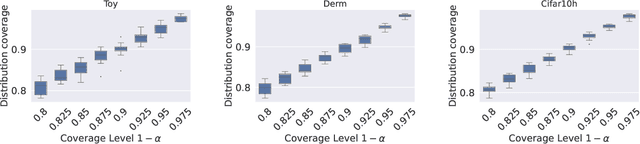
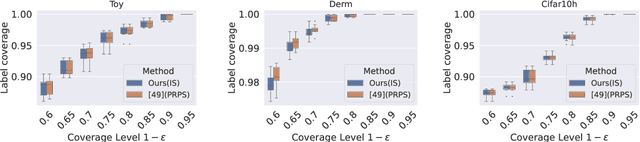
Abstract:An open question in \emph{Imprecise Probabilistic Machine Learning} is how to empirically derive a credal region (i.e., a closed and convex family of probabilities on the output space) from the available data, without any prior knowledge or assumption. In classification problems, credal regions are a tool that is able to provide provable guarantees under realistic assumptions by characterizing the uncertainty about the distribution of the labels. Building on previous work, we show that credal regions can be directly constructed using conformal methods. This allows us to provide a novel extension of classical conformal prediction to problems with ambiguous ground truth, that is, when the exact labels for given inputs are not exactly known. The resulting construction enjoys desirable practical and theoretical properties: (i) conformal coverage guarantees, (ii) smaller prediction sets (compared to classical conformal prediction regions) and (iii) disentanglement of uncertainty sources (epistemic, aleatoric). We empirically verify our findings on both synthetic and real datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge