Ivan Marsic
MaskMatch: Boosting Semi-Supervised Learning Through Mask Autoencoder-Driven Feature Learning
May 10, 2024



Abstract:Conventional methods in semi-supervised learning (SSL) often face challenges related to limited data utilization, mainly due to their reliance on threshold-based techniques for selecting high-confidence unlabeled data during training. Various efforts (e.g., FreeMatch) have been made to enhance data utilization by tweaking the thresholds, yet none have managed to use 100% of the available data. To overcome this limitation and improve SSL performance, we introduce \algo, a novel algorithm that fully utilizes unlabeled data to boost semi-supervised learning. \algo integrates a self-supervised learning strategy, i.e., Masked Autoencoder (MAE), that uses all available data to enforce the visual representation learning. This enables the SSL algorithm to leverage all available data, including samples typically filtered out by traditional methods. In addition, we propose a synthetic data training approach to further increase data utilization and improve generalization. These innovations lead \algo to achieve state-of-the-art results on challenging datasets. For instance, on CIFAR-100 with 2 labels per class, STL-10 with 4 labels per class, and Euro-SAT with 2 labels per class, \algo achieves low error rates of 18.71%, 9.47%, and 3.07%, respectively. The code will be made publicly available.
Improving Label Assignments Learning by Dynamic Sample Dropout Combined with Layer-wise Optimization in Speech Separation
Nov 20, 2023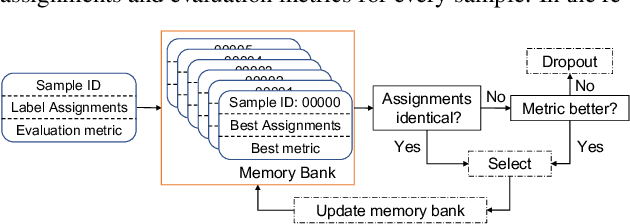
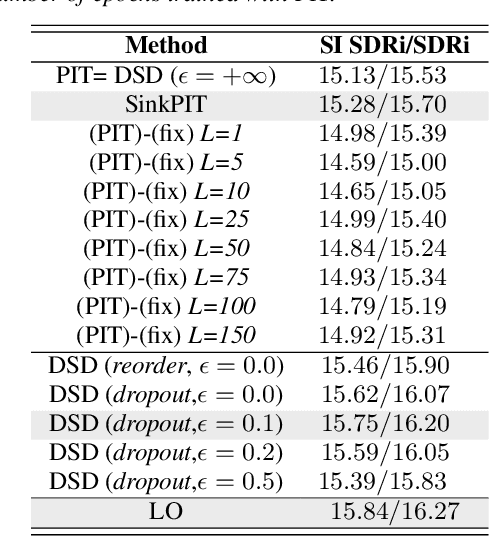
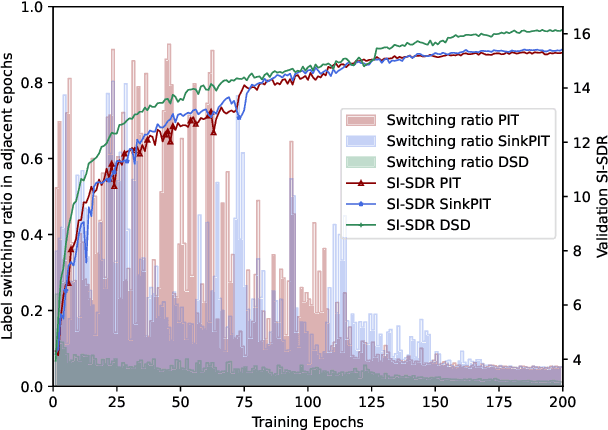
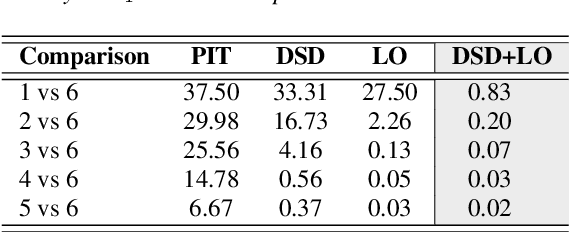
Abstract:In supervised speech separation, permutation invariant training (PIT) is widely used to handle label ambiguity by selecting the best permutation to update the model. Despite its success, previous studies showed that PIT is plagued by excessive label assignment switching in adjacent epochs, impeding the model to learn better label assignments. To address this issue, we propose a novel training strategy, dynamic sample dropout (DSD), which considers previous best label assignments and evaluation metrics to exclude the samples that may negatively impact the learned label assignments during training. Additionally, we include layer-wise optimization (LO) to improve the performance by solving layer-decoupling. Our experiments showed that combining DSD and LO outperforms the baseline and solves excessive label assignment switching and layer-decoupling issues. The proposed DSD and LO approach is easy to implement, requires no extra training sets or steps, and shows generality to various speech separation tasks.
Exploring Runtime Decision Support for Trauma Resuscitation
Jul 06, 2022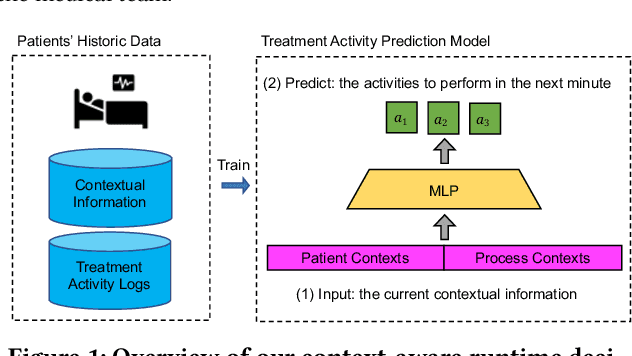
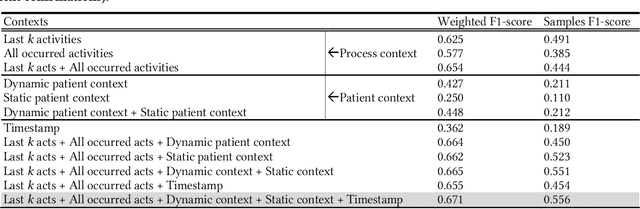
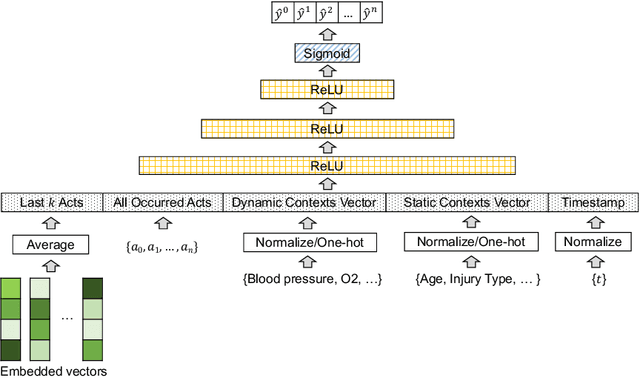
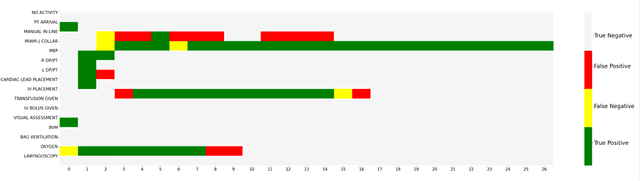
Abstract:AI-based recommender systems have been successfully applied in many domains (e.g., e-commerce, feeds ranking). Medical experts believe that incorporating such methods into a clinical decision support system may help reduce medical team errors and improve patient outcomes during treatment processes (e.g., trauma resuscitation, surgical processes). Limited research, however, has been done to develop automatic data-driven treatment decision support. We explored the feasibility of building a treatment recommender system to provide runtime next-minute activity predictions. The system uses patient context (e.g., demographics and vital signs) and process context (e.g., activities) to continuously predict activities that will be performed in the next minute. We evaluated our system on a pre-recorded dataset of trauma resuscitation and conducted an ablation study on different model variants. The best model achieved an average F1-score of 0.67 for 61 activity types. We include medical team feedback and discuss the future work.
Generating Privacy-Preserving Process Data with Deep Generative Models
Mar 15, 2022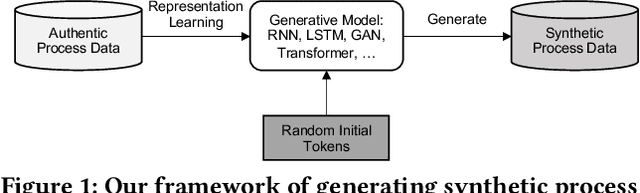
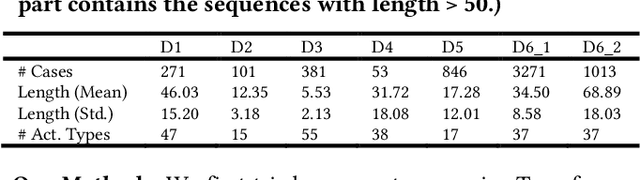
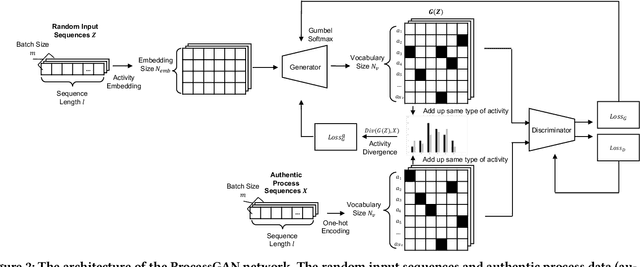
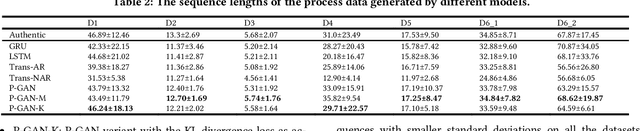
Abstract:Process data with confidential information cannot be shared directly in public, which hinders the research in process data mining and analytics. Data encryption methods have been studied to protect the data, but they still may be decrypted, which leads to individual identification. We experimented with different models of representation learning and used the learned model to generate synthetic process data. We introduced an adversarial generative network for process data generation (ProcessGAN) with two Transformer networks for the generator and the discriminator. We evaluated ProcessGAN and traditional models on six real-world datasets, of which two are public and four are collected in medical domains. We used statistical metrics and supervised learning scores to evaluate the synthetic data. We also used process mining to discover workflows for the authentic and synthetic datasets and had medical experts evaluate the clinical applicability of the synthetic workflows. We found that ProcessGAN outperformed traditional sequential models when trained on small authentic datasets of complex processes. ProcessGAN better represented the long-range dependencies between the activities, which is important for complicated processes such as the medical processes. Traditional sequential models performed better when trained on large data of simple processes. We conclude that ProcessGAN can generate a large amount of sharable synthetic process data indistinguishable from authentic data.
Time-Domain Mapping Based Single-Channel Speech Separation With Hierarchical Constraint Training
Oct 20, 2021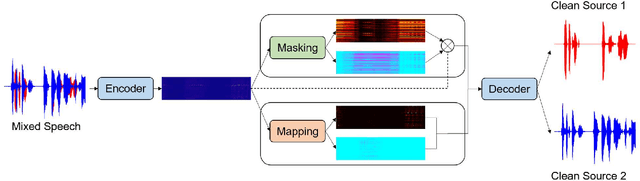
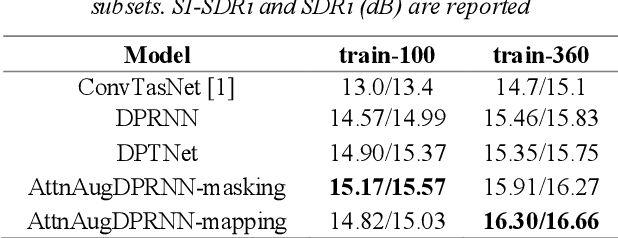
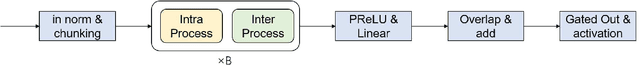
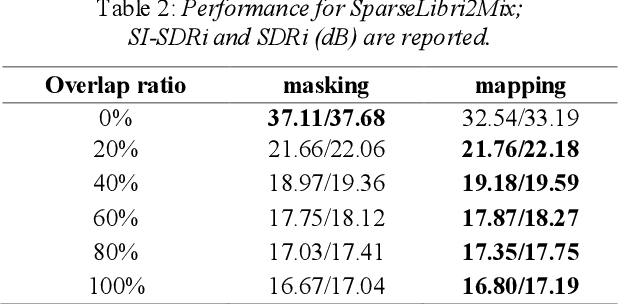
Abstract:Single-channel speech separation is required for multi-speaker speech recognition. Recent deep learning-based approaches focused on time-domain audio separation net (TasNet) because it has superior performance and lower latency compared to the conventional time-frequency-based (T-F-based) approaches. Most of these works rely on the masking-based method that estimates a linear mapping function (mask) for each speaker. However, the other commonly used method, the mapping-based method that is less sensitive to SNR variations, is inadequately studied in the time domain. We explore the potential of the mapping-based method by introducing attention augmented DPRNN (AttnAugDPRNN) which directly approximates the clean sources from the mixture for speech separation. Permutation Invariant Training (PIT) has been a paradigm to solve the label ambiguity problem for speech separation but usually leads to suboptimal performance. To solve this problem, we propose an efficient training strategy called Hierarchical Constraint Training (HCT) to regularize the training, which could effectively improve the model performance. When using PIT, our results showed that mapping-based AttnAugDPRNN outperformed masking-based AttnAugDPRNN when the training corpus is large. Mapping-based AttnAugDPRNN with HCT significantly improved the SI-SDR by 10.1% compared to the masking-based AttnAugDPRNN without HCT.
VidTr: Video Transformer Without Convolutions
Apr 23, 2021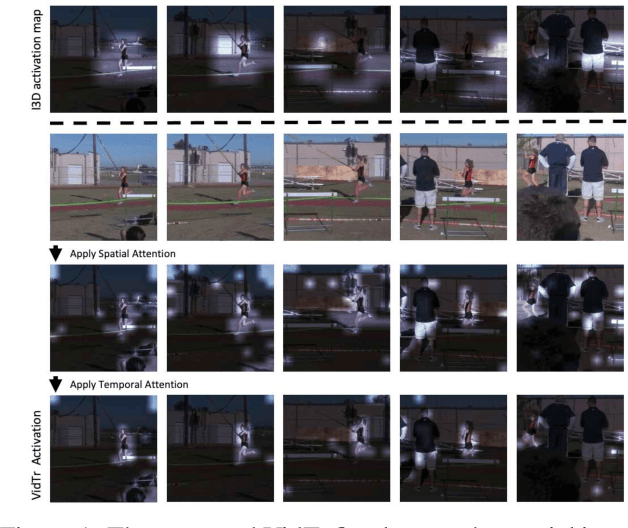
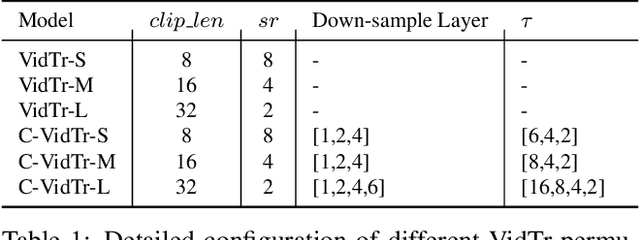
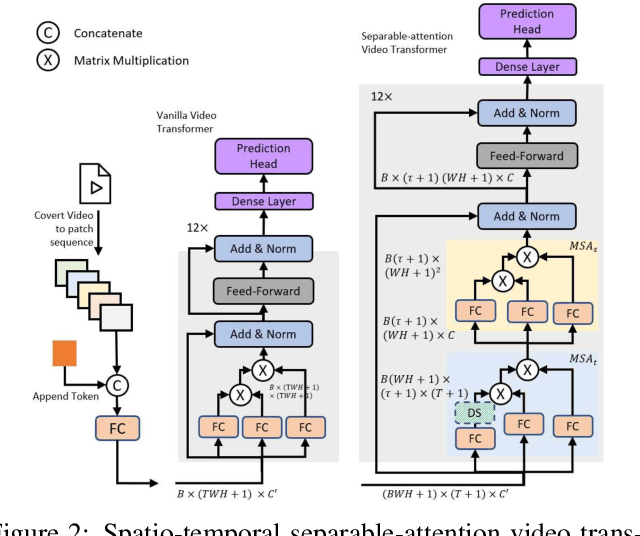
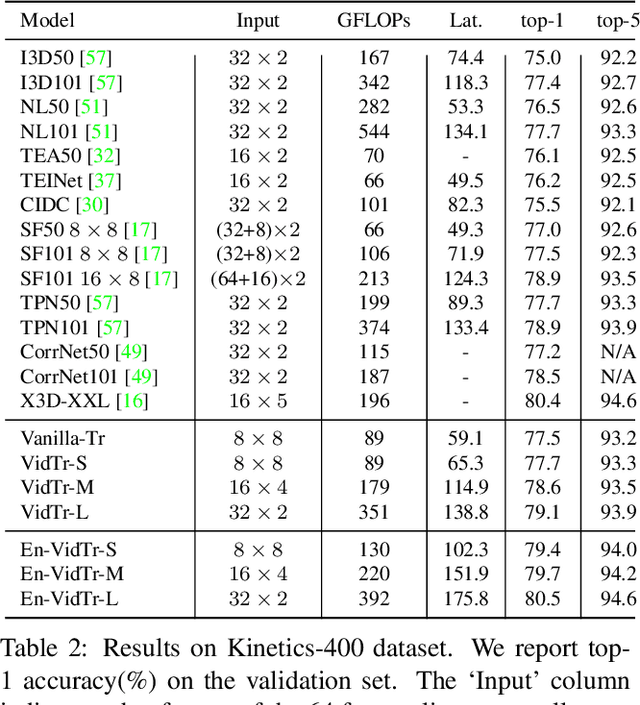
Abstract:We introduce Video Transformer (VidTr) with separable-attention for video classification. Comparing with commonly used 3D networks, VidTr is able to aggregate spatio-temporal information via stacked attentions and provide better performance with higher efficiency. We first introduce the vanilla video transformer and show that transformer module is able to perform spatio-temporal modeling from raw pixels, but with heavy memory usage. We then present VidTr which reduces the memory cost by 3.3$\times$ while keeping the same performance. To further compact the model, we propose the standard deviation based topK pooling attention, which reduces the computation by dropping non-informative features. VidTr achieves state-of-the-art performance on five commonly used dataset with lower computational requirement, showing both the efficiency and effectiveness of our design. Finally, error analysis and visualization show that VidTr is especially good at predicting actions that require long-term temporal reasoning. The code and pre-trained weights will be released.
Multi-Label Activity Recognition using Activity-specific Features
Sep 16, 2020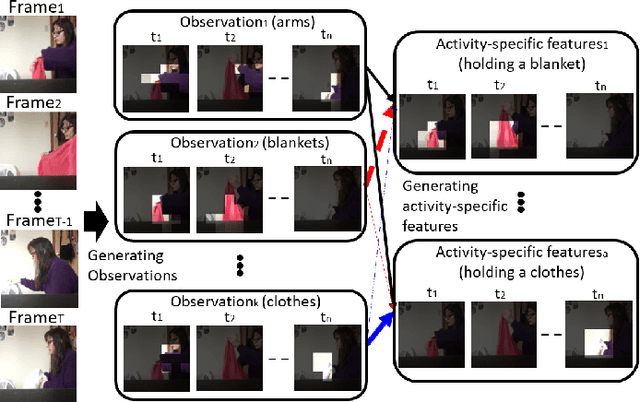



Abstract:We introduce an approach to multi-label activity recognition by extracting independent feature descriptors for each activity. Our approach first extracts a set of independent feature snippets, focused on different spatio-temporal regions of a video, that we call "observations". We then generate independent feature descriptors for each activity, that we call "activity-specific features" by combining these observations with attention, and further make action prediction based on these activity-specific features. This structure can be trained end-to-end and plugged into any existing network structures for video classification. Our method outperformed state-of-the-art approaches on three multi-label activity recognition datasets. We also evaluated the method and achieved state-of-the-art performance on two single-activity recognition datasets to show the generalizability of our approach. Furthermore, to better understand the activity-specific features that the system generates, we visualized these activity-specific features in the Charades dataset.
RHR-Net: A Residual Hourglass Recurrent Neural Network for Speech Enhancement
Apr 15, 2019
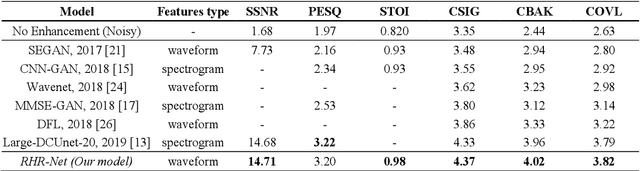


Abstract:Most current speech enhancement models use spectrogram features that require an expensive transformation and result in phase information loss. Previous work has overcome these issues by using convolutional networks to learn long-range temporal correlations across high-resolution waveforms. These models, however, are limited by memory-intensive dilated convolution and aliasing artifacts from upsampling. We introduce an end-to-end fully-recurrent hourglass-shaped neural network architecture with residual connections for waveform-based single-channel speech enhancement. Our model can efficiently capture long-range temporal dependencies by reducing the features resolution without information loss. Experimental results show that our model outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in six evaluation metrics.
Tri-axial Self-Attention for Concurrent Activity Recognition
Dec 06, 2018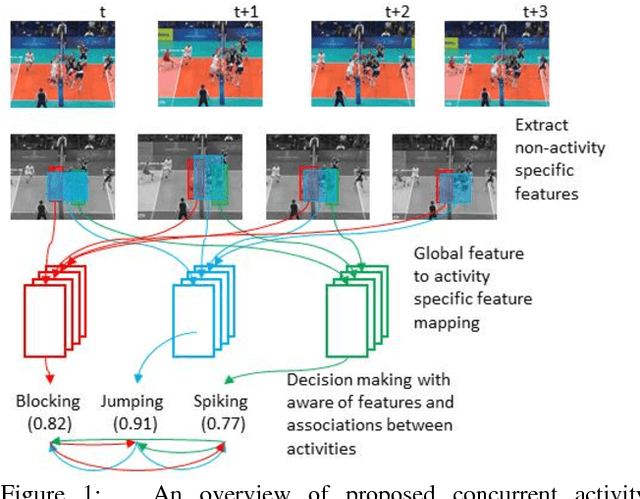
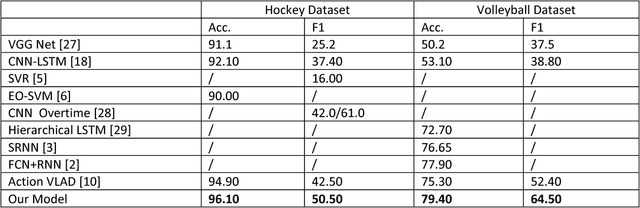
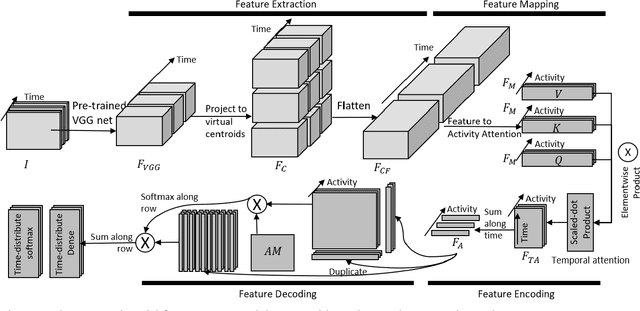
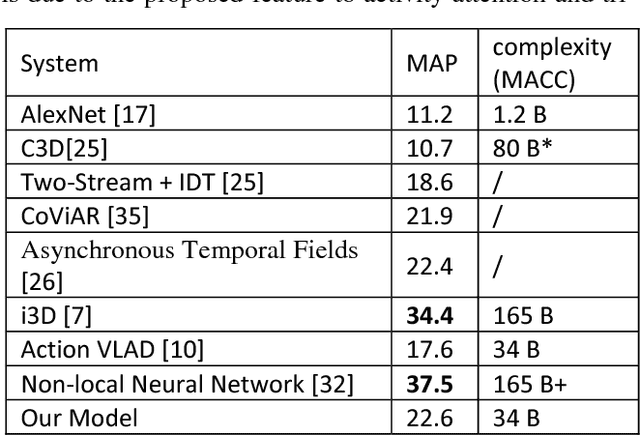
Abstract:We present a system for concurrent activity recognition. To extract features associated with different activities, we propose a feature-to-activity attention that maps the extracted global features to sub-features associated with individual activities. To model the temporal associations of individual activities, we propose a transformer-network encoder that models independent temporal associations for each activity. To make the concurrent activity prediction aware of the potential associations between activities, we propose self-attention with an association mask. Our system achieved state-of-the-art or comparable performance on three commonly used concurrent activity detection datasets. Our visualizations demonstrate that our system is able to locate the important spatial-temporal features for final decision making. We also showed that our system can be applied to general multilabel classification problems.
Multimodal Affective Analysis Using Hierarchical Attention Strategy with Word-Level Alignment
May 22, 2018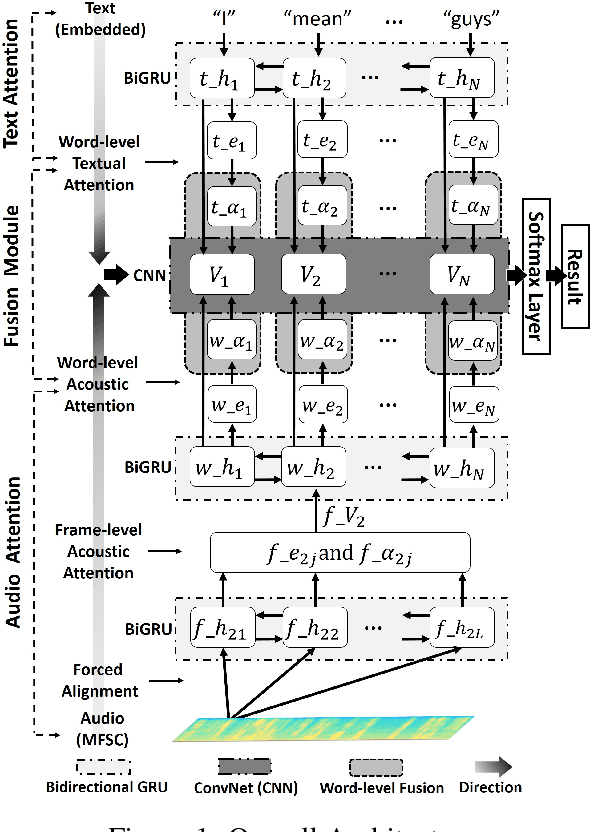
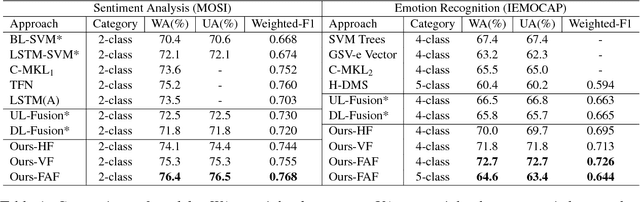
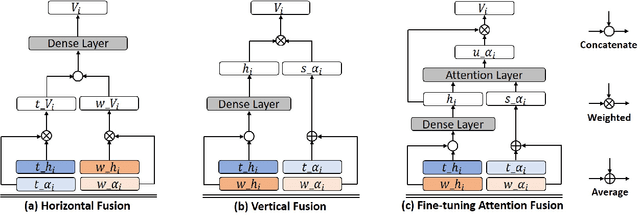
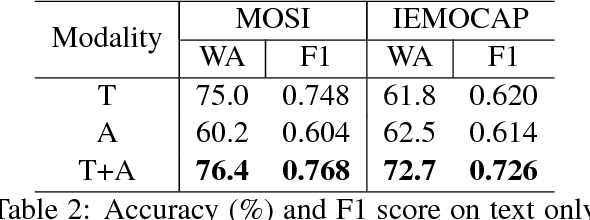
Abstract:Multimodal affective computing, learning to recognize and interpret human affects and subjective information from multiple data sources, is still challenging because: (i) it is hard to extract informative features to represent human affects from heterogeneous inputs; (ii) current fusion strategies only fuse different modalities at abstract level, ignoring time-dependent interactions between modalities. Addressing such issues, we introduce a hierarchical multimodal architecture with attention and word-level fusion to classify utter-ance-level sentiment and emotion from text and audio data. Our introduced model outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches on published datasets and we demonstrated that our model is able to visualize and interpret the synchronized attention over modalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge