Junhao Zhao
HI-TransPA: Hearing Impairments Translation Personal Assistant
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Hearing-impaired individuals often face significant barriers in daily communication due to the inherent challenges of producing clear speech. To address this, we introduce the Omni-Model paradigm into assistive technology and present HI-TransPA, an instruction-driven audio-visual personal assistant. The model fuses indistinct speech with lip dynamics, enabling both translation and dialogue within a single multimodal framework. To address the distinctive pronunciation patterns of hearing-impaired speech and the limited adaptability of existing models, we develop a multimodal preprocessing and curation pipeline that detects facial landmarks, stabilizes the lip region, and quantitatively evaluates sample quality. These quality scores guide a curriculum learning strategy that first trains on clean, high-confidence samples and progressively incorporates harder cases to strengthen model robustness. Architecturally, we employs a novel unified 3D-Resampler to efficiently encode the lip dynamics, which is critical for accurate interpretation. Experiments on purpose-built HI-Dialogue dataset show that HI-TransPA achieves state-of-the-art performance in both literal accuracy and semantic fidelity. Our work establishes a foundation for applying Omni-Models to assistive communication technology, providing an end-to-end modeling framework and essential processing tools for future research.
Edge-guided inverse design of digital metamaterials for ultra-high-capacity on-chip multi-dimensional interconnect
Oct 10, 2024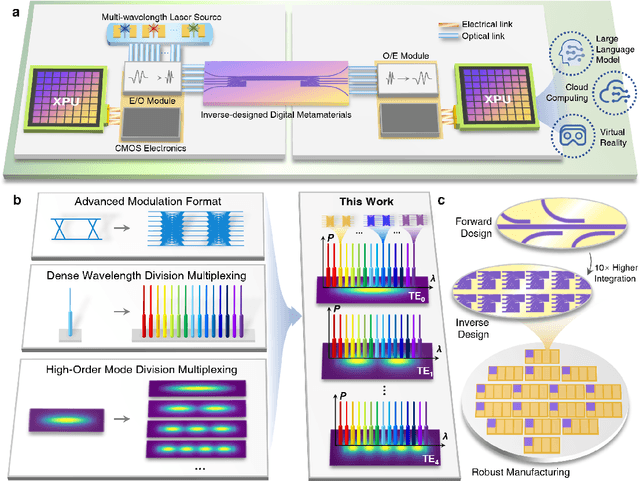
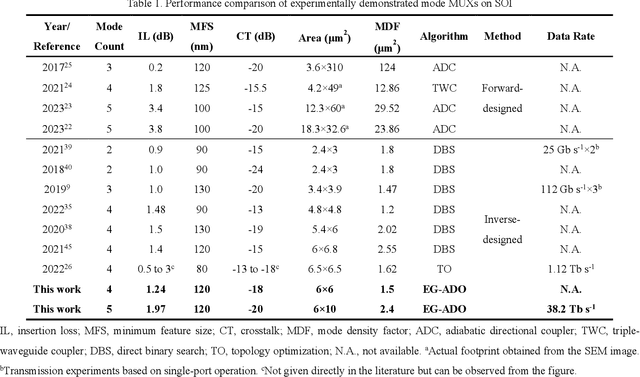
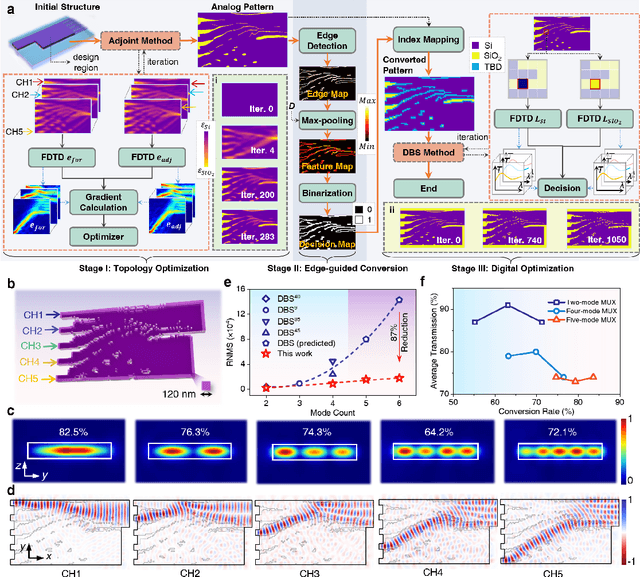
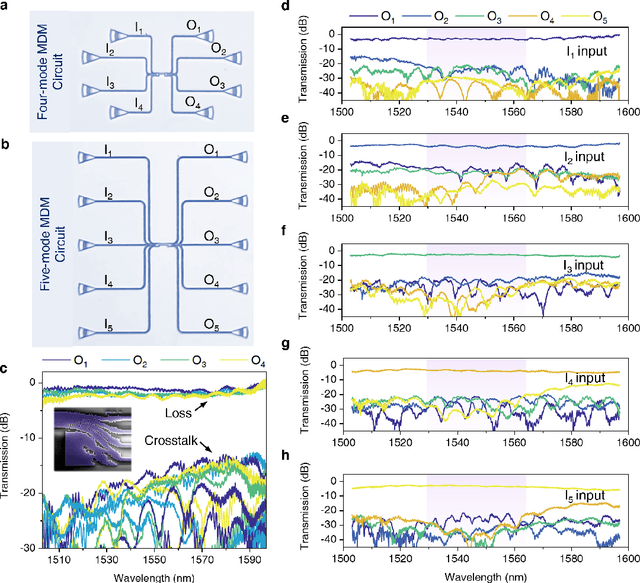
Abstract:The escalating demands of compute-intensive applications, including artificial intelligence, urgently necessitate the adoption of sophisticated optical on-chip interconnect technologies to overcome critical bottlenecks in scaling future computing systems. This transition requires leveraging the inherent parallelism of wavelength and mode dimensions of light, complemented by high-order modulation formats, to significantly enhance data throughput. Here we experimentally demonstrate a novel synergy of these three dimensions, achieving multi-tens-of-terabits-per-second on-chip interconnects using ultra-broadband, multi-mode digital metamaterials. Employing a highly efficient edge-guided analog-and-digital optimization method, we inversely design foundry-compatible, robust, and multi-port digital metamaterials with an 8xhigher computational efficiency. Using a packaged five-mode multiplexing chip, we demonstrate a single-wavelength interconnect capacity of 1.62 Tbit s-1 and a record-setting multi-dimensional interconnect capacity of 38.2 Tbit s-1 across 5 modes and 88 wavelength channels. A theoretical analysis suggests that further system optimization can enable on-chip interconnects to reach sub-petabit-per-second data transmission rates. This study highlights the transformative potential of optical interconnect technologies to surmount the constraints of electronic links, thus setting the stage for next-generation datacenter and optical compute interconnects.
Everything to the Synthetic: Diffusion-driven Test-time Adaptation via Synthetic-Domain Alignment
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:Test-time adaptation (TTA) aims to enhance the performance of source-domain pretrained models when tested on unknown shifted target domains. Traditional TTA methods primarily adapt model weights based on target data streams, making model performance sensitive to the amount and order of target data. Recently, diffusion-driven TTA methods have demonstrated strong performance by using an unconditional diffusion model, which is also trained on the source domain to transform target data into synthetic data as a source domain projection. This allows the source model to make predictions without weight adaptation. In this paper, we argue that the domains of the source model and the synthetic data in diffusion-driven TTA methods are not aligned. To adapt the source model to the synthetic domain of the unconditional diffusion model, we introduce a Synthetic-Domain Alignment (SDA) framework to fine-tune the source model with synthetic data. Specifically, we first employ a conditional diffusion model to generate labeled samples, creating a synthetic dataset. Subsequently, we use the aforementioned unconditional diffusion model to add noise to and denoise each sample before fine-tuning. This process mitigates the potential domain gap between the conditional and unconditional models. Extensive experiments across various models and benchmarks demonstrate that SDA achieves superior domain alignment and consistently outperforms existing diffusion-driven TTA methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/SHI-Labs/Diffusion-Driven-Test-Time-Adaptation-via-Synthetic-Domain-Alignment.
Multi-view 3D Face Reconstruction Based on Flame
Aug 15, 2023Abstract:At present, face 3D reconstruction has broad application prospects in various fields, but the research on it is still in the development stage. In this paper, we hope to achieve better face 3D reconstruction quality by combining multi-view training framework with face parametric model Flame, propose a multi-view training and testing model MFNet (Multi-view Flame Network). We build a self-supervised training framework and implement constraints such as multi-view optical flow loss function and face landmark loss, and finally obtain a complete MFNet. We propose innovative implementations of multi-view optical flow loss and the covisible mask. We test our model on AFLW and facescape datasets and also take pictures of our faces to reconstruct 3D faces while simulating actual scenarios as much as possible, which achieves good results. Our work mainly addresses the problem of combining parametric models of faces with multi-view face 3D reconstruction and explores the implementation of a Flame based multi-view training and testing framework for contributing to the field of face 3D reconstruction.
Multimodal Short Video Rumor Detection System Based on Contrastive Learning
Apr 18, 2023



Abstract:With short video platforms becoming one of the important channels for news sharing, major short video platforms in China have gradually become new breeding grounds for fake news. However, it is not easy to distinguish short video rumors due to the great amount of information and features contained in short videos, as well as the serious homogenization and similarity of features among videos. In order to mitigate the spread of short video rumors, our group decides to detect short video rumors by constructing multimodal feature fusion and introducing external knowledge after considering the advantages and disadvantages of each algorithm. The ideas of detection are as follows: (1) dataset creation: to build a short video dataset with multiple features; (2) multimodal rumor detection model: firstly, we use TSN (Temporal Segment Networks) video coding model to extract video features; then, we use OCR (Optical Character Recognition) and ASR (Automatic Character Recognition) to extract video features. Recognition) and ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition) fusion to extract text, and then use the BERT model to fuse text features with video features (3) Finally, use contrast learning to achieve distinction: first crawl external knowledge, then use the vector database to achieve the introduction of external knowledge and the final structure of the classification output. Our research process is always oriented to practical needs, and the related knowledge results will play an important role in many practical scenarios such as short video rumor identification and social opinion control.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge