Mert Gurbuzbalaban
DIGing--SGLD: Decentralized and Scalable Langevin Sampling over Time--Varying Networks
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Sampling from a target distribution induced by training data is central to Bayesian learning, with Stochastic Gradient Langevin Dynamics (SGLD) serving as a key tool for scalable posterior sampling and decentralized variants enabling learning when data are distributed across a network of agents. This paper introduces DIGing-SGLD, a decentralized SGLD algorithm designed for scalable Bayesian learning in multi-agent systems operating over time-varying networks. Existing decentralized SGLD methods are restricted to static network topologies, and many exhibit steady-state sampling bias caused by network effects, even when full batches are used. DIGing-SGLD overcomes these limitations by integrating Langevin-based sampling with the gradient-tracking mechanism of the DIGing algorithm, originally developed for decentralized optimization over time-varying networks, thereby enabling efficient and bias-free sampling without a central coordinator. To our knowledge, we provide the first finite-time non-asymptotic Wasserstein convergence guarantees for decentralized SGLD-based sampling over time-varying networks, with explicit constants. Under standard strong convexity and smoothness assumptions, DIGing-SGLD achieves geometric convergence to an $O(\sqrtη)$ neighborhood of the target distribution, where $η$ is the stepsize, with dependence on the target accuracy matching the best-known rates for centralized and static-network SGLD algorithms using constant stepsize. Numerical experiments on Bayesian linear and logistic regression validate the theoretical results and demonstrate the strong empirical performance of DIGing-SGLD under dynamically evolving network conditions.
High-Order Langevin Monte Carlo Algorithms
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:Langevin algorithms are popular Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods for large-scale sampling problems that often arise in data science. We propose Monte Carlo algorithms based on the discretizations of $P$-th order Langevin dynamics for any $P\geq 3$. Our design of $P$-th order Langevin Monte Carlo (LMC) algorithms is by combining splitting and accurate integration methods. We obtain Wasserstein convergence guarantees for sampling from distributions with log-concave and smooth densities. Specifically, the mixing time of the $P$-th order LMC algorithm scales as $O\left(d^{\frac{1}{R}}/\epsilon^{\frac{1}{2R}}\right)$ for $R=4\cdot 1_{\{ P=3\}}+ (2P-1)\cdot 1_{\{ P\geq 4\}}$, which has a better dependence on the dimension $d$ and the accuracy level $\epsilon$ as $P$ grows. Numerical experiments illustrate the efficiency of our proposed algorithms.
RESIST: Resilient Decentralized Learning Using Consensus Gradient Descent
Feb 11, 2025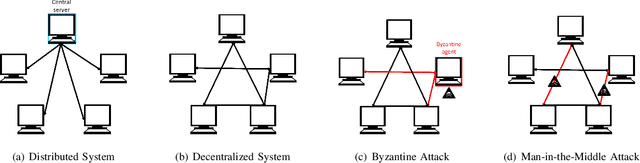
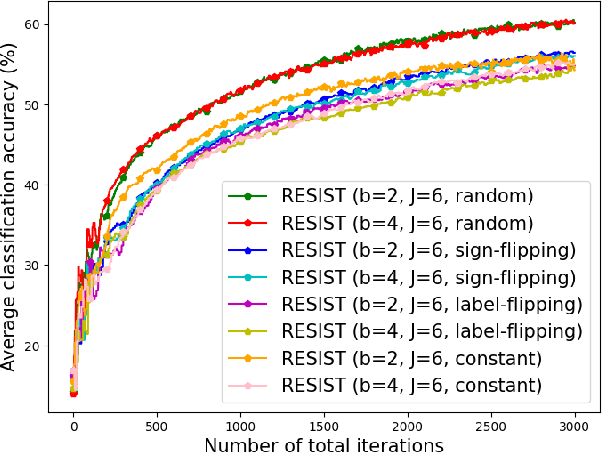
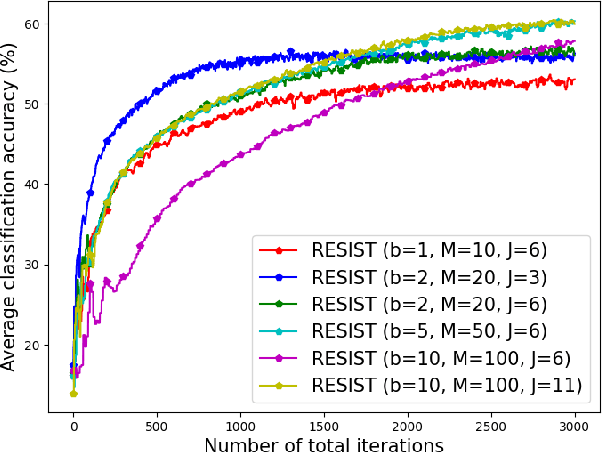
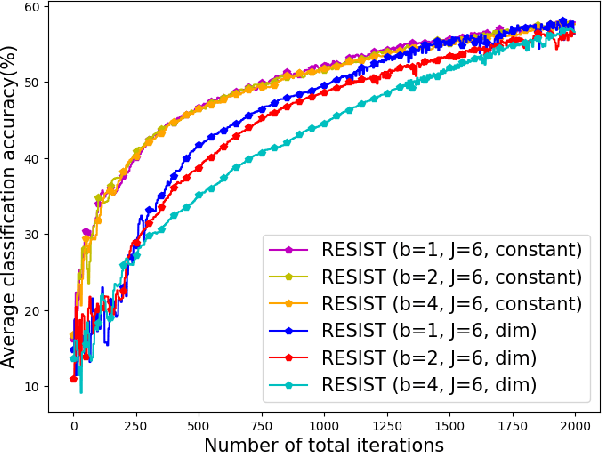
Abstract:Empirical risk minimization (ERM) is a cornerstone of modern machine learning (ML), supported by advances in optimization theory that ensure efficient solutions with provable algorithmic convergence rates, which measure the speed at which optimization algorithms approach a solution, and statistical learning rates, which characterize how well the solution generalizes to unseen data. Privacy, memory, computational, and communications constraints increasingly necessitate data collection, processing, and storage across network-connected devices. In many applications, these networks operate in decentralized settings where a central server cannot be assumed, requiring decentralized ML algorithms that are both efficient and resilient. Decentralized learning, however, faces significant challenges, including an increased attack surface for adversarial interference during decentralized learning processes. This paper focuses on the man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack, which can cause models to deviate significantly from their intended ERM solutions. To address this challenge, we propose RESIST (Resilient dEcentralized learning using conSensus gradIent deScenT), an optimization algorithm designed to be robust against adversarially compromised communication links. RESIST achieves algorithmic and statistical convergence for strongly convex, Polyak-Lojasiewicz, and nonconvex ERM problems. Experimental results demonstrate the robustness and scalability of RESIST for real-world decentralized learning in adversarial environments.
Algorithmic Stability of Stochastic Gradient Descent with Momentum under Heavy-Tailed Noise
Feb 02, 2025Abstract:Understanding the generalization properties of optimization algorithms under heavy-tailed noise has gained growing attention. However, the existing theoretical results mainly focus on stochastic gradient descent (SGD) and the analysis of heavy-tailed optimizers beyond SGD is still missing. In this work, we establish generalization bounds for SGD with momentum (SGDm) under heavy-tailed gradient noise. We first consider the continuous-time limit of SGDm, i.e., a Levy-driven stochastic differential equation (SDE), and establish quantitative Wasserstein algorithmic stability bounds for a class of potentially non-convex loss functions. Our bounds reveal a remarkable observation: For quadratic loss functions, we show that SGDm admits a worse generalization bound in the presence of heavy-tailed noise, indicating that the interaction of momentum and heavy tails can be harmful for generalization. We then extend our analysis to discrete-time and develop a uniform-in-time discretization error bound, which, to our knowledge, is the first result of its kind for SDEs with degenerate noise. This result shows that, with appropriately chosen step-sizes, the discrete dynamics retain the generalization properties of the limiting SDE. We illustrate our theory on both synthetic quadratic problems and neural networks.
Generalized EXTRA stochastic gradient Langevin dynamics
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:Langevin algorithms are popular Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods for Bayesian learning, particularly when the aim is to sample from the posterior distribution of a parametric model, given the input data and the prior distribution over the model parameters. Their stochastic versions such as stochastic gradient Langevin dynamics (SGLD) allow iterative learning based on randomly sampled mini-batches of large datasets and are scalable to large datasets. However, when data is decentralized across a network of agents subject to communication and privacy constraints, standard SGLD algorithms cannot be applied. Instead, we employ decentralized SGLD (DE-SGLD) algorithms, where Bayesian learning is performed collaboratively by a network of agents without sharing individual data. Nonetheless, existing DE-SGLD algorithms induce a bias at every agent that can negatively impact performance; this bias persists even when using full batches and is attributable to network effects. Motivated by the EXTRA algorithm and its generalizations for decentralized optimization, we propose the generalized EXTRA stochastic gradient Langevin dynamics, which eliminates this bias in the full-batch setting. Moreover, we show that, in the mini-batch setting, our algorithm provides performance bounds that significantly improve upon those of standard DE-SGLD algorithms in the literature. Our numerical results also demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed approach.
Accelerated gradient methods for nonconvex optimization: Escape trajectories from strict saddle points and convergence to local minima
Jul 13, 2023



Abstract:This paper considers the problem of understanding the behavior of a general class of accelerated gradient methods on smooth nonconvex functions. Motivated by some recent works that have proposed effective algorithms, based on Polyak's heavy ball method and the Nesterov accelerated gradient method, to achieve convergence to a local minimum of nonconvex functions, this work proposes a broad class of Nesterov-type accelerated methods and puts forth a rigorous study of these methods encompassing the escape from saddle-points and convergence to local minima through a both asymptotic and a non-asymptotic analysis. In the asymptotic regime, this paper answers an open question of whether Nesterov's accelerated gradient method (NAG) with variable momentum parameter avoids strict saddle points almost surely. This work also develops two metrics of asymptotic rate of convergence and divergence, and evaluates these two metrics for several popular standard accelerated methods such as the NAG, and Nesterov's accelerated gradient with constant momentum (NCM) near strict saddle points. In the local regime, this work provides an analysis that leads to the "linear" exit time estimates from strict saddle neighborhoods for trajectories of these accelerated methods as well the necessary conditions for the existence of such trajectories. Finally, this work studies a sub-class of accelerated methods that can converge in convex neighborhoods of nonconvex functions with a near optimal rate to a local minima and at the same time this sub-class offers superior saddle-escape behavior compared to that of NAG.
Uniform-in-Time Wasserstein Stability Bounds for (Noisy) Stochastic Gradient Descent
May 20, 2023Abstract:Algorithmic stability is an important notion that has proven powerful for deriving generalization bounds for practical algorithms. The last decade has witnessed an increasing number of stability bounds for different algorithms applied on different classes of loss functions. While these bounds have illuminated various properties of optimization algorithms, the analysis of each case typically required a different proof technique with significantly different mathematical tools. In this study, we make a novel connection between learning theory and applied probability and introduce a unified guideline for proving Wasserstein stability bounds for stochastic optimization algorithms. We illustrate our approach on stochastic gradient descent (SGD) and we obtain time-uniform stability bounds (i.e., the bound does not increase with the number of iterations) for strongly convex losses and non-convex losses with additive noise, where we recover similar results to the prior art or extend them to more general cases by using a single proof technique. Our approach is flexible and can be generalizable to other popular optimizers, as it mainly requires developing Lyapunov functions, which are often readily available in the literature. It also illustrates that ergodicity is an important component for obtaining time-uniform bounds -- which might not be achieved for convex or non-convex losses unless additional noise is injected to the iterates. Finally, we slightly stretch our analysis technique and prove time-uniform bounds for SGD under convex and non-convex losses (without additional additive noise), which, to our knowledge, is novel.
Heavy-Tail Phenomenon in Decentralized SGD
May 16, 2022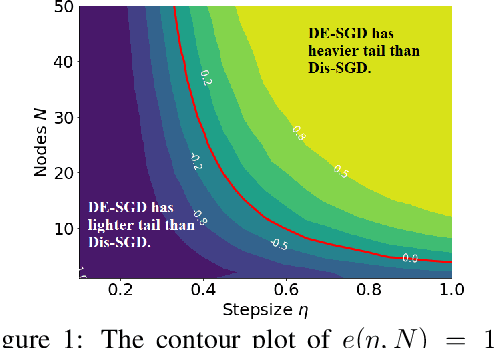
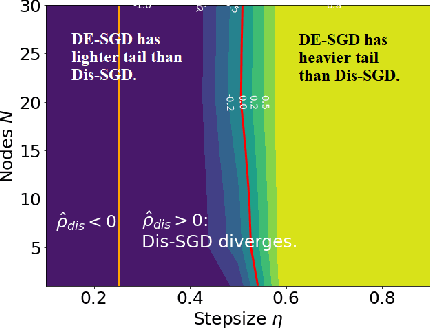
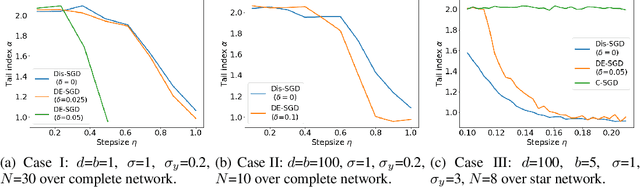
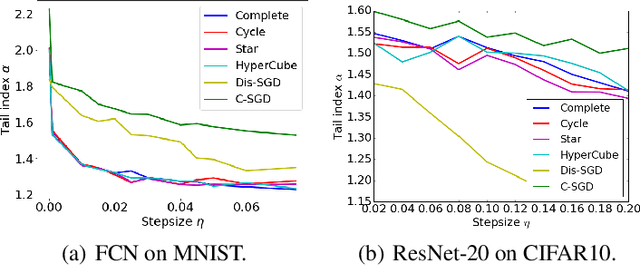
Abstract:Recent theoretical studies have shown that heavy-tails can emerge in stochastic optimization due to `multiplicative noise', even under surprisingly simple settings, such as linear regression with Gaussian data. While these studies have uncovered several interesting phenomena, they consider conventional stochastic optimization problems, which exclude decentralized settings that naturally arise in modern machine learning applications. In this paper, we study the emergence of heavy-tails in decentralized stochastic gradient descent (DE-SGD), and investigate the effect of decentralization on the tail behavior. We first show that, when the loss function at each computational node is twice continuously differentiable and strongly convex outside a compact region, the law of the DE-SGD iterates converges to a distribution with polynomially decaying (heavy) tails. To have a more explicit control on the tail exponent, we then consider the case where the loss at each node is a quadratic, and show that the tail-index can be estimated as a function of the step-size, batch-size, and the topological properties of the network of the computational nodes. Then, we provide theoretical and empirical results showing that DE-SGD has heavier tails than centralized SGD. We also compare DE-SGD to disconnected SGD where nodes distribute the data but do not communicate. Our theory uncovers an interesting interplay between the tails and the network structure: we identify two regimes of parameters (stepsize and network size), where DE-SGD can have lighter or heavier tails than disconnected SGD depending on the regime. Finally, to support our theoretical results, we provide numerical experiments conducted on both synthetic data and neural networks.
A Variance-Reduced Stochastic Accelerated Primal Dual Algorithm
Feb 19, 2022

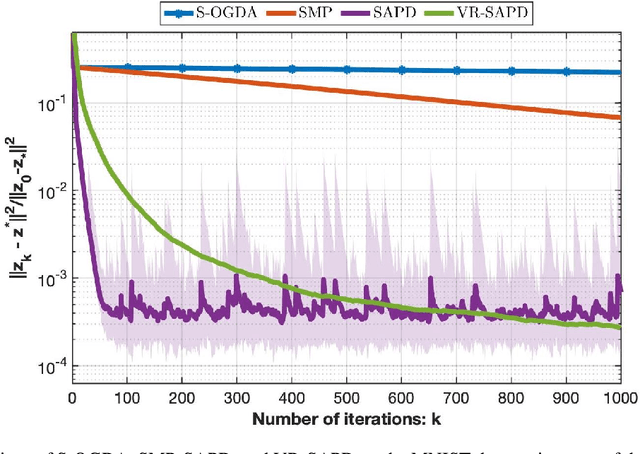
Abstract:In this work, we consider strongly convex strongly concave (SCSC) saddle point (SP) problems $\min_{x\in\mathbb{R}^{d_x}}\max_{y\in\mathbb{R}^{d_y}}f(x,y)$ where $f$ is $L$-smooth, $f(.,y)$ is $\mu$-strongly convex for every $y$, and $f(x,.)$ is $\mu$-strongly concave for every $x$. Such problems arise frequently in machine learning in the context of robust empirical risk minimization (ERM), e.g. $\textit{distributionally robust}$ ERM, where partial gradients are estimated using mini-batches of data points. Assuming we have access to an unbiased stochastic first-order oracle we consider the stochastic accelerated primal dual (SAPD) algorithm recently introduced in Zhang et al. [2021] for SCSC SP problems as a robust method against gradient noise. In particular, SAPD recovers the well-known stochastic gradient descent ascent (SGDA) as a special case when the momentum parameter is set to zero and can achieve an accelerated rate when the momentum parameter is properly tuned, i.e., improving the $\kappa \triangleq L/\mu$ dependence from $\kappa^2$ for SGDA to $\kappa$. We propose efficient variance-reduction strategies for SAPD based on Richardson-Romberg extrapolation and show that our method improves upon SAPD both in practice and in theory.
Differentially Private Accelerated Optimization Algorithms
Aug 05, 2020
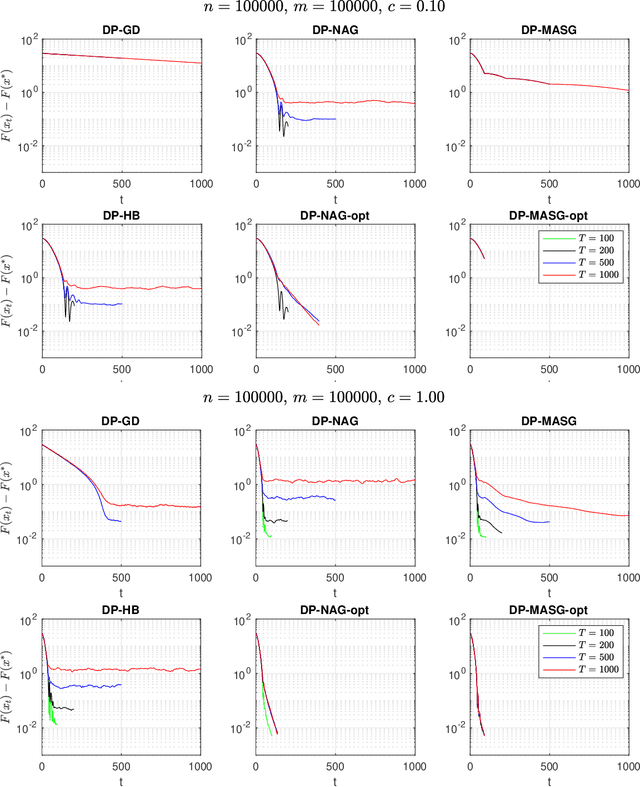
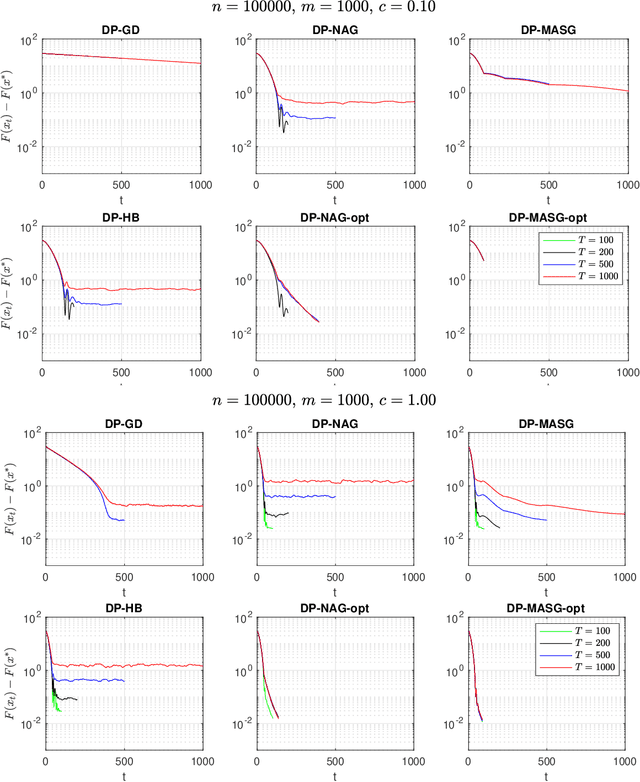
Abstract:We present two classes of differentially private optimization algorithms derived from the well-known accelerated first-order methods. The first algorithm is inspired by Polyak's heavy ball method and employs a smoothing approach to decrease the accumulated noise on the gradient steps required for differential privacy. The second class of algorithms are based on Nesterov's accelerated gradient method and its recent multi-stage variant. We propose a noise dividing mechanism for the iterations of Nesterov's method in order to improve the error behavior of the algorithm. The convergence rate analyses are provided for both the heavy ball and the Nesterov's accelerated gradient method with the help of the dynamical system analysis techniques. Finally, we conclude with our numerical experiments showing that the presented algorithms have advantages over the well-known differentially private algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge