Lei Dai
Listen, Disentangle, and Control: Controllable Speech-Driven Talking Head Generation
May 12, 2024Abstract:Most earlier investigations on talking face generation have focused on the synchronization of lip motion and speech content. However, human head pose and facial emotions are equally important characteristics of natural human faces. While audio-driven talking face generation has seen notable advancements, existing methods either overlook facial emotions or are limited to specific individuals and cannot be applied to arbitrary subjects. In this paper, we propose a one-shot Talking Head Generation framework (SPEAK) that distinguishes itself from general Talking Face Generation by enabling emotional and postural control. Specifically, we introduce the Inter-Reconstructed Feature Disentanglement (IRFD) method to decouple human facial features into three latent spaces. We then design a face editing module that modifies speech content and facial latent codes into a single latent space. Subsequently, we present a novel generator that employs modified latent codes derived from the editing module to regulate emotional expression, head poses, and speech content in synthesizing facial animations. Extensive trials demonstrate that our method can generate realistic talking head with coordinated lip motions, authentic facial emotions, and smooth head movements. The demo video is available at the anonymous link: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/SPEAK-F56E
A Granular Sieving Algorithm for Deterministic Global Optimization
Jul 14, 2021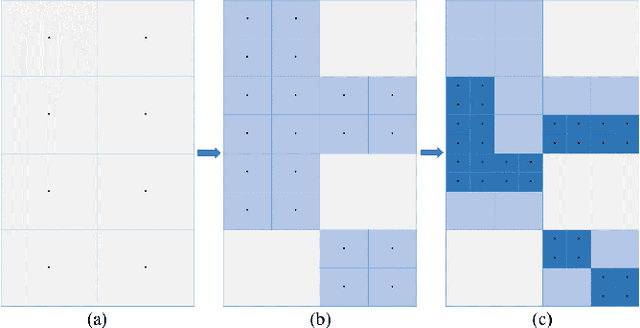

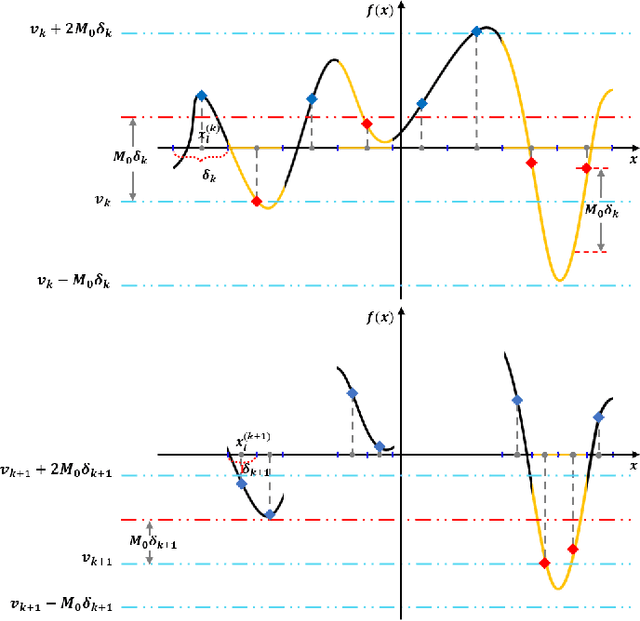
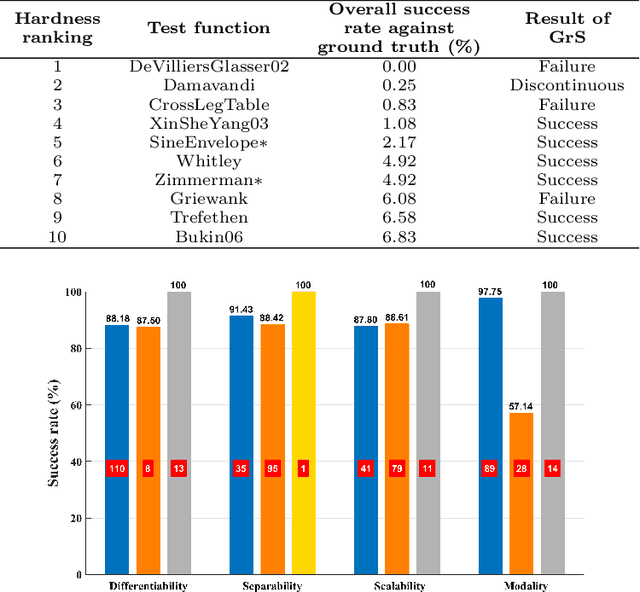
Abstract:A gradient-free deterministic method is developed to solve global optimization problems for Lipschitz continuous functions defined in arbitrary path-wise connected compact sets in Euclidean spaces. The method can be regarded as granular sieving with synchronous analysis in both the domain and range of the objective function. With straightforward mathematical formulation applicable to both univariate and multivariate objective functions, the global minimum value and all the global minimizers are located through two decreasing sequences of compact sets in, respectively, the domain and range spaces. The algorithm is easy to implement with moderate computational cost. The method is tested against extensive benchmark functions in the literature. The experimental results show remarkable effectiveness and applicability of the algorithm.
PGU-net+: Progressive Growing of U-net+ for Automated Cervical Nuclei Segmentation
Nov 12, 2019

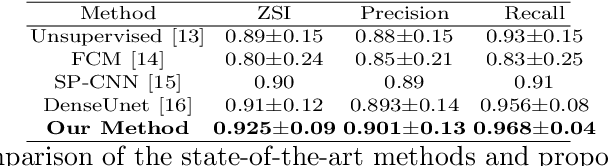

Abstract:Automated cervical nucleus segmentation based on deep learning can effectively improve the quantitative analysis of cervical cancer. However, accurate nuclei segmentation is still challenging. The classic U-net has not achieved satisfactory results on this task, because it mixes the information of different scales that affect each other, which limits the segmentation accuracy of the model. To solve this problem, we propose a progressive growing U-net (PGU-net+) model, which uses two paradigms to extract image features at different scales in a more independent way. First, we add residual modules between different scales of U-net, which enforces the model to learn the approximate shape of the annotation in the coarser scale, and to learn the residual between the annotation and the approximate shape in the finer scale. Second, we start to train the model with the coarsest part and then progressively add finer part to the training until the full model is included. When we train a finer part, we will reduce the learning rate of the previous coarser part, which further ensures that the model independently extracts information from different scales. We conduct several comparative experiments on the Herlev dataset. The experimental results show that the PGU-net+ has superior accuracy than the previous state-of-the-art methods on cervical nuclei segmentation.
Cascade Feature Aggregation for Human Pose Estimation
Apr 08, 2019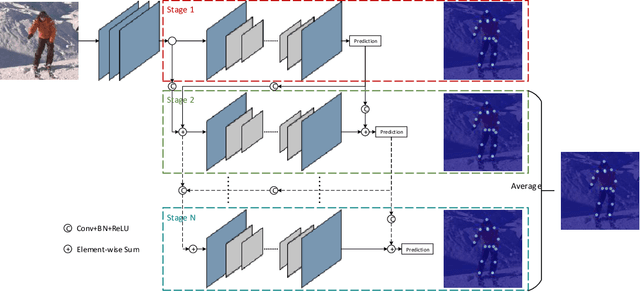
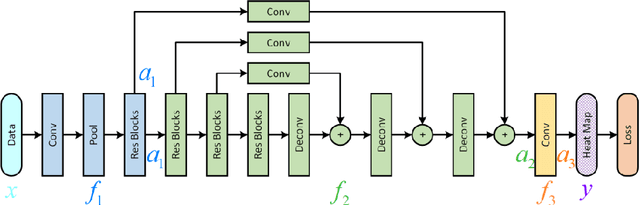
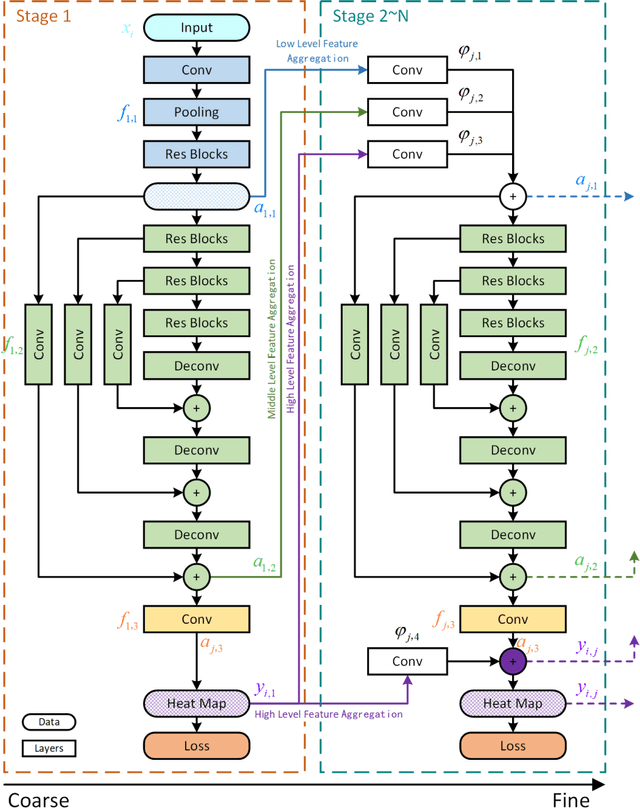
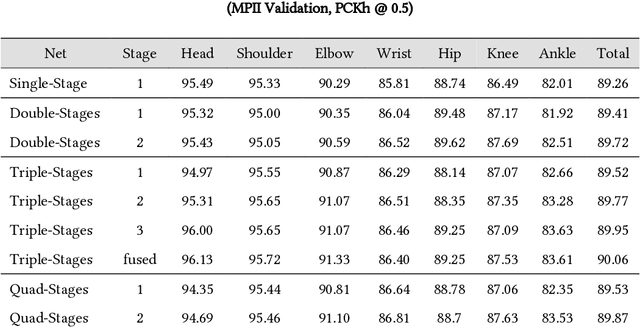
Abstract:Human pose estimation plays an important role in many computer vision tasks and has been studied for many decades. However, due to complex appearance variations from poses, illuminations, occlusions and low resolutions, it still remains a challenging problem. Taking the advantage of high-level semantic information from deep convolutional neural networks is an effective way to improve the accuracy of human pose estimation. In this paper, we propose a novel Cascade Feature Aggregation (CFA) method, which cascades several hourglass networks for robust human pose estimation. Features from different stages are aggregated to obtain abundant contextual information, leading to robustness to poses, partial occlusions and low resolution. Moreover, results from different stages are fused to further improve the localization accuracy. The extensive experiments on MPII datasets and LIP datasets demonstrate that our proposed CFA outperforms the state-of-the-art and achieves the best performance on the state-of-the-art benchmark MPII.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge