Junxiong Zhu
Q-Regularized Generative Auto-Bidding: From Suboptimal Trajectories to Optimal Policies
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:With the rapid development of e-commerce, auto-bidding has become a key asset in optimizing advertising performance under diverse advertiser environments. The current approaches focus on reinforcement learning (RL) and generative models. These efforts imitate offline historical behaviors by utilizing a complex structure with expensive hyperparameter tuning. The suboptimal trajectories further exacerbate the difficulty of policy learning. To address these challenges, we proposes QGA, a novel Q-value regularized Generative Auto-bidding method. In QGA, we propose to plug a Q-value regularization with double Q-learning strategy into the Decision Transformer backbone. This design enables joint optimization of policy imitation and action-value maximization, allowing the learned bidding policy to both leverage experience from the dataset and alleviate the adverse impact of the suboptimal trajectories. Furthermore, to safely explore the policy space beyond the data distribution, we propose a Q-value guided dual-exploration mechanism, in which the DT model is conditioned on multiple return-to-go targets and locally perturbed actions. This entire exploration process is dynamically guided by the aforementioned Q-value module, which provides principled evaluation for each candidate action. Experiments on public benchmarks and simulation environments demonstrate that QGA consistently achieves superior or highly competitive results compared to existing alternatives. Notably, in large-scale real-world A/B testing, QGA achieves a 3.27% increase in Ad GMV and a 2.49% improvement in Ad ROI.
MPPO: Multi Pair-wise Preference Optimization for LLMs with Arbitrary Negative Samples
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) with human feedback is crucial for their development. Existing preference optimization methods such as DPO and KTO, while improved based on Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), are inherently derived from PPO, requiring a reference model that adds GPU memory resources and relies heavily on abundant preference data. Meanwhile, current preference optimization research mainly targets single-question scenarios with two replies, neglecting optimization with multiple replies, which leads to a waste of data in the application. This study introduces the MPPO algorithm, which leverages the average likelihood of model responses to fit the reward function and maximizes the utilization of preference data. Through a comparison of Point-wise, Pair-wise, and List-wise implementations, we found that the Pair-wise approach achieves the best performance, significantly enhancing the quality of model responses. Experimental results demonstrate MPPO's outstanding performance across various benchmarks. On MT-Bench, MPPO outperforms DPO, ORPO, and SimPO. Notably, on Arena-Hard, MPPO surpasses DPO and ORPO by substantial margins. These achievements underscore the remarkable advantages of MPPO in preference optimization tasks.
Single-Layer Graph Convolutional Networks For Recommendation
Jun 07, 2020



Abstract:Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) and their variants have received significant attention and achieved start-of-the-art performances on various recommendation tasks. However, many existing GCN models tend to perform recursive aggregations among all related nodes, which arises severe computational burden. Moreover, they favor multi-layer architectures in conjunction with complicated modeling techniques. Though effective, the excessive amount of model parameters largely hinder their applications in real-world recommender systems. To this end, in this paper, we propose the single-layer GCN model which is able to achieve superior performance along with remarkably less complexity compared with existing models. Our main contribution is three-fold. First, we propose a principled similarity metric named distribution-aware similarity (DA similarity), which can guide the neighbor sampling process and evaluate the quality of the input graph explicitly. We also prove that DA similarity has a positive correlation with the final performance, through both theoretical analysis and empirical simulations. Second, we propose a simplified GCN architecture which employs a single GCN layer to aggregate information from the neighbors filtered by DA similarity and then generates the node representations. Moreover, the aggregation step is a parameter-free operation, such that it can be done in a pre-processing manner to further reduce red the training and inference costs. Third, we conduct extensive experiments on four datasets. The results verify that the proposed model outperforms existing GCN models considerably and yields up to a few orders of magnitude speedup in training, in terms of the recommendation performance.
Query-based Interactive Recommendation by Meta-Path and Adapted Attention-GRU
Jun 24, 2019



Abstract:Recently, interactive recommender systems are becoming increasingly popular. The insight is that, with the interaction between users and the system, (1) users can actively intervene the recommendation results rather than passively receive them, and (2) the system learns more about users so as to provide better recommendation. We focus on the single-round interaction, i.e. the system asks the user a question (Step 1), and exploits his feedback to generate better recommendation (Step 2). A novel query-based interactive recommender system is proposed in this paper, where \textbf{personalized questions are accurately generated from millions of automatically constructed questions} in Step 1, and \textbf{the recommendation is ensured to be closely-related to users' feedback} in Step 2. We achieve this by transforming Step 1 into a query recommendation task and Step 2 into a retrieval task. The former task is our key challenge. We firstly propose a model based on Meta-Path to efficiently retrieve hundreds of query candidates from the large query pool. Then an adapted Attention-GRU model is developed to effectively rank these candidates for recommendation. Offline and online experiments on Taobao, a large-scale e-commerce platform in China, verify the effectiveness of our interactive system. The system has already gone into production in the homepage of Taobao App since Nov. 11, 2018 (see https://v.qq.com/x/page/s0833tkp1uo.html on how it works online). Our code and dataset are public in https://github.com/zyody/QueryQR.
A Brand-level Ranking System with the Customized Attention-GRU Model
Aug 11, 2018
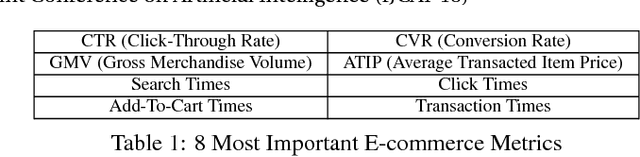
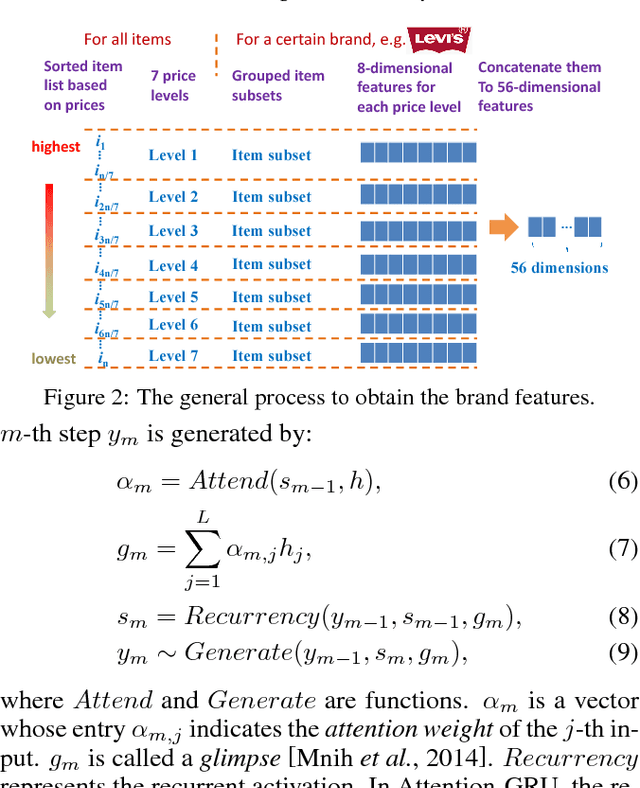
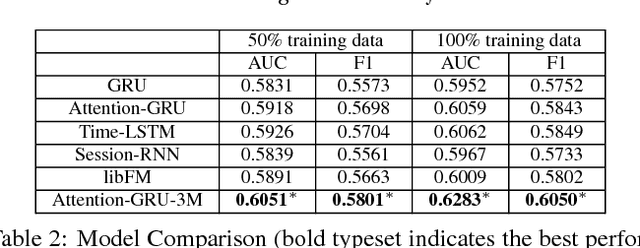
Abstract:In e-commerce websites like Taobao, brand is playing a more important role in influencing users' decision of click/purchase, partly because users are now attaching more importance to the quality of products and brand is an indicator of quality. However, existing ranking systems are not specifically designed to satisfy this kind of demand. Some design tricks may partially alleviate this problem, but still cannot provide satisfactory results or may create additional interaction cost. In this paper, we design the first brand-level ranking system to address this problem. The key challenge of this system is how to sufficiently exploit users' rich behavior in e-commerce websites to rank the brands. In our solution, we firstly conduct the feature engineering specifically tailored for the personalized brand ranking problem and then rank the brands by an adapted Attention-GRU model containing three important modifications. Note that our proposed modifications can also apply to many other machine learning models on various tasks. We conduct a series of experiments to evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed ranking model and test the response to the brand-level ranking system from real users on a large-scale e-commerce platform, i.e. Taobao.
* 7 pages, 6 figures, 3 tables. Published in IJCAI 2018. Make some figures and tables more clear
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge