Liansheng Zhuang
Enhancing Large Language Models with Reward-guided Tree Search for Knowledge Graph Question and Answering
May 18, 2025Abstract:Recently, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance in Knowledge Graph Question Answering (KGQA) tasks, which aim to find answers based on knowledge graphs (KGs) for natural language questions. Existing LLMs-based KGQA methods typically follow the Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation (GraphRAG) paradigm, which first retrieves reasoning paths from the large KGs, and then generates the answers based on them. However, these methods emphasize the exploration of new optimal reasoning paths in KGs while ignoring the exploitation of historical reasoning paths, which may lead to sub-optimal reasoning paths. Additionally, the complex semantics contained in questions may lead to the retrieval of inaccurate reasoning paths. To address these issues, this paper proposes a novel and training-free framework for KGQA tasks called Reward-guided Tree Search on Graph (RTSoG). RTSoG decomposes an original question into a series of simpler and well-defined sub-questions to handle the complex semantics. Then, a Self-Critic Monte Carlo Tree Search (SC-MCTS) guided by a reward model is introduced to iteratively retrieve weighted reasoning paths as contextual knowledge. Finally, it stacks the weighted reasoning paths according to their weights to generate the final answers. Extensive experiments on four datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of RTSoG. Notably, it achieves 8.7\% and 7.0\% performance improvement over the state-of-the-art method on the GrailQA and the WebQSP respectively.
EPERM: An Evidence Path Enhanced Reasoning Model for Knowledge Graph Question and Answering
Feb 22, 2025Abstract:Due to the remarkable reasoning ability, Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance in knowledge graph question answering (KGQA) tasks, which find answers to natural language questions over knowledge graphs (KGs). To alleviate the hallucinations and lack of knowledge issues of LLMs, existing methods often retrieve the question-related information from KGs to enrich the input context. However, most methods focus on retrieving the relevant information while ignoring the importance of different types of knowledge in reasoning, which degrades their performance. To this end, this paper reformulates the KGQA problem as a graphical model and proposes a three-stage framework named the Evidence Path Enhanced Reasoning Model (EPERM) for KGQA. In the first stage, EPERM uses the fine-tuned LLM to retrieve a subgraph related to the question from the original knowledge graph. In the second stage, EPERM filters out the evidence paths that faithfully support the reasoning of the questions, and score their importance in reasoning. Finally, EPERM uses the weighted evidence paths to reason the final answer. Since considering the importance of different structural information in KGs for reasoning, EPERM can improve the reasoning ability of LLMs in KGQA tasks. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that EPERM achieves superior performances in KGQA tasks.
Test-time Loss Landscape Adaptation for Zero-Shot Generalization in Vision-Language Models
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:Test-time adaptation of pre-trained vision-language models has emerged as a technique for tackling distribution shifts during the test time. Although existing methods, especially those based on Test-time Prompt Tuning (TPT), have shown promising results, their high computational cost associated with parameter optimization presents challenges for scalability and practical application. This paper unveils the unnecessary nature of backpropagation in existing methods from a loss landscape perspective. Building on this insight, this paper proposes a simple yet effective framework called Test-time Loss Landscape Adaptation (TLLA). TLLA leverages the relative position between the training minimum and test loss landscapes to guide the adaptation process, avoiding the update of model parameters at test time. Specifically, it mainly consists of two main stages: In the prompt tuning stage, a Sharpness-Aware Prompt Tuning (SAPT) method is introduced to identify the training flat minimum, setting the foundation for the subsequent test-time adaptation; In the test stage, a Sharpness-based Test Sample Selection (STSS) approach is utilized to ensure the alignment of flat minima within the training loss landscape and each augmented test sample's loss landscape. Extensive experiments on both domain generalization and cross-dataset benchmarks demonstrate that TLLA achieves state-of-the-art performances while significantly reducing computational overhead. Notably, TLLA surpasses TPT by an average of 5.32\% and 6.98\% on four ImageNet variant datasets when employing ResNet50 and ViT-B/16 image encoders, respectively. The code will be available soon.
SceneBooth: Diffusion-based Framework for Subject-preserved Text-to-Image Generation
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Due to the demand for personalizing image generation, subject-driven text-to-image generation method, which creates novel renditions of an input subject based on text prompts, has received growing research interest. Existing methods often learn subject representation and incorporate it into the prompt embedding to guide image generation, but they struggle with preserving subject fidelity. To solve this issue, this paper approaches a novel framework named SceneBooth for subject-preserved text-to-image generation, which consumes inputs of a subject image, object phrases and text prompts. Instead of learning the subject representation and generating a subject, our SceneBooth fixes the given subject image and generates its background image guided by the text prompts. To this end, our SceneBooth introduces two key components, i.e., a multimodal layout generation module and a background painting module. The former determines the position and scale of the subject by generating appropriate scene layouts that align with text captions, object phrases, and subject visual information. The latter integrates two adapters (ControlNet and Gated Self-Attention) into the latent diffusion model to generate a background that harmonizes with the subject guided by scene layouts and text descriptions. In this manner, our SceneBooth ensures accurate preservation of the subject's appearance in the output. Quantitative and qualitative experimental results demonstrate that SceneBooth significantly outperforms baseline methods in terms of subject preservation, image harmonization and overall quality.
Seeking Consistent Flat Minima for Better Domain Generalization via Refining Loss Landscapes
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Domain generalization aims to learn a model from multiple training domains and generalize it to unseen test domains. Recent theory has shown that seeking the deep models, whose parameters lie in the flat minima of the loss landscape, can significantly reduce the out-of-domain generalization error. However, existing methods often neglect the consistency of loss landscapes in different domains, resulting in models that are not simultaneously in the optimal flat minima in all domains, which limits their generalization ability. To address this issue, this paper proposes an iterative Self-Feedback Training (SFT) framework to seek consistent flat minima that are shared across different domains by progressively refining loss landscapes during training. It alternatively generates a feedback signal by measuring the inconsistency of loss landscapes in different domains and refines these loss landscapes for greater consistency using this feedback signal. Benefiting from the consistency of the flat minima within these refined loss landscapes, our SFT helps achieve better out-of-domain generalization. Extensive experiments on DomainBed demonstrate superior performances of SFT when compared to state-of-the-art sharpness-aware methods and other prevalent DG baselines. On average across five DG benchmarks, SFT surpasses the sharpness-aware minimization by 2.6% with ResNet-50 and 1.5% with ViT-B/16, respectively. The code will be available soon.
Hierarchical Prompts for Rehearsal-free Continual Learning
Jan 21, 2024Abstract:Continual learning endeavors to equip the model with the capability to integrate current task knowledge while mitigating the forgetting of past task knowledge. Inspired by prompt tuning, prompt-based methods maintain a frozen backbone and train with slight learnable prompts to minimize the catastrophic forgetting that arises due to updating a large number of backbone parameters. Nonetheless, these learnable prompts tend to concentrate on the discriminatory knowledge of the current task while ignoring past task knowledge, leading to that learnable prompts still suffering from catastrophic forgetting. This paper introduces a novel rehearsal-free paradigm for continual learning termed Hierarchical Prompts (H-Prompts), comprising three categories of prompts -- class prompt, task prompt, and general prompt. To effectively depict the knowledge of past classes, class prompt leverages Bayesian Distribution Alignment to model the distribution of classes in each task. To reduce the forgetting of past task knowledge, task prompt employs Cross-task Knowledge Excavation to amalgamate the knowledge encapsulated in the learned class prompts of past tasks and current task knowledge. Furthermore, general prompt utilizes Generalized Knowledge Exploration to deduce highly generalized knowledge in a self-supervised manner. Evaluations on two benchmarks substantiate the efficacy of the proposed H-Prompts, exemplified by an average accuracy of 87.8% in Split CIFAR-100 and 70.6% in Split ImageNet-R.
Hierarchical Augmentation and Distillation for Class Incremental Audio-Visual Video Recognition
Jan 11, 2024



Abstract:Audio-visual video recognition (AVVR) aims to integrate audio and visual clues to categorize videos accurately. While existing methods train AVVR models using provided datasets and achieve satisfactory results, they struggle to retain historical class knowledge when confronted with new classes in real-world situations. Currently, there are no dedicated methods for addressing this problem, so this paper concentrates on exploring Class Incremental Audio-Visual Video Recognition (CIAVVR). For CIAVVR, since both stored data and learned model of past classes contain historical knowledge, the core challenge is how to capture past data knowledge and past model knowledge to prevent catastrophic forgetting. We introduce Hierarchical Augmentation and Distillation (HAD), which comprises the Hierarchical Augmentation Module (HAM) and Hierarchical Distillation Module (HDM) to efficiently utilize the hierarchical structure of data and models, respectively. Specifically, HAM implements a novel augmentation strategy, segmental feature augmentation, to preserve hierarchical model knowledge. Meanwhile, HDM introduces newly designed hierarchical (video-distribution) logical distillation and hierarchical (snippet-video) correlative distillation to capture and maintain the hierarchical intra-sample knowledge of each data and the hierarchical inter-sample knowledge between data, respectively. Evaluations on four benchmarks (AVE, AVK-100, AVK-200, and AVK-400) demonstrate that the proposed HAD effectively captures hierarchical information in both data and models, resulting in better preservation of historical class knowledge and improved performance. Furthermore, we provide a theoretical analysis to support the necessity of the segmental feature augmentation strategy.
Learning Differentially Private Probabilistic Models for Privacy-Preserving Image Generation
May 18, 2023Abstract:A number of deep models trained on high-quality and valuable images have been deployed in practical applications, which may pose a leakage risk of data privacy. Learning differentially private generative models can sidestep this challenge through indirect data access. However, such differentially private generative models learned by existing approaches can only generate images with a low-resolution of less than 128x128, hindering the widespread usage of generated images in downstream training. In this work, we propose learning differentially private probabilistic models (DPPM) to generate high-resolution images with differential privacy guarantee. In particular, we first train a model to fit the distribution of the training data and make it satisfy differential privacy by performing a randomized response mechanism during training process. Then we perform Hamiltonian dynamics sampling along with the differentially private movement direction predicted by the trained probabilistic model to obtain the privacy-preserving images. In this way, it is possible to apply these images to different downstream tasks while protecting private information. Notably, compared to other state-of-the-art differentially private generative approaches, our approach can generate images up to 256x256 with remarkable visual quality and data utility. Extensive experiments show the effectiveness of our approach.
LayoutDM: Transformer-based Diffusion Model for Layout Generation
May 04, 2023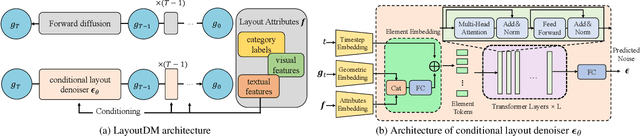
Abstract:Automatic layout generation that can synthesize high-quality layouts is an important tool for graphic design in many applications. Though existing methods based on generative models such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Auto-Encoders (VAEs) have progressed, they still leave much room for improving the quality and diversity of the results. Inspired by the recent success of diffusion models in generating high-quality images, this paper explores their potential for conditional layout generation and proposes Transformer-based Layout Diffusion Model (LayoutDM) by instantiating the conditional denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM) with a purely transformer-based architecture. Instead of using convolutional neural networks, a transformer-based conditional Layout Denoiser is proposed to learn the reverse diffusion process to generate samples from noised layout data. Benefitting from both transformer and DDPM, our LayoutDM is of desired properties such as high-quality generation, strong sample diversity, faithful distribution coverage, and stationary training in comparison to GANs and VAEs. Quantitative and qualitative experimental results show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art generative models in terms of quality and diversity.
Estimation of Reliable Proposal Quality for Temporal Action Detection
Apr 25, 2022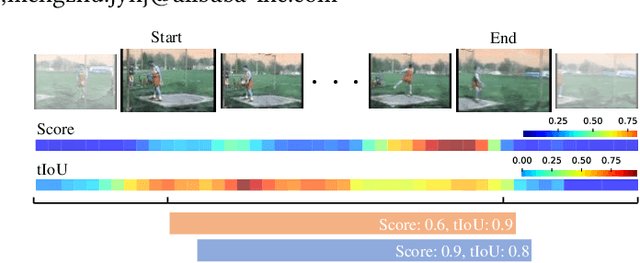

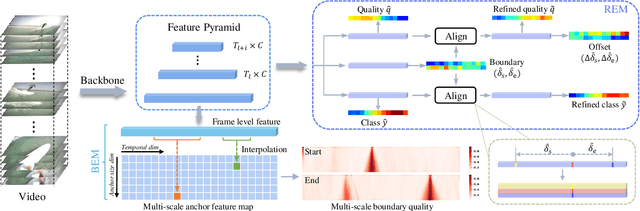

Abstract:Temporal action detection (TAD) aims to locate and recognize the actions in an untrimmed video. Anchor-free methods have made remarkable progress which mainly formulate TAD into two tasks: classification and localization using two separate branches. This paper reveals the temporal misalignment between the two tasks hindering further progress. To address this, we propose a new method that gives insights into moment and region perspectives simultaneously to align the two tasks by acquiring reliable proposal quality. For the moment perspective, Boundary Evaluate Module (BEM) is designed which focuses on local appearance and motion evolvement to estimate boundary quality and adopts a multi-scale manner to deal with varied action durations. For the region perspective, we introduce Region Evaluate Module (REM) which uses a new and efficient sampling method for proposal feature representation containing more contextual information compared with point feature to refine category score and proposal boundary. The proposed Boundary Evaluate Module and Region Evaluate Module (BREM) are generic, and they can be easily integrated with other anchor-free TAD methods to achieve superior performance. In our experiments, BREM is combined with two different frameworks and improves the performance on THUMOS14 by 3.6$\%$ and 1.0$\%$ respectively, reaching a new state-of-the-art (63.6$\%$ average $m$AP). Meanwhile, a competitive result of 36.2\% average $m$AP is achieved on ActivityNet-1.3 with the consistent improvement of BREM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge