Marco Romanelli
The Disparate Impacts of Speculative Decoding
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:The practice of speculative decoding, whereby inference is probabilistically supported by a smaller, cheaper, ``drafter'' model, has become a standard technique for systematically reducing the decoding time of large language models. This paper conducts an analysis of speculative decoding through the lens of its potential disparate speed-up rates across tasks. Crucially, the paper shows that speed-up gained from speculative decoding is not uniformly distributed across tasks, consistently diminishing for under-fit, and often underrepresented tasks. To better understand this phenomenon, we derive an analysis to quantify this observed ``unfairness'' and draw attention to the factors that motivate such disparate speed-ups to emerge. Further, guided by these insights, the paper proposes a mitigation strategy designed to reduce speed-up disparities and validates the approach across several model pairs, revealing on average a 12% improvement in our fairness metric.
Beyond the Norms: Detecting Prediction Errors in Regression Models
Jun 11, 2024Abstract:This paper tackles the challenge of detecting unreliable behavior in regression algorithms, which may arise from intrinsic variability (e.g., aleatoric uncertainty) or modeling errors (e.g., model uncertainty). First, we formally introduce the notion of unreliability in regression, i.e., when the output of the regressor exceeds a specified discrepancy (or error). Then, using powerful tools for probabilistic modeling, we estimate the discrepancy density, and we measure its statistical diversity using our proposed metric for statistical dissimilarity. In turn, this allows us to derive a data-driven score that expresses the uncertainty of the regression outcome. We show empirical improvements in error detection for multiple regression tasks, consistently outperforming popular baseline approaches, and contributing to the broader field of uncertainty quantification and safe machine learning systems. Our code is available at https://zenodo.org/records/11281964.
Low-rank finetuning for LLMs: A fairness perspective
May 28, 2024



Abstract:Low-rank approximation techniques have become the de facto standard for fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) due to their reduced computational and memory requirements. This paper investigates the effectiveness of these methods in capturing the shift of fine-tuning datasets from the initial pre-trained data distribution. Our findings reveal that there are cases in which low-rank fine-tuning falls short in learning such shifts. This, in turn, produces non-negligible side effects, especially when fine-tuning is adopted for toxicity mitigation in pre-trained models, or in scenarios where it is important to provide fair models. Through comprehensive empirical evidence on several models, datasets, and tasks, we show that low-rank fine-tuning inadvertently preserves undesirable biases and toxic behaviors. We also show that this extends to sequential decision-making tasks, emphasizing the need for careful evaluation to promote responsible LLMs development.
Optimal Zero-Shot Detector for Multi-Armed Attacks
Feb 27, 2024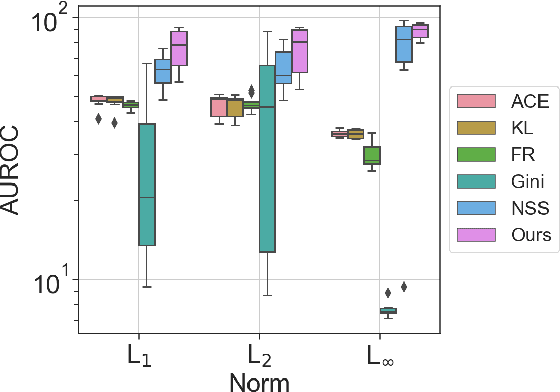
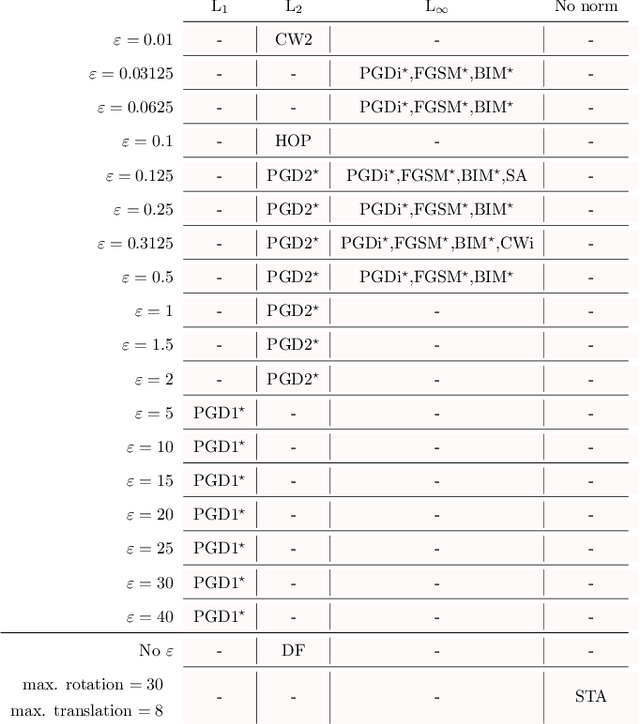
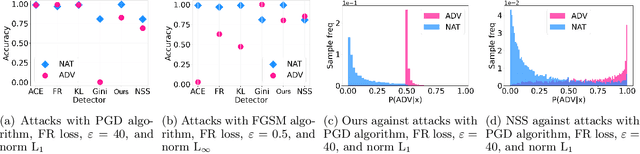
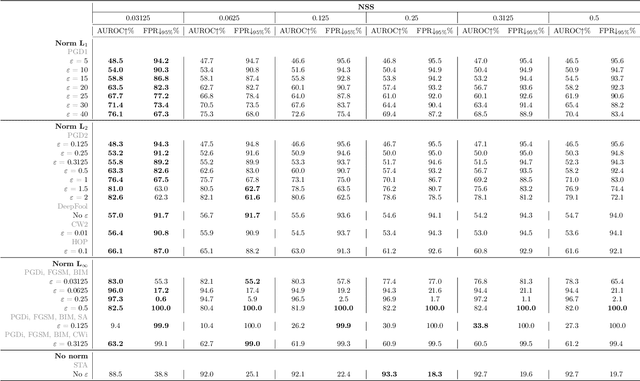
Abstract:This paper explores a scenario in which a malicious actor employs a multi-armed attack strategy to manipulate data samples, offering them various avenues to introduce noise into the dataset. Our central objective is to protect the data by detecting any alterations to the input. We approach this defensive strategy with utmost caution, operating in an environment where the defender possesses significantly less information compared to the attacker. Specifically, the defender is unable to utilize any data samples for training a defense model or verifying the integrity of the channel. Instead, the defender relies exclusively on a set of pre-existing detectors readily available "off the shelf". To tackle this challenge, we derive an innovative information-theoretic defense approach that optimally aggregates the decisions made by these detectors, eliminating the need for any training data. We further explore a practical use-case scenario for empirical evaluation, where the attacker possesses a pre-trained classifier and launches well-known adversarial attacks against it. Our experiments highlight the effectiveness of our proposed solution, even in scenarios that deviate from the optimal setup.
On the feasibility of ML Backdoor Detection as an Hypothesis Testing Problem
Feb 26, 2024



Abstract:We introduce a formal statistical definition for the problem of backdoor detection in machine learning systems and use it to analyze the feasibility of such problems, providing evidence for the utility and applicability of our definition. The main contributions of this work are an impossibility result and an achievability result for backdoor detection. We show a no-free-lunch theorem, proving that universal (adversary-unaware) backdoor detection is impossible, except for very small alphabet sizes. Thus, we argue, that backdoor detection methods need to be either explicitly, or implicitly adversary-aware. However, our work does not imply that backdoor detection cannot work in specific scenarios, as evidenced by successful backdoor detection methods in the scientific literature. Furthermore, we connect our definition to the probably approximately correct (PAC) learnability of the out-of-distribution detection problem.
Disparate Impact on Group Accuracy of Linearization for Private Inference
Feb 06, 2024



Abstract:Ensuring privacy-preserving inference on cryptographically secure data is a well-known computational challenge. To alleviate the bottleneck of costly cryptographic computations in non-linear activations, recent methods have suggested linearizing a targeted portion of these activations in neural networks. This technique results in significantly reduced runtimes with often negligible impacts on accuracy. In this paper, we demonstrate that such computational benefits may lead to increased fairness costs. Specifically, we find that reducing the number of ReLU activations disproportionately decreases the accuracy for minority groups compared to majority groups. To explain these observations, we provide a mathematical interpretation under restricted assumptions about the nature of the decision boundary, while also showing the prevalence of this problem across widely used datasets and architectures. Finally, we show how a simple procedure altering the fine-tuning step for linearized models can serve as an effective mitigation strategy.
Retrieval-Guided Reinforcement Learning for Boolean Circuit Minimization
Jan 22, 2024Abstract:Logic synthesis, a pivotal stage in chip design, entails optimizing chip specifications encoded in hardware description languages like Verilog into highly efficient implementations using Boolean logic gates. The process involves a sequential application of logic minimization heuristics (``synthesis recipe"), with their arrangement significantly impacting crucial metrics such as area and delay. Addressing the challenge posed by the broad spectrum of design complexities - from variations of past designs (e.g., adders and multipliers) to entirely novel configurations (e.g., innovative processor instructions) - requires a nuanced `synthesis recipe` guided by human expertise and intuition. This study conducts a thorough examination of learning and search techniques for logic synthesis, unearthing a surprising revelation: pre-trained agents, when confronted with entirely novel designs, may veer off course, detrimentally affecting the search trajectory. We present ABC-RL, a meticulously tuned $\alpha$ parameter that adeptly adjusts recommendations from pre-trained agents during the search process. Computed based on similarity scores through nearest neighbor retrieval from the training dataset, ABC-RL yields superior synthesis recipes tailored for a wide array of hardware designs. Our findings showcase substantial enhancements in the Quality-of-result (QoR) of synthesized circuits, boasting improvements of up to 24.8% compared to state-of-the-art techniques. Furthermore, ABC-RL achieves an impressive up to 9x reduction in runtime (iso-QoR) when compared to current state-of-the-art methodologies.
A Data-Driven Measure of Relative Uncertainty for Misclassification Detection
Jun 02, 2023Abstract:Misclassification detection is an important problem in machine learning, as it allows for the identification of instances where the model's predictions are unreliable. However, conventional uncertainty measures such as Shannon entropy do not provide an effective way to infer the real uncertainty associated with the model's predictions. In this paper, we introduce a novel data-driven measure of relative uncertainty to an observer for misclassification detection. By learning patterns in the distribution of soft-predictions, our uncertainty measure can identify misclassified samples based on the predicted class probabilities. Interestingly, according to the proposed measure, soft-predictions that correspond to misclassified instances can carry a large amount of uncertainty, even though they may have low Shannon entropy. We demonstrate empirical improvements over multiple image classification tasks, outperforming state-of-the-art misclassification detection methods.
INVICTUS: Optimizing Boolean Logic Circuit Synthesis via Synergistic Learning and Search
May 25, 2023



Abstract:Logic synthesis is the first and most vital step in chip design. This steps converts a chip specification written in a hardware description language (such as Verilog) into an optimized implementation using Boolean logic gates. State-of-the-art logic synthesis algorithms have a large number of logic minimization heuristics, typically applied sequentially based on human experience and intuition. The choice of the order greatly impacts the quality (e.g., area and delay) of the synthesized circuit. In this paper, we propose INVICTUS, a model-based offline reinforcement learning (RL) solution that automatically generates a sequence of logic minimization heuristics ("synthesis recipe") based on a training dataset of previously seen designs. A key challenge is that new designs can range from being very similar to past designs (e.g., adders and multipliers) to being completely novel (e.g., new processor instructions). %Compared to prior work, INVICTUS is the first solution that uses a mix of RL and search methods joint with an online out-of-distribution detector to generate synthesis recipes over a wide range of benchmarks. Our results demonstrate significant improvement in area-delay product (ADP) of synthesized circuits with up to 30\% improvement over state-of-the-art techniques. Moreover, INVICTUS achieves up to $6.3\times$ runtime reduction (iso-ADP) compared to the state-of-the-art.
A Minimax Approach Against Multi-Armed Adversarial Attacks Detection
Feb 04, 2023Abstract:Multi-armed adversarial attacks, in which multiple algorithms and objective loss functions are simultaneously used at evaluation time, have been shown to be highly successful in fooling state-of-the-art adversarial examples detectors while requiring no specific side information about the detection mechanism. By formalizing the problem at hand, we can propose a solution that aggregates the soft-probability outputs of multiple pre-trained detectors according to a minimax approach. The proposed framework is mathematically sound, easy to implement, and modular, allowing for integrating existing or future detectors. Through extensive evaluation on popular datasets (e.g., CIFAR10 and SVHN), we show that our aggregation consistently outperforms individual state-of-the-art detectors against multi-armed adversarial attacks, making it an effective solution to improve the resilience of available methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge