Longji Yin
Efficient Swept Volume-Based Trajectory Generation for Arbitrary-Shaped Ground Robot Navigation
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Navigating an arbitrary-shaped ground robot safely in cluttered environments remains a challenging problem. The existing trajectory planners that account for the robot's physical geometry severely suffer from the intractable runtime. To achieve both computational efficiency and Continuous Collision Avoidance (CCA) of arbitrary-shaped ground robot planning, we proposed a novel coarse-to-fine navigation framework that significantly accelerates planning. In the first stage, a sampling-based method selectively generates distinct topological paths that guarantee a minimum inflated margin. In the second stage, a geometry-aware front-end strategy is designed to discretize these topologies into full-state robot motion sequences while concurrently partitioning the paths into SE(2) sub-problems and simpler R2 sub-problems for back-end optimization. In the final stage, an SVSDF-based optimizer generates trajectories tailored to these sub-problems and seamlessly splices them into a continuous final motion plan. Extensive benchmark comparisons show that the proposed method is one to several orders of magnitude faster than the cutting-edge methods in runtime while maintaining a high planning success rate and ensuring CCA.
Swarm-LIO2: Decentralized, Efficient LiDAR-inertial Odometry for UAV Swarms
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:Aerial swarm systems possess immense potential in various aspects, such as cooperative exploration, target tracking, search and rescue. Efficient, accurate self and mutual state estimation are the critical preconditions for completing these swarm tasks, which remain challenging research topics. This paper proposes Swarm-LIO2: a fully decentralized, plug-and-play, computationally efficient, and bandwidth-efficient LiDAR-inertial odometry for aerial swarm systems. Swarm-LIO2 uses a decentralized, plug-and-play network as the communication infrastructure. Only bandwidth-efficient and low-dimensional information is exchanged, including identity, ego-state, mutual observation measurements, and global extrinsic transformations. To support the plug-and-play of new teammate participants, Swarm-LIO2 detects potential teammate UAVs and initializes the temporal offset and global extrinsic transformation all automatically. To enhance the initialization efficiency, novel reflectivity-based UAV detection, trajectory matching, and factor graph optimization methods are proposed. For state estimation, Swarm-LIO2 fuses LiDAR, IMU, and mutual observation measurements within an efficient ESIKF framework, with careful compensation of temporal delay and modeling of measurements to enhance the accuracy and consistency.
Formation Flight in Dense Environments
Oct 08, 2022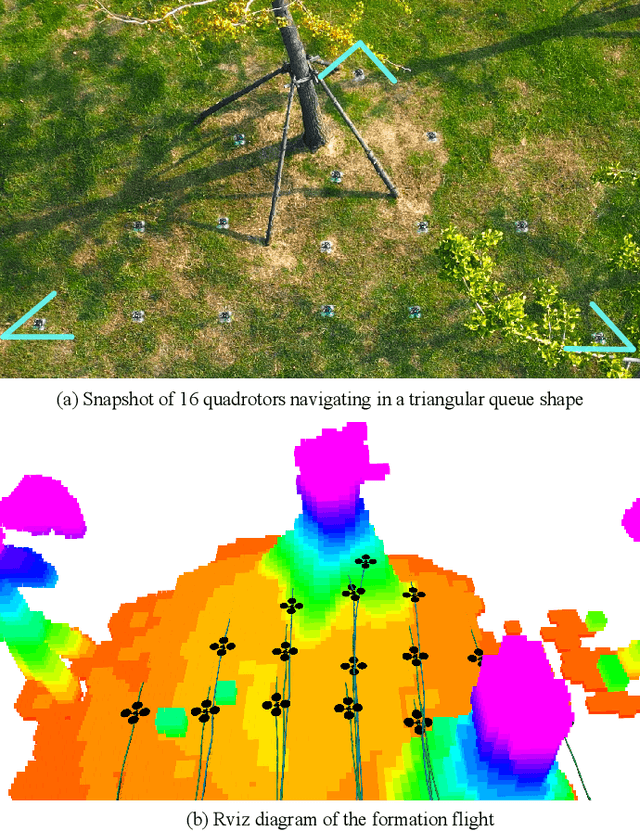
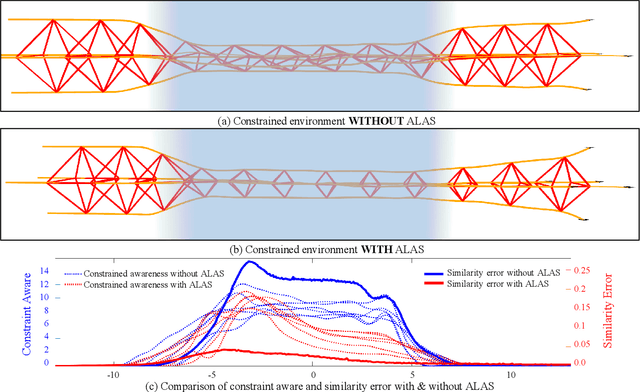
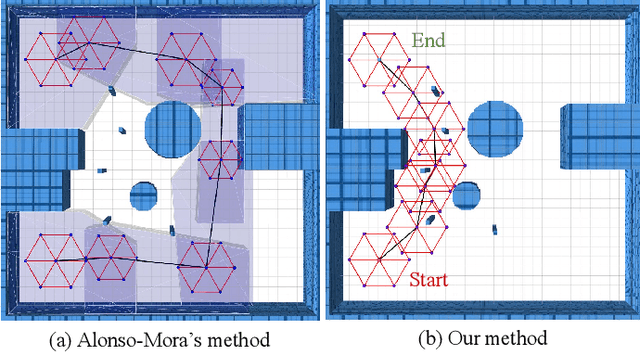
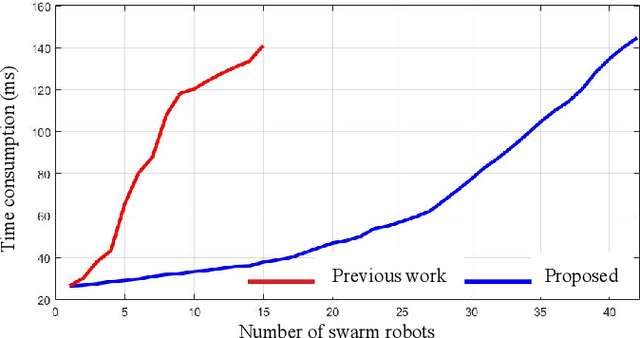
Abstract:Formation flight has a vast potential for aerial robot swarms in various applications. However, existing methods lack the capability to achieve fully autonomous large-scale formation flight in dense environments. To bridge the gap, we present a complete formation flight system that effectively integrates real-world constraints into aerial formation navigation. This paper proposes a differentiable graph-based metric to quantify the overall similarity error between formations. This metric is invariant to rotation, translation, and scaling, providing more freedom for formation coordination. We design a distributed trajectory optimization framework that considers formation similarity, obstacle avoidance, and dynamic feasibility. The optimization is decoupled to make large-scale formation flights computationally feasible. To improve the elasticity of formation navigation in highly constrained scenes, we present a swarm reorganization method which adaptively adjusts the formation parameters and task assignments by generating local navigation goals. A novel swarm agreement strategy called global-remap-local-replan and a formation-level path planner is proposed in this work to coordinate the swarm global planning and local trajectory optimizations efficiently. To validate the proposed method, we design comprehensive benchmarks and simulations with other cutting-edge works in terms of adaptability, predictability, elasticity, resilience, and efficiency. Finally, integrated with palm-sized swarm platforms with onboard computers and sensors, the proposed method demonstrates its efficiency and robustness by achieving the largest scale formation flight in dense outdoor environments.
Certifiably Optimal Mutual Localization with Anonymous Bearing Measurements
Mar 17, 2022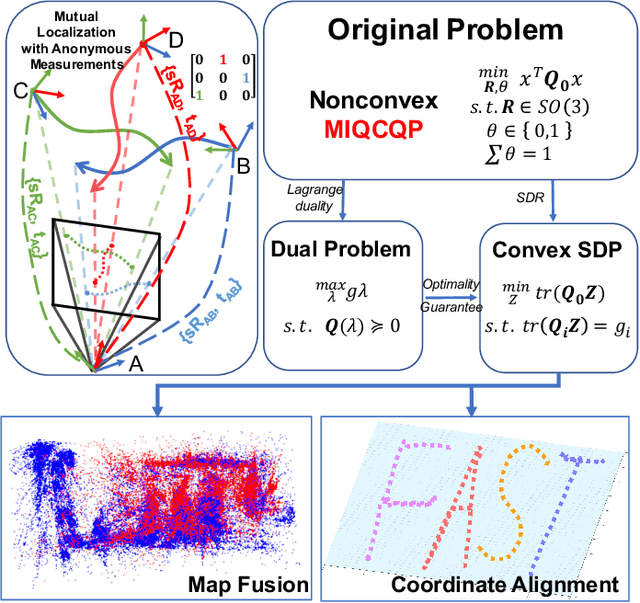
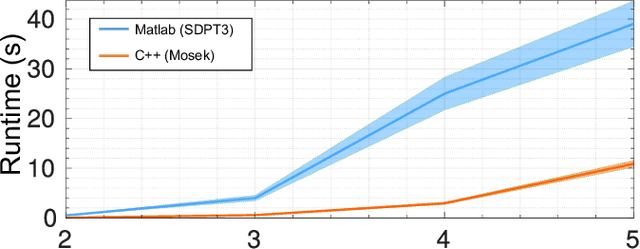
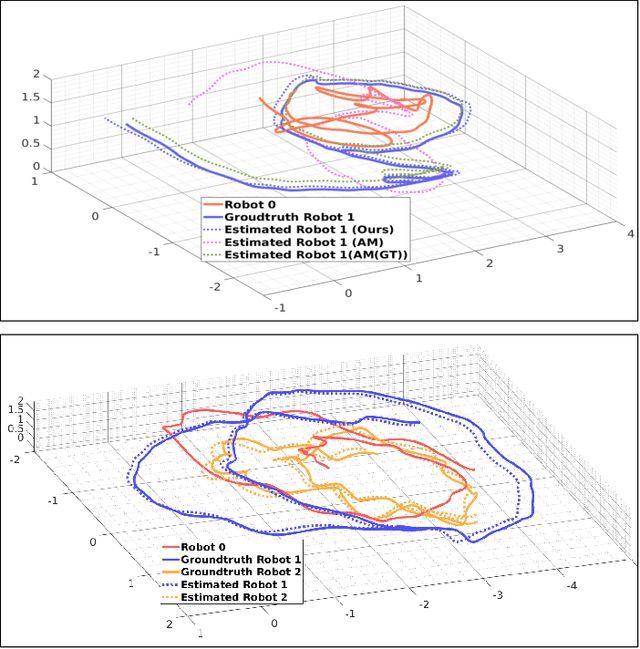
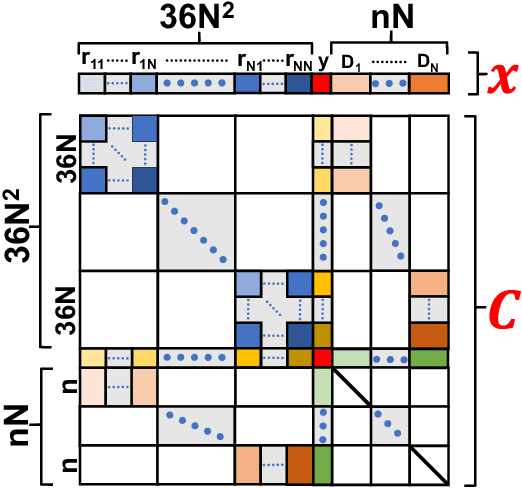
Abstract:Mutual localization is essential for coordination and cooperation in multi-robot systems. Previous works have tackled this problem by assuming available correspondences between measurements and received odometry estimations, which are difficult to acquire, especially for unified robot teams. Furthermore, most local optimization methods ask for initial guesses and are sensitive to their quality. In this paper, we present a certifiably optimal algorithm that uses only anonymous bearing measurements to formulate a novel mixed-integer quadratically constrained quadratic problem (MIQCQP). Then, we relax the original nonconvex problem into a semidefinite programming (SDP) problem and obtain a certifiably global optimum using with off-the-shelf solvers. As a result, our method can determine bearing-pose correspondences and furthermore recover the initial relative poses between robots under a certain condition. We compare the performance with local optimization methods on extensive simulations under different noise levels to show our advantage in global optimality and robustness. Real-world experiments are conducted to show the practicality and robustness.
Distributed Swarm Trajectory Optimization for Formation Flight in Dense Environments
Sep 16, 2021
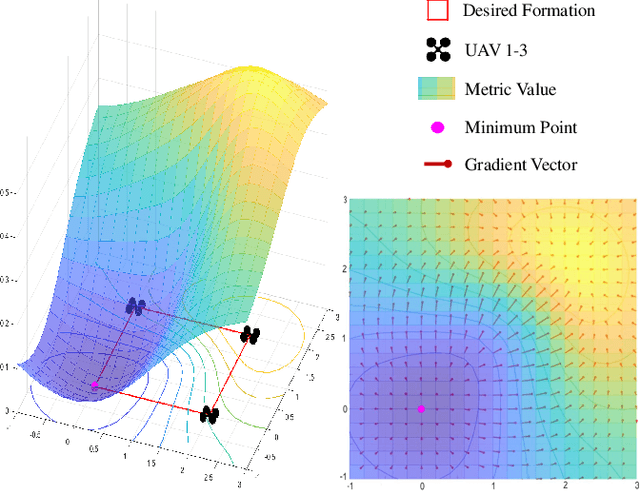


Abstract:For aerial swarms, navigation in a prescribed formation is widely practiced in various scenarios. However, the associated planning strategies typically lack the capability of avoiding obstacles in cluttered environments. To address this deficiency, we present an optimization-based method that ensures collision-free trajectory generation for formation flight. In this paper, a novel differentiable metric is proposed to quantify the overall similarity distance between formations. We then formulate this metric into an optimization framework, which achieves spatial-temporal planning using polynomial trajectories. Minimization over collision penalty is also incorporated into the framework, so that formation preservation and obstacle avoidance can be handled simultaneously. To validate the efficiency of our method, we conduct benchmark comparisons with other cutting-edge works. Integrated with an autonomous distributed aerial swarm system, the proposed method demonstrates its efficiency and robustness in real-world experiments with obstacle-rich surroundings. We will release the source code for the reference of the community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge