Maoguo Gong
A Spatial-Spectral-Frequency Interactive Network for Multimodal Remote Sensing Classification
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Deep learning-based methods have achieved significant success in remote sensing Earth observation data analysis. Numerous feature fusion techniques address multimodal remote sensing image classification by integrating global and local features. However, these techniques often struggle to extract structural and detail features from heterogeneous and redundant multimodal images. With the goal of introducing frequency domain learning to model key and sparse detail features, this paper introduces the spatial-spectral-frequency interaction network (S$^2$Fin), which integrates pairwise fusion modules across the spatial, spectral, and frequency domains. Specifically, we propose a high-frequency sparse enhancement transformer that employs sparse spatial-spectral attention to optimize the parameters of the high-frequency filter. Subsequently, a two-level spatial-frequency fusion strategy is introduced, comprising an adaptive frequency channel module that fuses low-frequency structures with enhanced high-frequency details, and a high-frequency resonance mask that emphasizes sharp edges via phase similarity. In addition, a spatial-spectral attention fusion module further enhances feature extraction at intermediate layers of the network. Experiments on four benchmark multimodal datasets with limited labeled data demonstrate that S$^2$Fin performs superior classification, outperforming state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at https://github.com/HaoLiu-XDU/SSFin.
EyeSim-VQA: A Free-Energy-Guided Eye Simulation Framework for Video Quality Assessment
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Free-energy-guided self-repair mechanisms have shown promising results in image quality assessment (IQA), but remain under-explored in video quality assessment (VQA), where temporal dynamics and model constraints pose unique challenges. Unlike static images, video content exhibits richer spatiotemporal complexity, making perceptual restoration more difficult. Moreover, VQA systems often rely on pre-trained backbones, which limits the direct integration of enhancement modules without affecting model stability. To address these issues, we propose EyeSimVQA, a novel VQA framework that incorporates free-energy-based self-repair. It adopts a dual-branch architecture, with an aesthetic branch for global perceptual evaluation and a technical branch for fine-grained structural and semantic analysis. Each branch integrates specialized enhancement modules tailored to distinct visual inputs-resized full-frame images and patch-based fragments-to simulate adaptive repair behaviors. We also explore a principled strategy for incorporating high-level visual features without disrupting the original backbone. In addition, we design a biologically inspired prediction head that models sweeping gaze dynamics to better fuse global and local representations for quality prediction. Experiments on five public VQA benchmarks demonstrate that EyeSimVQA achieves competitive or superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods, while offering improved interpretability through its biologically grounded design.
FCA2: Frame Compression-Aware Autoencoder for Modular and Fast Compressed Video Super-Resolution
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:State-of-the-art (SOTA) compressed video super-resolution (CVSR) models face persistent challenges, including prolonged inference time, complex training pipelines, and reliance on auxiliary information. As video frame rates continue to increase, the diminishing inter-frame differences further expose the limitations of traditional frame-to-frame information exploitation methods, which are inadequate for addressing current video super-resolution (VSR) demands. To overcome these challenges, we propose an efficient and scalable solution inspired by the structural and statistical similarities between hyperspectral images (HSI) and video data. Our approach introduces a compression-driven dimensionality reduction strategy that reduces computational complexity, accelerates inference, and enhances the extraction of temporal information across frames. The proposed modular architecture is designed for seamless integration with existing VSR frameworks, ensuring strong adaptability and transferability across diverse applications. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves performance on par with, or surpassing, the current SOTA models, while significantly reducing inference time. By addressing key bottlenecks in CVSR, our work offers a practical and efficient pathway for advancing VSR technology. Our code will be publicly available at https://github.com/handsomewzy/FCA2.
Enhanced Ideal Objective Vector Estimation for Evolutionary Multi-Objective Optimization
May 28, 2025Abstract:The ideal objective vector, which comprises the optimal values of the $m$ objective functions in an $m$-objective optimization problem, is an important concept in evolutionary multi-objective optimization. Accurate estimation of this vector has consistently been a crucial task, as it is frequently used to guide the search process and normalize the objective space. Prevailing estimation methods all involve utilizing the best value concerning each objective function achieved by the individuals in the current or accumulated population. However, this paper reveals that the population-based estimation method can only work on simple problems but falls short on problems with substantial bias. The biases in multi-objective optimization problems can be divided into three categories, and an analysis is performed to illustrate how each category hinders the estimation of the ideal objective vector. Subsequently, a set of test instances is proposed to quantitatively evaluate the impact of various biases on the ideal objective vector estimation method. Beyond that, a plug-and-play component called enhanced ideal objective vector estimation (EIE) is introduced for multi-objective evolutionary algorithms (MOEAs). EIE features adaptive and fine-grained searches over $m$ subproblems defined by the extreme weighted sum method. EIE finally outputs $m$ solutions that can well approximate the ideal objective vector. In the experiments, EIE is integrated into three representative MOEAs. To demonstrate the wide applicability of EIE, algorithms are tested not only on the newly proposed test instances but also on existing ones. The results consistently show that EIE improves the ideal objective vector estimation and enhances the MOEA's performance.
CL-BioGAN: Biologically-Inspired Cross-Domain Continual Learning for Hyperspectral Anomaly Detection
May 17, 2025Abstract:Memory stability and learning flexibility in continual learning (CL) is a core challenge for cross-scene Hyperspectral Anomaly Detection (HAD) task. Biological neural networks can actively forget history knowledge that conflicts with the learning of new experiences by regulating learning-triggered synaptic expansion and synaptic convergence. Inspired by this phenomenon, we propose a novel Biologically-Inspired Continual Learning Generative Adversarial Network (CL-BioGAN) for augmenting continuous distribution fitting ability for cross-domain HAD task, where Continual Learning Bio-inspired Loss (CL-Bio Loss) and self-attention Generative Adversarial Network (BioGAN) are incorporated to realize forgetting history knowledge as well as involving replay strategy in the proposed BioGAN. Specifically, a novel Bio-Inspired Loss composed with an Active Forgetting Loss (AF Loss) and a CL loss is designed to realize parameters releasing and enhancing between new task and history tasks from a Bayesian perspective. Meanwhile, BioGAN loss with L2-Norm enhances self-attention (SA) to further balance the stability and flexibility for better fitting background distribution for open scenario HAD (OHAD) tasks. Experiment results underscore that the proposed CL-BioGAN can achieve more robust and satisfying accuracy for cross-domain HAD with fewer parameters and computation cost. This dual contribution not only elevates CL performance but also offers new insights into neural adaptation mechanisms in OHAD task.
CL-CaGAN: Capsule differential adversarial continuous learning for cross-domain hyperspectral anomaly detection
May 17, 2025
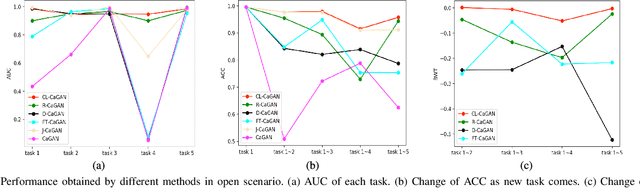
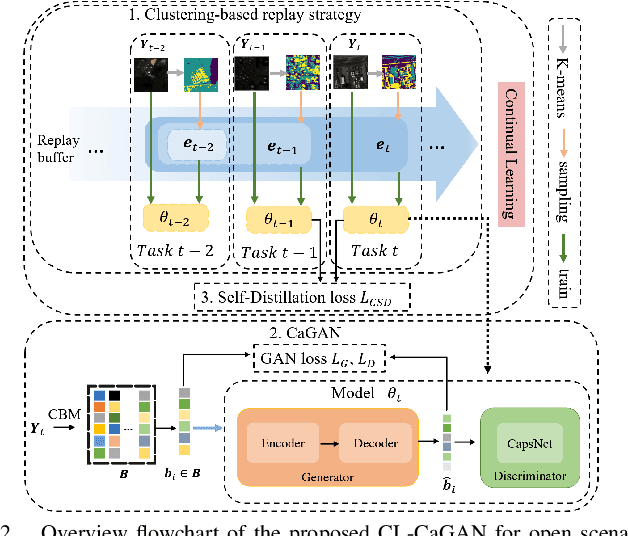
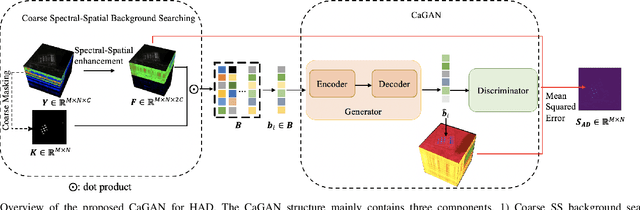
Abstract:Anomaly detection (AD) has attracted remarkable attention in hyperspectral image (HSI) processing fields, and most existing deep learning (DL)-based algorithms indicate dramatic potential for detecting anomaly samples through specific training process under current scenario. However, the limited prior information and the catastrophic forgetting problem indicate crucial challenges for existing DL structure in open scenarios cross-domain detection. In order to improve the detection performance, a novel continual learning-based capsule differential generative adversarial network (CL-CaGAN) is proposed to elevate the cross-scenario learning performance for facilitating the real application of DL-based structure in hyperspectral AD (HAD) task. First, a modified capsule structure with adversarial learning network is constructed to estimate the background distribution for surmounting the deficiency of prior information. To mitigate the catastrophic forgetting phenomenon, clustering-based sample replay strategy and a designed extra self-distillation regularization are integrated for merging the history and future knowledge in continual AD task, while the discriminative learning ability from previous detection scenario to current scenario is retained by the elaborately designed structure with continual learning (CL) strategy. In addition, the differentiable enhancement is enforced to augment the generation performance of the training data. This further stabilizes the training process with better convergence and efficiently consolidates the reconstruction ability of background samples. To verify the effectiveness of our proposed CL-CaGAN, we conduct experiments on several real HSIs, and the results indicate that the proposed CL-CaGAN demonstrates higher detection performance and continuous learning capacity for mitigating the catastrophic forgetting under cross-domain scenarios.
Generative Adversarial Patches for Physical Attacks on Cross-Modal Pedestrian Re-Identification
Oct 26, 2024



Abstract:Visible-infrared pedestrian Re-identification (VI-ReID) aims to match pedestrian images captured by infrared cameras and visible cameras. However, VI-ReID, like other traditional cross-modal image matching tasks, poses significant challenges due to its human-centered nature. This is evidenced by the shortcomings of existing methods, which struggle to extract common features across modalities, while losing valuable information when bridging the gap between them in the implicit feature space, potentially compromising security. To address this vulnerability, this paper introduces the first physical adversarial attack against VI-ReID models. Our method, termed Edge-Attack, specifically tests the models' ability to leverage deep-level implicit features by focusing on edge information, the most salient explicit feature differentiating individuals across modalities. Edge-Attack utilizes a novel two-step approach. First, a multi-level edge feature extractor is trained in a self-supervised manner to capture discriminative edge representations for each individual. Second, a generative model based on Vision Transformer Generative Adversarial Networks (ViTGAN) is employed to generate adversarial patches conditioned on the extracted edge features. By applying these patches to pedestrian clothing, we create realistic, physically-realizable adversarial samples. This black-box, self-supervised approach ensures the generalizability of our attack against various VI-ReID models. Extensive experiments on SYSU-MM01 and RegDB datasets, including real-world deployments, demonstrate the effectiveness of Edge- Attack in significantly degrading the performance of state-of-the-art VI-ReID methods.
Triple Point Masking
Sep 26, 2024Abstract:Existing 3D mask learning methods encounter performance bottlenecks under limited data, and our objective is to overcome this limitation. In this paper, we introduce a triple point masking scheme, named TPM, which serves as a scalable framework for pre-training of masked autoencoders to achieve multi-mask learning for 3D point clouds. Specifically, we augment the baselines with two additional mask choices (i.e., medium mask and low mask) as our core insight is that the recovery process of an object can manifest in diverse ways. Previous high-masking schemes focus on capturing the global representation but lack the fine-grained recovery capability, so that the generated pre-trained weights tend to play a limited role in the fine-tuning process. With the support of the proposed TPM, available methods can exhibit more flexible and accurate completion capabilities, enabling the potential autoencoder in the pre-training stage to consider multiple representations of a single 3D object. In addition, an SVM-guided weight selection module is proposed to fill the encoder parameters for downstream networks with the optimal weight during the fine-tuning stage, maximizing linear accuracy and facilitating the acquisition of intricate representations for new objects. Extensive experiments show that the four baselines equipped with the proposed TPM achieve comprehensive performance improvements on various downstream tasks.
Enhancing Hyperspectral Images via Diffusion Model and Group-Autoencoder Super-resolution Network
Feb 27, 2024Abstract:Existing hyperspectral image (HSI) super-resolution (SR) methods struggle to effectively capture the complex spectral-spatial relationships and low-level details, while diffusion models represent a promising generative model known for their exceptional performance in modeling complex relations and learning high and low-level visual features. The direct application of diffusion models to HSI SR is hampered by challenges such as difficulties in model convergence and protracted inference time. In this work, we introduce a novel Group-Autoencoder (GAE) framework that synergistically combines with the diffusion model to construct a highly effective HSI SR model (DMGASR). Our proposed GAE framework encodes high-dimensional HSI data into low-dimensional latent space where the diffusion model works, thereby alleviating the difficulty of training the diffusion model while maintaining band correlation and considerably reducing inference time. Experimental results on both natural and remote sensing hyperspectral datasets demonstrate that the proposed method is superior to other state-of-the-art methods both visually and metrically.
Diffusion Model Based Visual Compensation Guidance and Visual Difference Analysis for No-Reference Image Quality Assessment
Feb 22, 2024



Abstract:Existing free-energy guided No-Reference Image Quality Assessment (NR-IQA) methods still suffer from finding a balance between learning feature information at the pixel level of the image and capturing high-level feature information and the efficient utilization of the obtained high-level feature information remains a challenge. As a novel class of state-of-the-art (SOTA) generative model, the diffusion model exhibits the capability to model intricate relationships, enabling a comprehensive understanding of images and possessing a better learning of both high-level and low-level visual features. In view of these, we pioneer the exploration of the diffusion model into the domain of NR-IQA. Firstly, we devise a new diffusion restoration network that leverages the produced enhanced image and noise-containing images, incorporating nonlinear features obtained during the denoising process of the diffusion model, as high-level visual information. Secondly, two visual evaluation branches are designed to comprehensively analyze the obtained high-level feature information. These include the visual compensation guidance branch, grounded in the transformer architecture and noise embedding strategy, and the visual difference analysis branch, built on the ResNet architecture and the residual transposed attention block. Extensive experiments are conducted on seven public NR-IQA datasets, and the results demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms SOTA methods for NR-IQA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge