Jakob Gawlikowski
Exploiting Text-Image Latent Spaces for the Description of Visual Concepts
Oct 23, 2024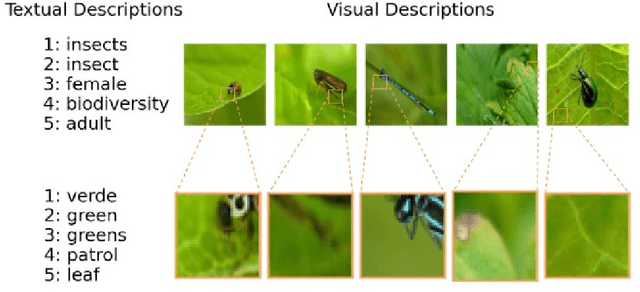
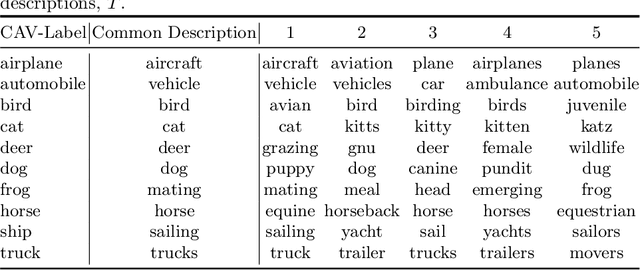


Abstract:Concept Activation Vectors (CAVs) offer insights into neural network decision-making by linking human friendly concepts to the model's internal feature extraction process. However, when a new set of CAVs is discovered, they must still be translated into a human understandable description. For image-based neural networks, this is typically done by visualizing the most relevant images of a CAV, while the determination of the concept is left to humans. In this work, we introduce an approach to aid the interpretation of newly discovered concept sets by suggesting textual descriptions for each CAV. This is done by mapping the most relevant images representing a CAV into a text-image embedding where a joint description of these relevant images can be computed. We propose utilizing the most relevant receptive fields instead of full images encoded. We demonstrate the capabilities of this approach in multiple experiments with and without given CAV labels, showing that the proposed approach provides accurate descriptions for the CAVs and reduces the challenge of concept interpretation.
Lightning UQ Box: A Comprehensive Framework for Uncertainty Quantification in Deep Learning
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:Uncertainty quantification (UQ) is an essential tool for applying deep neural networks (DNNs) to real world tasks, as it attaches a degree of confidence to DNN outputs. However, despite its benefits, UQ is often left out of the standard DNN workflow due to the additional technical knowledge required to apply and evaluate existing UQ procedures. Hence there is a need for a comprehensive toolbox that allows the user to integrate UQ into their modelling workflow, without significant overhead. We introduce \texttt{Lightning UQ Box}: a unified interface for applying and evaluating various approaches to UQ. In this paper, we provide a theoretical and quantitative comparison of the wide range of state-of-the-art UQ methods implemented in our toolbox. We focus on two challenging vision tasks: (i) estimating tropical cyclone wind speeds from infrared satellite imagery and (ii) estimating the power output of solar panels from RGB images of the sky. By highlighting the differences between methods our results demonstrate the need for a broad and approachable experimental framework for UQ, that can be used for benchmarking UQ methods. The toolbox, example implementations, and further information are available at: https://github.com/lightning-uq-box/lightning-uq-box
Unraveling Anomalies in Time: Unsupervised Discovery and Isolation of Anomalous Behavior in Bio-regenerative Life Support System Telemetry
Jun 14, 2024Abstract:The detection of abnormal or critical system states is essential in condition monitoring. While much attention is given to promptly identifying anomalies, a retrospective analysis of these anomalies can significantly enhance our comprehension of the underlying causes of observed undesired behavior. This aspect becomes particularly critical when the monitored system is deployed in a vital environment. In this study, we delve into anomalies within the domain of Bio-Regenerative Life Support Systems (BLSS) for space exploration and analyze anomalies found in telemetry data stemming from the EDEN ISS space greenhouse in Antarctica. We employ time series clustering on anomaly detection results to categorize various types of anomalies in both uni- and multivariate settings. We then assess the effectiveness of these methods in identifying systematic anomalous behavior. Additionally, we illustrate that the anomaly detection methods MDI and DAMP produce complementary results, as previously indicated by research.
The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Evidential Regression
May 20, 2022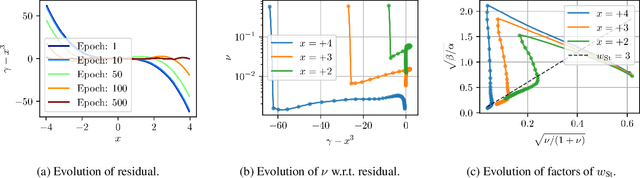
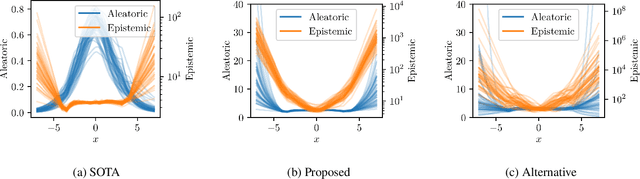
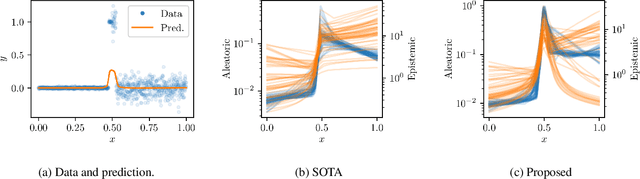
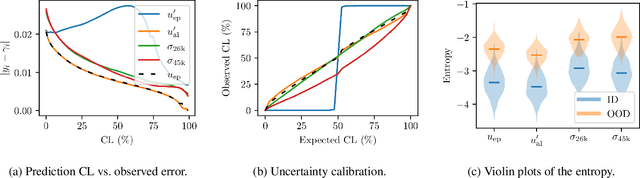
Abstract:There is a significant need for principled uncertainty reasoning in machine learning systems as they are increasingly deployed in safety-critical domains. A new approach with uncertainty-aware regression-based neural networks (NNs), based on learning evidential distributions for aleatoric and epistemic uncertainties, shows promise over traditional deterministic methods and typical Bayesian NNs, notably with the capabilities to disentangle aleatoric and epistemic uncertainties. Despite some empirical success of Deep Evidential Regression (DER), there are important gaps in the mathematical foundation that raise the question of why the proposed technique seemingly works. We detail the theoretical shortcomings and analyze the performance on synthetic and real-world data sets, showing that Deep Evidential Regression is a heuristic rather than an exact uncertainty quantification. We go on to propose corrections and redefinitions of how aleatoric and epistemic uncertainties should be extracted from NNs.
A Survey of Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks
Jul 07, 2021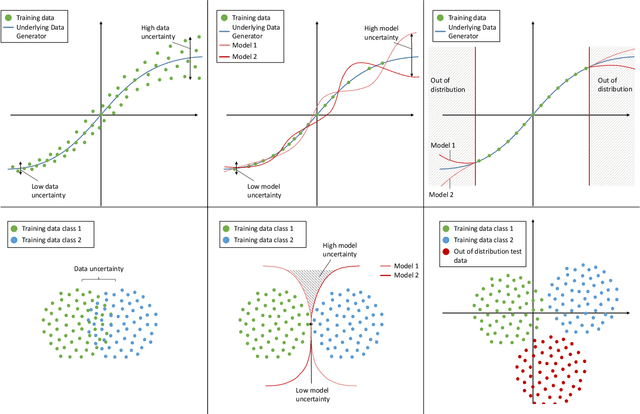
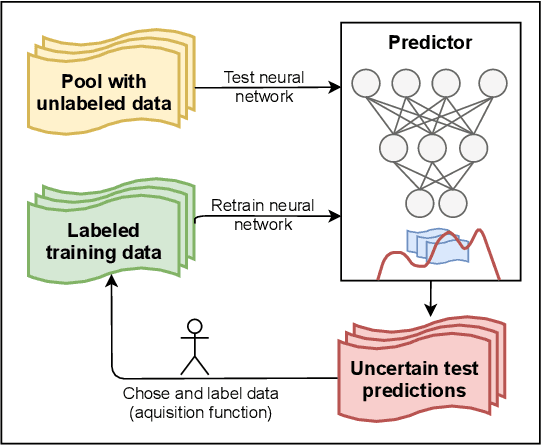
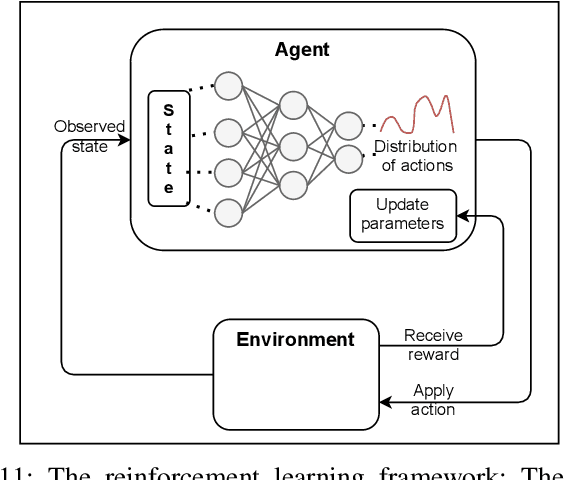
Abstract:Due to their increasing spread, confidence in neural network predictions became more and more important. However, basic neural networks do not deliver certainty estimates or suffer from over or under confidence. Many researchers have been working on understanding and quantifying uncertainty in a neural network's prediction. As a result, different types and sources of uncertainty have been identified and a variety of approaches to measure and quantify uncertainty in neural networks have been proposed. This work gives a comprehensive overview of uncertainty estimation in neural networks, reviews recent advances in the field, highlights current challenges, and identifies potential research opportunities. It is intended to give anyone interested in uncertainty estimation in neural networks a broad overview and introduction, without presupposing prior knowledge in this field. A comprehensive introduction to the most crucial sources of uncertainty is given and their separation into reducible model uncertainty and not reducible data uncertainty is presented. The modeling of these uncertainties based on deterministic neural networks, Bayesian neural networks, ensemble of neural networks, and test-time data augmentation approaches is introduced and different branches of these fields as well as the latest developments are discussed. For a practical application, we discuss different measures of uncertainty, approaches for the calibration of neural networks and give an overview of existing baselines and implementations. Different examples from the wide spectrum of challenges in different fields give an idea of the needs and challenges regarding uncertainties in practical applications. Additionally, the practical limitations of current methods for mission- and safety-critical real world applications are discussed and an outlook on the next steps towards a broader usage of such methods is given.
Leveraging Evidential Deep Learning Uncertainties with Graph-based Clustering to Detect Anomalies
Jul 04, 2021



Abstract:Understanding and representing traffic patterns are key to detecting anomalies in the maritime domain. To this end, we propose a novel graph-based traffic representation and association scheme to cluster trajectories of vessels using automatic identification system (AIS) data. We utilize the (un)clustered data to train a recurrent neural network (RNN)-based evidential regression model, which can predict a vessel's trajectory at future timesteps with its corresponding prediction uncertainty. This paper proposes the usage of a deep learning (DL)-based uncertainty estimation in detecting maritime anomalies, such as unusual vessel maneuvering. Furthermore, we utilize the evidential deep learning classifiers to detect unusual turns of vessels and the loss of AIS signal using predicted class probabilities with associated uncertainties. Our experimental results suggest that using graph-based clustered data improves the ability of the DL models to learn the temporal-spatial correlation of data and associated uncertainties. Using different AIS datasets and experiments, we demonstrate that the estimated prediction uncertainty yields fundamental information for the detection of traffic anomalies in the maritime and, possibly in other domains.
Out-of-distribution detection in satellite image classification
Apr 09, 2021



Abstract:In satellite image analysis, distributional mismatch between the training and test data may arise due to several reasons, including unseen classes in the test data and differences in the geographic area. Deep learning based models may behave in unexpected manner when subjected to test data that has such distributional shifts from the training data, also called out-of-distribution (OOD) examples. Predictive uncertainly analysis is an emerging research topic which has not been explored much in context of satellite image analysis. Towards this, we adopt a Dirichlet Prior Network based model to quantify distributional uncertainty of deep learning models for remote sensing. The approach seeks to maximize the representation gap between the in-domain and OOD examples for a better identification of unknown examples at test time. Experimental results on three exemplary test scenarios show the efficacy of the model in satellite image analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge