Johnson Liu
TIC-VLA: A Think-in-Control Vision-Language-Action Model for Robot Navigation in Dynamic Environments
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Robots in dynamic, human-centric environments must follow language instructions while maintaining real-time reactive control. Vision-language-action (VLA) models offer a promising framework, but they assume temporally aligned reasoning and control, despite semantic inference being inherently delayed relative to real-time action. We introduce Think-in-Control (TIC)-VLA, a latency-aware framework that explicitly models delayed semantic reasoning during action generation. TIC-VLA defines a delayed semantic-control interface that conditions action generation on delayed vision-language semantic states and explicit latency metadata, in addition to current observations, enabling policies to compensate for asynchronous reasoning. We further propose a latency-consistent training pipeline that injects reasoning inference delays during imitation learning and online reinforcement learning, aligning training with asynchronous deployment. To support realistic evaluation, we present DynaNav, a physics-accurate, photo-realistic simulation suite for language-guided navigation in dynamic environments. Extensive experiments in simulation and on a real robot show that TIC-VLA consistently outperforms prior VLA models while maintaining robust real-time control under multi-second reasoning latency. Project website: https://ucla-mobility.github.io/TIC-VLA/
Imaging for All-Day Wearable Smart Glasses
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:In recent years smart glasses technology has rapidly advanced, opening up entirely new areas for mobile computing. We expect future smart glasses will need to be all-day wearable, adopting a small form factor to meet the requirements of volume, weight, fashionability and social acceptability, which puts significant constraints on the space of possible solutions. Additional challenges arise due to the fact that smart glasses are worn in arbitrary environments while their wearer moves and performs everyday activities. In this paper, we systematically analyze the space of imaging from smart glasses and derive several fundamental limits that govern this imaging domain. We discuss the impact of these limits on achievable image quality and camera module size -- comparing in particular to related devices such as mobile phones. We then propose a novel distributed imaging approach that allows to minimize the size of the individual camera modules when compared to a standard monolithic camera design. Finally, we demonstrate the properties of this novel approach in a series of experiments using synthetic data as well as images captured with two different prototype implementations.
InSPE: Rapid Evaluation of Heterogeneous Multi-Modal Infrastructure Sensor Placement
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Infrastructure sensing is vital for traffic monitoring at safety hotspots (e.g., intersections) and serves as the backbone of cooperative perception in autonomous driving. While vehicle sensing has been extensively studied, infrastructure sensing has received little attention, especially given the unique challenges of diverse intersection geometries, complex occlusions, varying traffic conditions, and ambient environments like lighting and weather. To address these issues and ensure cost-effective sensor placement, we propose Heterogeneous Multi-Modal Infrastructure Sensor Placement Evaluation (InSPE), a perception surrogate metric set that rapidly assesses perception effectiveness across diverse infrastructure and environmental scenarios with combinations of multi-modal sensors. InSPE systematically evaluates perception capabilities by integrating three carefully designed metrics, i.e., sensor coverage, perception occlusion, and information gain. To support large-scale evaluation, we develop a data generation tool within the CARLA simulator and also introduce Infra-Set, a dataset covering diverse intersection types and environmental conditions. Benchmarking experiments with state-of-the-art perception algorithms demonstrate that InSPE enables efficient and scalable sensor placement analysis, providing a robust solution for optimizing intelligent intersection infrastructure.
V2XPnP: Vehicle-to-Everything Spatio-Temporal Fusion for Multi-Agent Perception and Prediction
Dec 02, 2024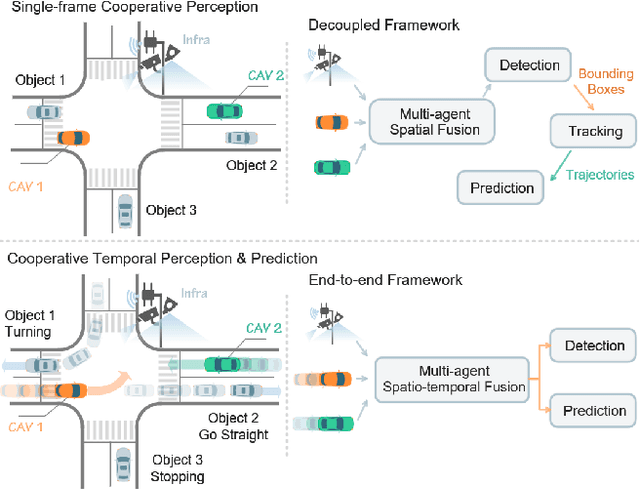
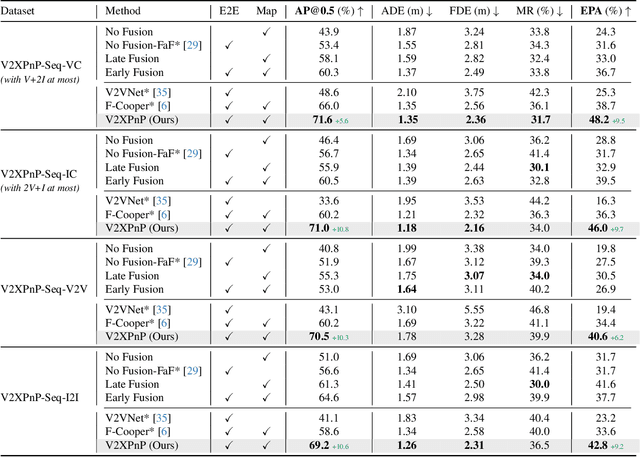
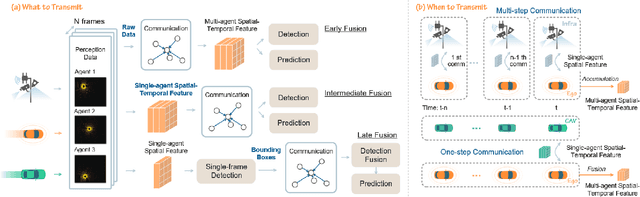
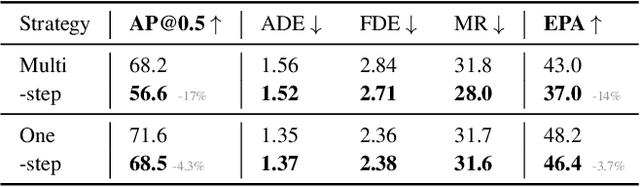
Abstract:Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) technologies offer a promising paradigm to mitigate the limitations of constrained observability in single-vehicle systems. Prior work primarily focuses on single-frame cooperative perception, which fuses agents' information across different spatial locations but ignores temporal cues and temporal tasks (e.g., temporal perception and prediction). In this paper, we focus on temporal perception and prediction tasks in V2X scenarios and design one-step and multi-step communication strategies (when to transmit) as well as examine their integration with three fusion strategies - early, late, and intermediate (what to transmit), providing comprehensive benchmarks with various fusion models (how to fuse). Furthermore, we propose V2XPnP, a novel intermediate fusion framework within one-step communication for end-to-end perception and prediction. Our framework employs a unified Transformer-based architecture to effectively model complex spatiotemporal relationships across temporal per-frame, spatial per-agent, and high-definition map. Moreover, we introduce the V2XPnP Sequential Dataset that supports all V2X cooperation modes and addresses the limitations of existing real-world datasets, which are restricted to single-frame or single-mode cooperation. Extensive experiments demonstrate our framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both perception and prediction tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge