Javier Hernandez
Oggi
Longitudinal Study on Social and Emotional Use of AI Conversational Agent
Apr 19, 2025Abstract:Development in digital technologies has continuously reshaped how individuals seek and receive social and emotional support. While online platforms and communities have long served this need, the increased integration of general-purpose conversational AI into daily lives has introduced new dynamics in how support is provided and experienced. Existing research has highlighted both benefits (e.g., wider access to well-being resources) and potential risks (e.g., over-reliance) of using AI for support seeking. In this five-week, exploratory study, we recruited 149 participants divided into two usage groups: a baseline usage group (BU, n=60) that used the internet and AI as usual, and an active usage group (AU, n=89) encouraged to use one of four commercially available AI tools (Microsoft Copilot, Google Gemini, PI AI, ChatGPT) for social and emotional interactions. Our analysis revealed significant increases in perceived attachment towards AI (32.99 percentage points), perceived AI empathy (25.8 p.p.), and motivation to use AI for entertainment (22.90 p.p.) among the AU group. We also observed that individual differences (e.g., gender identity, prior AI usage) influenced perceptions of AI empathy and attachment. Lastly, the AU group expressed higher comfort in seeking personal help, managing stress, obtaining social support, and talking about health with AI, indicating potential for broader emotional support while highlighting the need for safeguards against problematic usage. Overall, our exploratory findings underscore the importance of developing consumer-facing AI tools that support emotional well-being responsibly, while empowering users to understand the limitations of these tools.
From Lived Experience to Insight: Unpacking the Psychological Risks of Using AI Conversational Agents
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:Recent gain in popularity of AI conversational agents has led to their increased use for improving productivity and supporting well-being. While previous research has aimed to understand the risks associated with interactions with AI conversational agents, these studies often fall short in capturing the lived experiences. Additionally, psychological risks have often been presented as a sub-category within broader AI-related risks in past taxonomy works, leading to under-representation of the impact of psychological risks of AI use. To address these challenges, our work presents a novel risk taxonomy focusing on psychological risks of using AI gathered through lived experience of individuals. We employed a mixed-method approach, involving a comprehensive survey with 283 individuals with lived mental health experience and workshops involving lived experience experts to develop a psychological risk taxonomy. Our taxonomy features 19 AI behaviors, 21 negative psychological impacts, and 15 contexts related to individuals. Additionally, we propose a novel multi-path vignette based framework for understanding the complex interplay between AI behaviors, psychological impacts, and individual user contexts. Finally, based on the feedback obtained from the workshop sessions, we present design recommendations for developing safer and more robust AI agents. Our work offers an in-depth understanding of the psychological risks associated with AI conversational agents and provides actionable recommendations for policymakers, researchers, and developers.
From User Surveys to Telemetry-Driven Agents: Exploring the Potential of Personalized Productivity Solutions
Jan 17, 2024
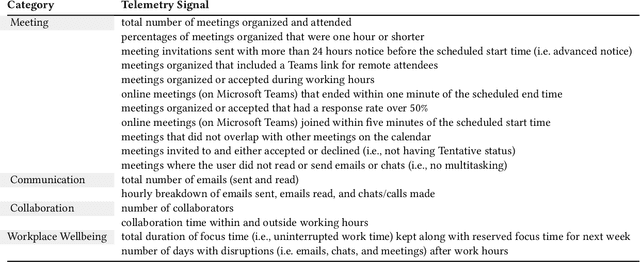
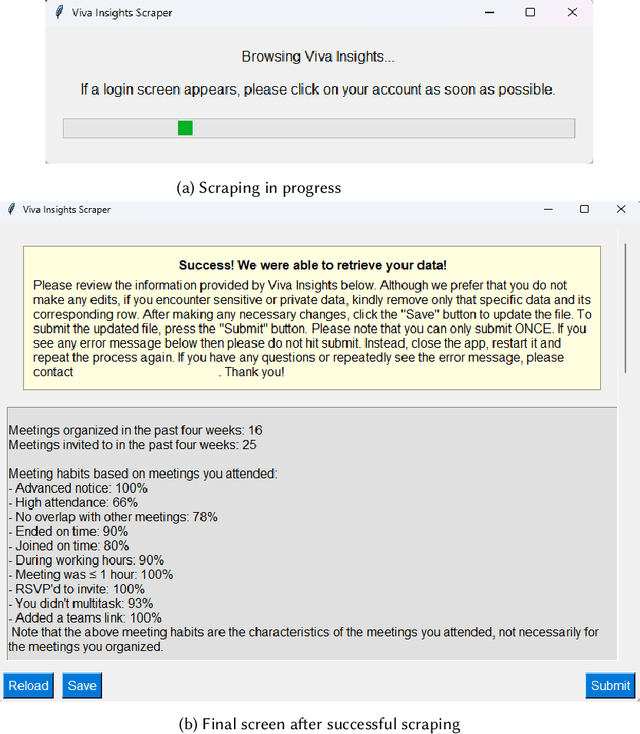
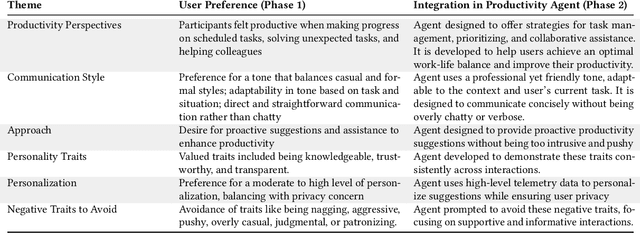
Abstract:We present a comprehensive, user-centric approach to understand preferences in AI-based productivity agents and develop personalized solutions tailored to users' needs. Utilizing a two-phase method, we first conducted a survey with 363 participants, exploring various aspects of productivity, communication style, agent approach, personality traits, personalization, and privacy. Drawing on the survey insights, we developed a GPT-4 powered personalized productivity agent that utilizes telemetry data gathered via Viva Insights from information workers to provide tailored assistance. We compared its performance with alternative productivity-assistive tools, such as dashboard and narrative, in a study involving 40 participants. Our findings highlight the importance of user-centric design, adaptability, and the balance between personalization and privacy in AI-assisted productivity tools. By building on the insights distilled from our study, we believe that our work can enable and guide future research to further enhance productivity solutions, ultimately leading to optimized efficiency and user experiences for information workers.
Affective Conversational Agents: Understanding Expectations and Personal Influences
Oct 19, 2023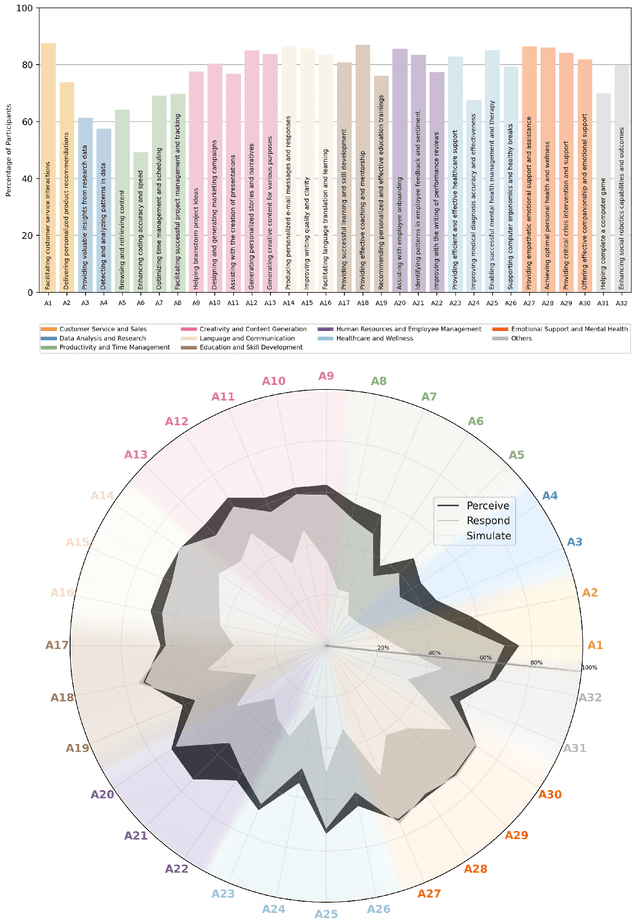
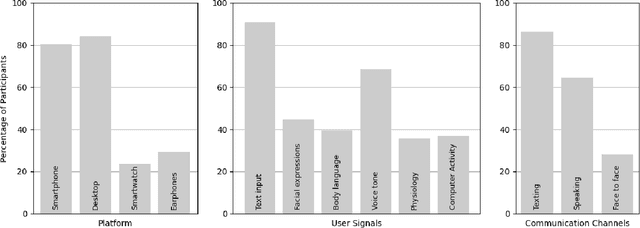
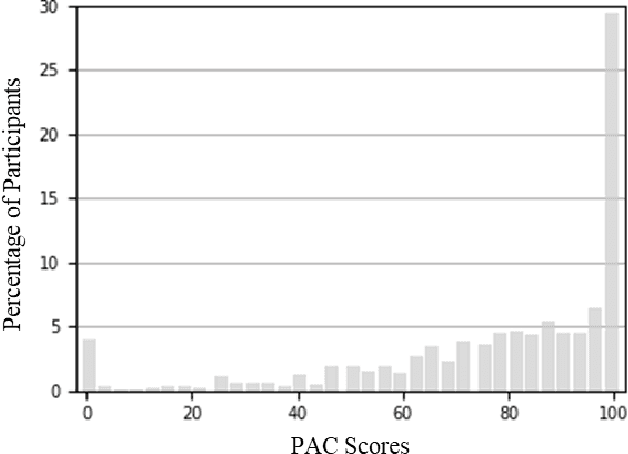

Abstract:The rise of AI conversational agents has broadened opportunities to enhance human capabilities across various domains. As these agents become more prevalent, it is crucial to investigate the impact of different affective abilities on their performance and user experience. In this study, we surveyed 745 respondents to understand the expectations and preferences regarding affective skills in various applications. Specifically, we assessed preferences concerning AI agents that can perceive, respond to, and simulate emotions across 32 distinct scenarios. Our results indicate a preference for scenarios that involve human interaction, emotional support, and creative tasks, with influences from factors such as emotional reappraisal and personality traits. Overall, the desired affective skills in AI agents depend largely on the application's context and nature, emphasizing the need for adaptability and context-awareness in the design of affective AI conversational agents.
SCAMPS: Synthetics for Camera Measurement of Physiological Signals
Jun 08, 2022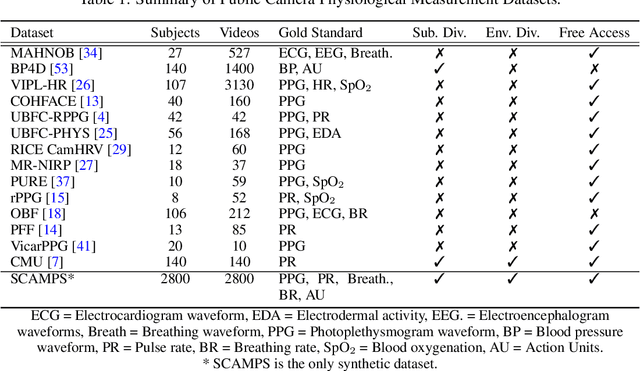
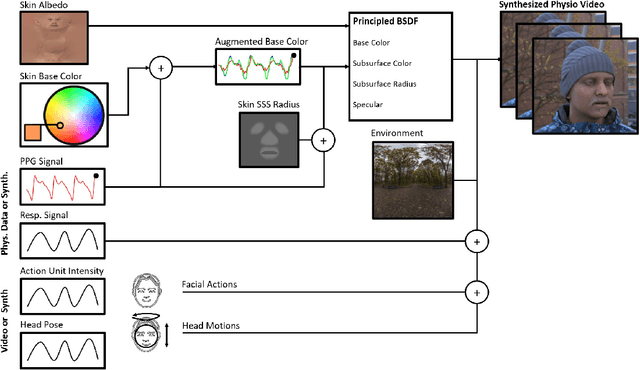
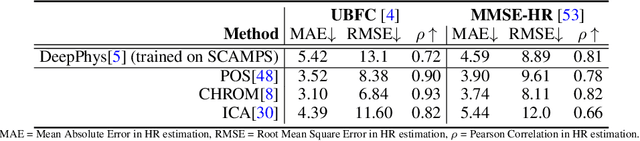

Abstract:The use of cameras and computational algorithms for noninvasive, low-cost and scalable measurement of physiological (e.g., cardiac and pulmonary) vital signs is very attractive. However, diverse data representing a range of environments, body motions, illumination conditions and physiological states is laborious, time consuming and expensive to obtain. Synthetic data have proven a valuable tool in several areas of machine learning, yet are not widely available for camera measurement of physiological states. Synthetic data offer "perfect" labels (e.g., without noise and with precise synchronization), labels that may not be possible to obtain otherwise (e.g., precise pixel level segmentation maps) and provide a high degree of control over variation and diversity in the dataset. We present SCAMPS, a dataset of synthetics containing 2,800 videos (1.68M frames) with aligned cardiac and respiratory signals and facial action intensities. The RGB frames are provided alongside segmentation maps. We provide precise descriptive statistics about the underlying waveforms, including inter-beat interval, heart rate variability, and pulse arrival time. Finally, we present baseline results training on these synthetic data and testing on real-world datasets to illustrate generalizability.
Synthetic Data for Multi-Parameter Camera-Based Physiological Sensing
Oct 10, 2021

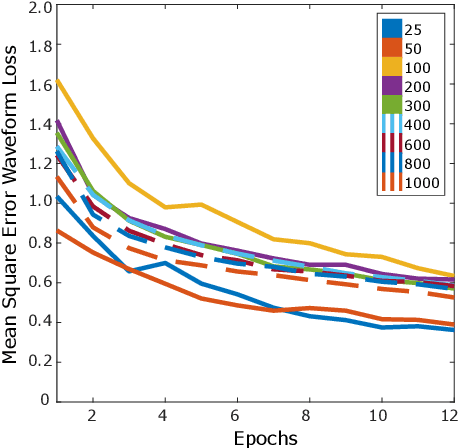
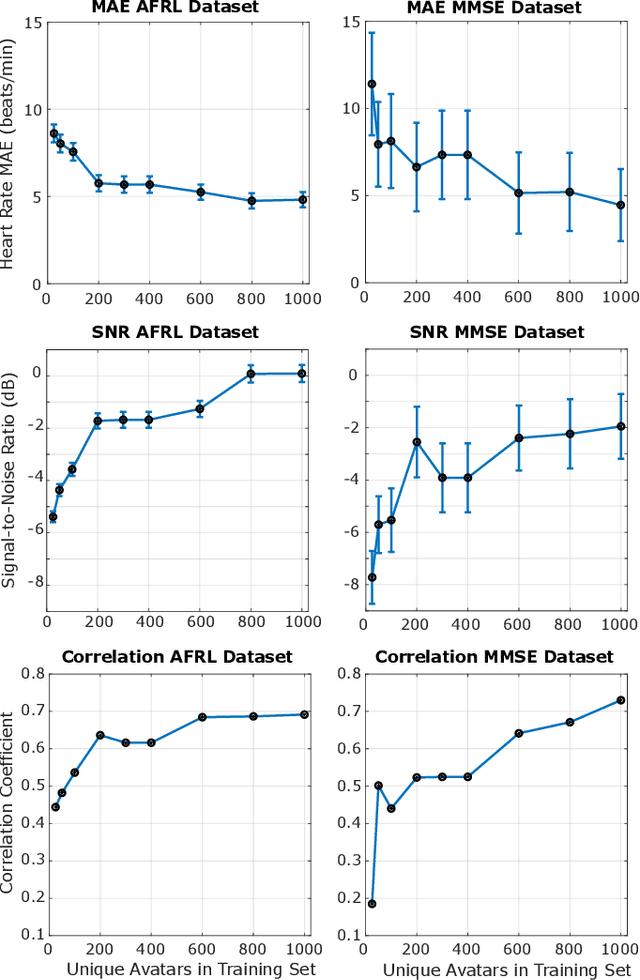
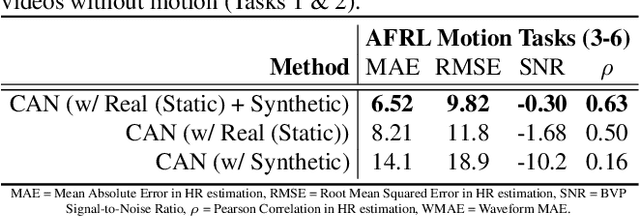
Abstract:Synthetic data is a powerful tool in training data hungry deep learning algorithms. However, to date, camera-based physiological sensing has not taken full advantage of these techniques. In this work, we leverage a high-fidelity synthetics pipeline for generating videos of faces with faithful blood flow and breathing patterns. We present systematic experiments showing how physiologically-grounded synthetic data can be used in training camera-based multi-parameter cardiopulmonary sensing. We provide empirical evidence that heart and breathing rate measurement accuracy increases with the number of synthetic avatars in the training set. Furthermore, training with avatars with darker skin types leads to better overall performance than training with avatars with lighter skin types. Finally, we discuss the opportunities that synthetics present in the domain of camera-based physiological sensing and limitations that need to be overcome.
DeepFN: Towards Generalizable Facial Action Unit Recognition with Deep Face Normalization
Mar 03, 2021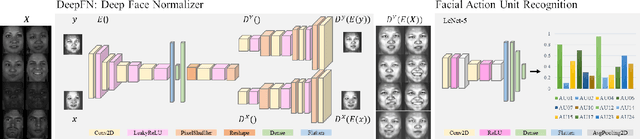
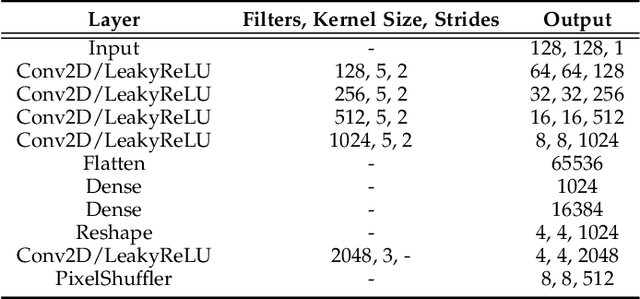
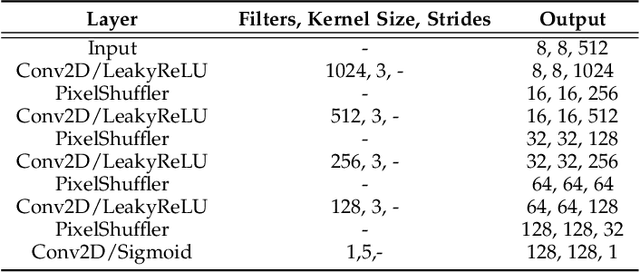
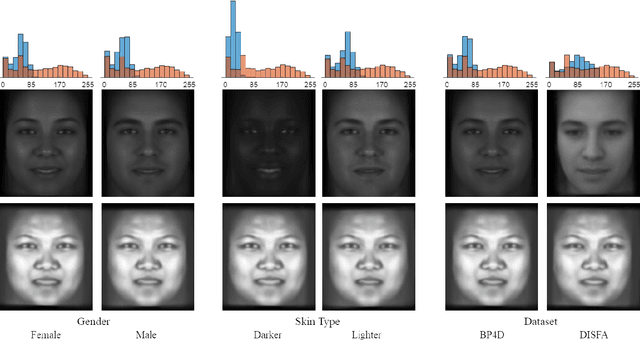
Abstract:Facial action unit recognition has many applications from market research to psychotherapy and from image captioning to entertainment. Despite its recent progress, deployment of these models has been impeded due to their limited generalization to unseen people and demographics. This work conducts an in-depth analysis of performance across several dimensions: individuals(40 subjects), genders (male and female), skin types (darker and lighter), and databases (BP4D and DISFA). To help suppress the variance in data, we use the notion of self-supervised denoising autoencoders to design a method for deep face normalization(DeepFN) that transfers facial expressions of different people onto a common facial template which is then used to train and evaluate facial action recognition models. We show that person-independent models yield significantly lower performance (55% average F1 and accuracy across 40 subjects) than person-dependent models (60.3%), leading to a generalization gap of 5.3%. However, normalizing the data with the newly introduced DeepFN significantly increased the performance of person-independent models (59.6%), effectively reducing the gap. Similarly, we observed generalization gaps when considering gender (2.4%), skin type (5.3%), and dataset (9.4%), which were significantly reduced with the use of DeepFN. These findings represent an important step towards the creation of more generalizable facial action unit recognition systems.
Advancing Non-Contact Vital Sign Measurement using Synthetic Avatars
Oct 24, 2020
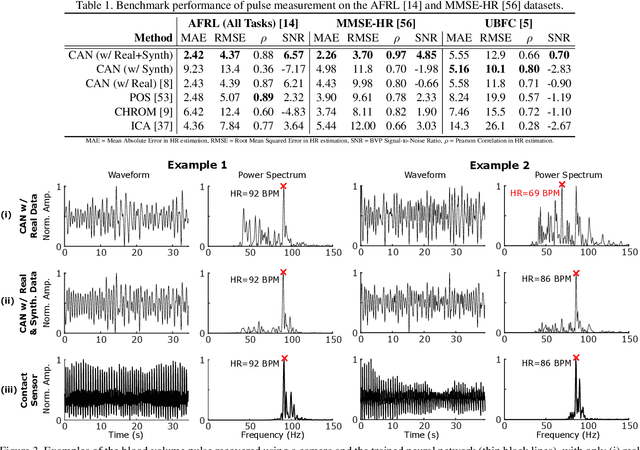
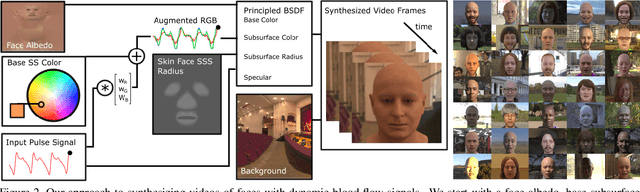
Abstract:Non-contact physiological measurement has the potential to provide low-cost, non-invasive health monitoring. However, machine vision approaches are often limited by the availability and diversity of annotated video datasets resulting in poor generalization to complex real-life conditions. To address these challenges, this work proposes the use of synthetic avatars that display facial blood flow changes and allow for systematic generation of samples under a wide variety of conditions. Our results show that training on both simulated and real video data can lead to performance gains under challenging conditions. We show state-of-the-art performance on three large benchmark datasets and improved robustness to skin type and motion.
Estimating Carotid Pulse and Breathing Rate from Near-infrared Video of the Neck
May 24, 2018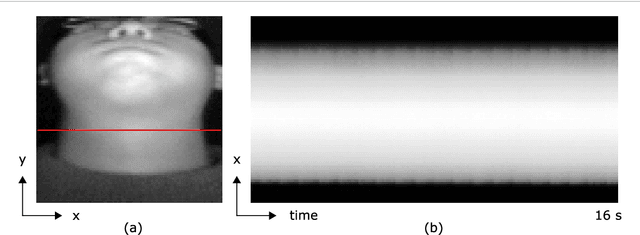
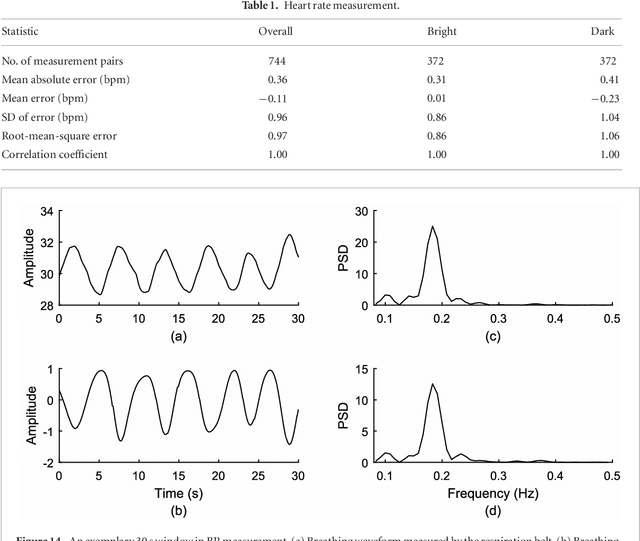
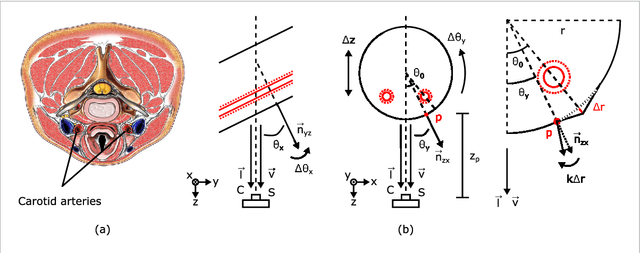
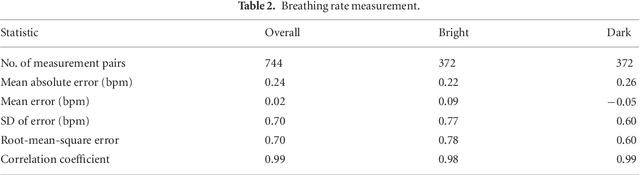
Abstract:Objective: Non-contact physiological measurement is a growing research area that allows capturing vital signs such as heart rate (HR) and breathing rate (BR) comfortably and unobtrusively with remote devices. However, most of the approaches work only in bright environments in which subtle photoplethysmographic and ballistocardiographic signals can be easily analyzed and/or require expensive and custom hardware to perform the measurements. Approach: This work introduces a low-cost method to measure subtle motions associated with the carotid pulse and breathing movement from the neck using near-infrared (NIR) video imaging. A skin reflection model of the neck was established to provide a theoretical foundation for the method. In particular, the method relies on template matching for neck detection, Principal Component Analysis for feature extraction, and Hidden Markov Models for data smoothing. Main Results: We compared the estimated HR and BR measures with ones provided by an FDA-cleared device in a 12-participant laboratory study: the estimates achieved a mean absolute error of 0.36 beats per minute and 0.24 breaths per minute under both bright and dark lighting. Significance: This work advances the possibilities of non-contact physiological measurement in real-life conditions in which environmental illumination is limited and in which the face of the person is not readily available or needs to be protected. Due to the increasing availability of NIR imaging devices, the described methods are readily scalable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge