Jize Jiang
VTool-R1: VLMs Learn to Think with Images via Reinforcement Learning on Multimodal Tool Use
May 25, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement Learning Finetuning (RFT) has significantly advanced the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by enabling long chains of thought, self-correction, and effective tool use. While recent works attempt to extend RFT to vision-language models (VLMs), these efforts largely produce text-only reasoning conditioned on static image inputs, falling short of true multimodal reasoning in the response. In contrast, test-time methods like Visual Sketchpad incorporate visual steps but lack training mechanisms. We introduce VTool-R1, the first framework that trains VLMs to generate multimodal chains of thought by interleaving text and intermediate visual reasoning steps. VTool-R1 integrates Python-based visual editing tools into the RFT process, enabling VLMs to learn when and how to generate visual reasoning steps that benefit final reasoning. Trained with outcome-based rewards tied to task accuracy, our approach elicits strategic visual tool use for reasoning without relying on process-based supervision. Experiments on structured visual question answering over charts and tables show that VTool-R1 enhances reasoning performance by teaching VLMs to "think with images" and generate multimodal chain of thoughts with tools.
Cache-of-Thought: Master-Apprentice Framework for Cost-Effective Vision Language Model Inference
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Vision Language Models (VLMs) have achieved remarkable success in a wide range of vision applications of increasing complexity and scales, yet choosing the right VLM model size involves a trade-off between response quality and cost. While smaller VLMs are cheaper to run, they typically produce responses only marginally better than random guessing on benchmarks such as MMMU. In this paper, we propose Cache of Thought (CoT), a master apprentice framework for collaborative inference between large and small VLMs. CoT manages high quality query results from large VLMs (master) in a cache, which are then selected via a novel multi modal retrieval and in-context learning to aid the performance of small VLMs (apprentice). We extensively evaluate CoT on various widely recognized and challenging general VQA benchmarks, and show that CoT increases overall VQA performance by up to 7.7% under the same budget, and specifically boosts the performance of apprentice VLMs by up to 36.6%.
UOUO: Uncontextualized Uncommon Objects for Measuring Knowledge Horizons of Vision Language Models
Jul 25, 2024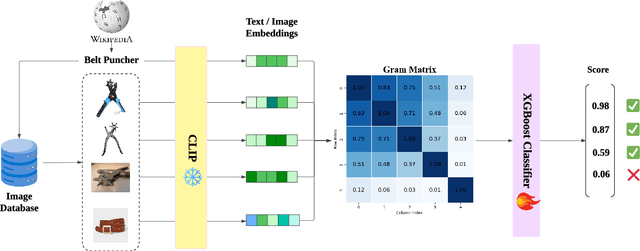
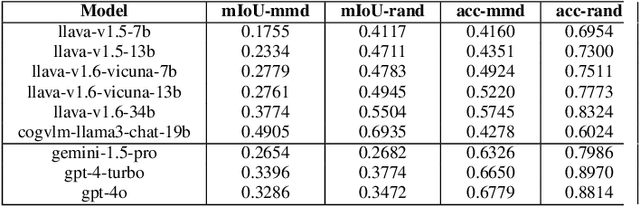
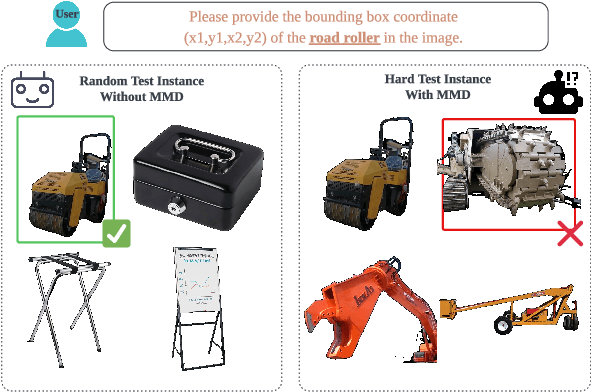
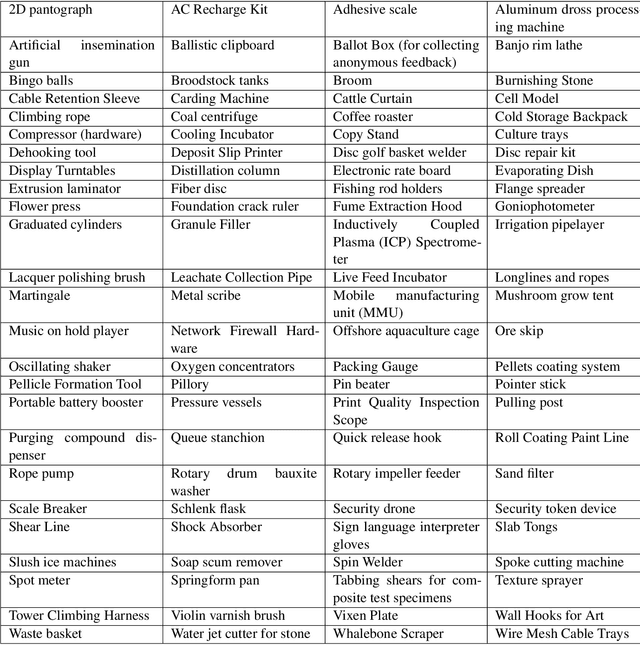
Abstract:Smaller-scale Vision-Langauge Models (VLMs) often claim to perform on par with larger models in general-domain visual grounding and question-answering benchmarks while offering advantages in computational efficiency and storage. However, their ability to handle rare objects, which fall into the long tail of data distributions, is less understood. To rigorously evaluate this aspect, we introduce the "Uncontextualized Uncommon Objects" (UOUO) benchmark. This benchmark focuses on systematically testing VLMs with both large and small parameter counts on rare and specialized objects. Our comprehensive analysis reveals that while smaller VLMs maintain competitive performance on common datasets, they significantly underperform on tasks involving uncommon objects. We also propose an advanced, scalable pipeline for data collection and cleaning, ensuring the UOUO benchmark provides high-quality, challenging instances. These findings highlight the need to consider long-tail distributions when assessing the true capabilities of VLMs.
Efficient Title Reranker for Fast and Improved Knowledge-Intense NLP
Dec 20, 2023Abstract:We introduce Efficient Title Reranker via Broadcasting Query Encoder, a novel title reranking technique to achieve efficient title reranking 20x-40x faster than vanilla passage reranker. However, one of the challenges with the training of Efficient Title Reranker is the instability. Analyzing the issue, we found some very difficult ground truths might act as noisy labels causing accuracy to drop as well as some extreme values in model probability output causing nan. To address these issues, we introduce the Sigmoid Trick, a novel technique that reduces the gradient update of both cases resulting in better retrieval efficacy. Experiments showed the effectiveness of ETR and sigmoid trick as we achieved four state-of-the-art positions on the kilt knowledge benchmark.
Competence-Based Analysis of Language Models
Mar 01, 2023



Abstract:Despite the recent success of large pretrained language models (LMs) on a variety of prompting tasks, these models can be alarmingly brittle to small changes in inputs or application contexts. To better understand such behavior and motivate the design of more robust LMs, we propose a general experimental framework, CALM (Competence-based Analysis of Language Models), where targeted causal interventions are utilized to damage an LM's internal representation of various linguistic properties in order to evaluate its use of each representation in performing a given task. We implement these interventions as gradient-based adversarial attacks, which (in contrast to prior causal probing methodologies) are able to target arbitrarily-encoded representations of relational properties, and carry out a case study of this approach to analyze how BERT-like LMs use representations of several relational properties in performing associated relation prompting tasks. We find that, while the representations LMs leverage in performing each task are highly entangled, they may be meaningfully interpreted in terms of the tasks where they are most utilized; and more broadly, that CALM enables an expanded scope of inquiry in LM analysis that may be useful in predicting and explaining weaknesses of existing LMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge