Jinzhu Mao
CrimeMind: Simulating Urban Crime with Multi-Modal LLM Agents
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Modeling urban crime is an important yet challenging task that requires understanding the subtle visual, social, and cultural cues embedded in urban environments. Previous work has predominantly focused on rule-based agent-based modeling (ABM) and deep learning methods. ABMs offer interpretability of internal mechanisms but exhibit limited predictive accuracy.In contrast, deep learning methods are often effective in prediction but are less interpretable and require extensive training data. Moreover, both lines of work lack the cognitive flexibility to adapt to changing environments. Leveraging the capabilities of large language models (LLMs), we propose CrimeMind, a novel LLM-driven ABM framework for simulating urban crime within a multi-modal urban context.A key innovation of our design is the integration of the Routine Activity Theory (RAT) into the agentic workflow of CrimeMind, enabling it to process rich multi-modal urban features and reason about criminal behavior.However, RAT requires LLM agents to infer subtle cues in evaluating environmental safety as part of assessing guardianship, which can be challenging for LLMs. To address this, we collect a small-scale human-annotated dataset and align CrimeMind's perception with human judgment via a training-free textual gradient method.Experiments across four major U.S. cities demonstrate that CrimeMind outperforms both traditional ABMs and deep learning baselines in crime hotspot prediction and spatial distribution accuracy, achieving up to a 24% improvement over the strongest baseline.Furthermore, we conduct counterfactual simulations of external incidents and policy interventions and it successfully captures the expected changes in crime patterns, demonstrating its ability to reflect counterfactual scenarios.Overall, CrimeMind enables fine-grained modeling of individual behaviors and facilitates evaluation of real-world interventions.
EmbodiedCity: A Benchmark Platform for Embodied Agent in Real-world City Environment
Oct 12, 2024Abstract:Embodied artificial intelligence emphasizes the role of an agent's body in generating human-like behaviors. The recent efforts on EmbodiedAI pay a lot of attention to building up machine learning models to possess perceiving, planning, and acting abilities, thereby enabling real-time interaction with the world. However, most works focus on bounded indoor environments, such as navigation in a room or manipulating a device, with limited exploration of embodying the agents in open-world scenarios. That is, embodied intelligence in the open and outdoor environment is less explored, for which one potential reason is the lack of high-quality simulators, benchmarks, and datasets. To address it, in this paper, we construct a benchmark platform for embodied intelligence evaluation in real-world city environments. Specifically, we first construct a highly realistic 3D simulation environment based on the real buildings, roads, and other elements in a real city. In this environment, we combine historically collected data and simulation algorithms to conduct simulations of pedestrian and vehicle flows with high fidelity. Further, we designed a set of evaluation tasks covering different EmbodiedAI abilities. Moreover, we provide a complete set of input and output interfaces for access, enabling embodied agents to easily take task requirements and current environmental observations as input and then make decisions and obtain performance evaluations. On the one hand, it expands the capability of existing embodied intelligence to higher levels. On the other hand, it has a higher practical value in the real world and can support more potential applications for artificial general intelligence. Based on this platform, we evaluate some popular large language models for embodied intelligence capabilities of different dimensions and difficulties.
Identify Critical Nodes in Complex Network with Large Language Models
Mar 01, 2024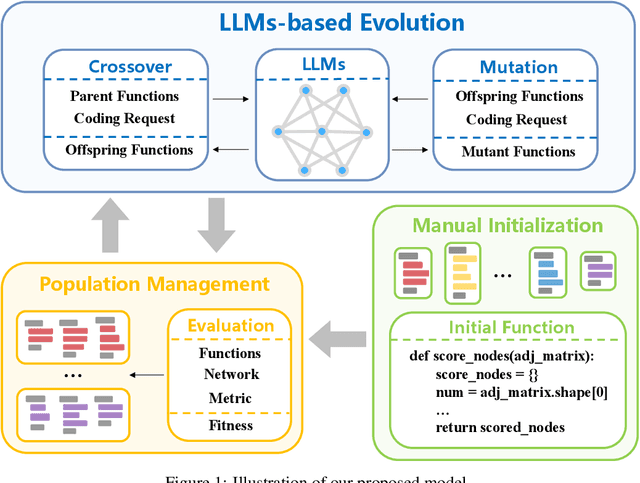
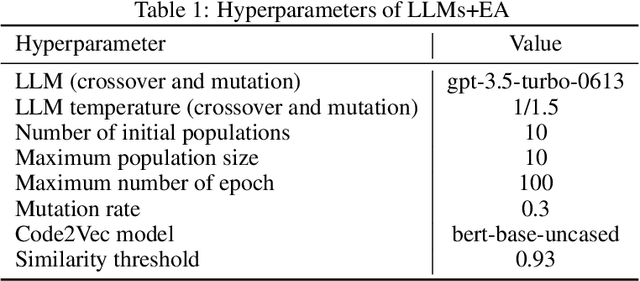
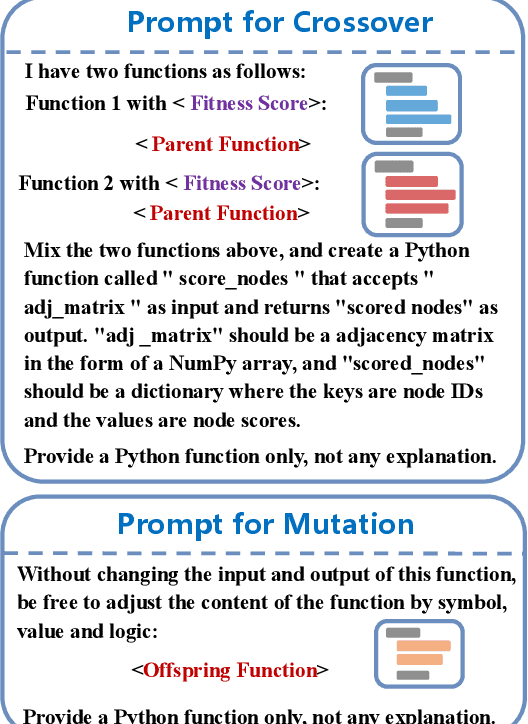
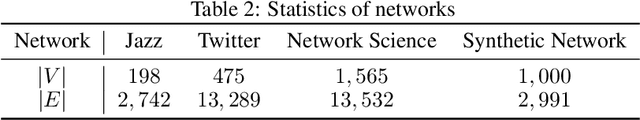
Abstract:Identifying critical nodes in networks is a classical decision-making task, and many methods struggle to strike a balance between adaptability and utility. Therefore, we propose an approach that empowers Evolutionary Algorithm (EA) with Large Language Models (LLMs), to generate a function called "score\_nodes" which can further be used to identify crucial nodes based on their assigned scores. Our model consists of three main components: Manual Initialization, Population Management, and LLMs-based Evolution. It evolves from initial populations with a set of designed node scoring functions created manually. LLMs leverage their strong contextual understanding and rich programming skills to perform crossover and mutation operations on the individuals, generating excellent new functions. These functions are then categorized, ranked, and eliminated to ensure the stable development of the populations while preserving diversity. Extensive experiments demonstrate the excellent performance of our method, showcasing its strong generalization ability compared to other state-of-the-art algorithms. It can consistently and orderly generate diverse and efficient node scoring functions. All source codes and models that can reproduce all results in this work are publicly available at this link: \url{https://anonymous.4open.science/r/LLM4CN-6520}
Detecting Vulnerable Nodes in Urban Infrastructure Interdependent Network
Aug 01, 2023Abstract:Understanding and characterizing the vulnerability of urban infrastructures, which refers to the engineering facilities essential for the regular running of cities and that exist naturally in the form of networks, is of great value to us. Potential applications include protecting fragile facilities and designing robust topologies, etc. Due to the strong correlation between different topological characteristics and infrastructure vulnerability and their complicated evolution mechanisms, some heuristic and machine-assisted analysis fall short in addressing such a scenario. In this paper, we model the interdependent network as a heterogeneous graph and propose a system based on graph neural network with reinforcement learning, which can be trained on real-world data, to characterize the vulnerability of the city system accurately. The presented system leverages deep learning techniques to understand and analyze the heterogeneous graph, which enables us to capture the risk of cascade failure and discover vulnerable infrastructures of cities. Extensive experiments with various requests demonstrate not only the expressive power of our system but also transferring ability and necessity of the specific components.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge