Chenyang Gao
MaskMatch: Boosting Semi-Supervised Learning Through Mask Autoencoder-Driven Feature Learning
May 10, 2024



Abstract:Conventional methods in semi-supervised learning (SSL) often face challenges related to limited data utilization, mainly due to their reliance on threshold-based techniques for selecting high-confidence unlabeled data during training. Various efforts (e.g., FreeMatch) have been made to enhance data utilization by tweaking the thresholds, yet none have managed to use 100% of the available data. To overcome this limitation and improve SSL performance, we introduce \algo, a novel algorithm that fully utilizes unlabeled data to boost semi-supervised learning. \algo integrates a self-supervised learning strategy, i.e., Masked Autoencoder (MAE), that uses all available data to enforce the visual representation learning. This enables the SSL algorithm to leverage all available data, including samples typically filtered out by traditional methods. In addition, we propose a synthetic data training approach to further increase data utilization and improve generalization. These innovations lead \algo to achieve state-of-the-art results on challenging datasets. For instance, on CIFAR-100 with 2 labels per class, STL-10 with 4 labels per class, and Euro-SAT with 2 labels per class, \algo achieves low error rates of 18.71%, 9.47%, and 3.07%, respectively. The code will be made publicly available.
Post-Training Embedding Alignment for Decoupling Enrollment and Runtime Speaker Recognition Models
Jan 23, 2024

Abstract:Automated speaker identification (SID) is a crucial step for the personalization of a wide range of speech-enabled services. Typical SID systems use a symmetric enrollment-verification framework with a single model to derive embeddings both offline for voice profiles extracted from enrollment utterances, and online from runtime utterances. Due to the distinct circumstances of enrollment and runtime, such as different computation and latency constraints, several applications would benefit from an asymmetric enrollment-verification framework that uses different models for enrollment and runtime embedding generation. To support this asymmetric SID where each of the two models can be updated independently, we propose using a lightweight neural network to map the embeddings from the two independent models to a shared speaker embedding space. Our results show that this approach significantly outperforms cosine scoring in a shared speaker logit space for models that were trained with a contrastive loss on large datasets with many speaker identities. This proposed Neural Embedding Speaker Space Alignment (NESSA) combined with an asymmetric update of only one of the models delivers at least 60% of the performance gain achieved by updating both models in the standard symmetric SID approach.
Improving Label Assignments Learning by Dynamic Sample Dropout Combined with Layer-wise Optimization in Speech Separation
Nov 20, 2023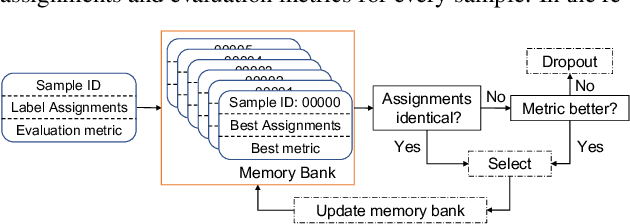
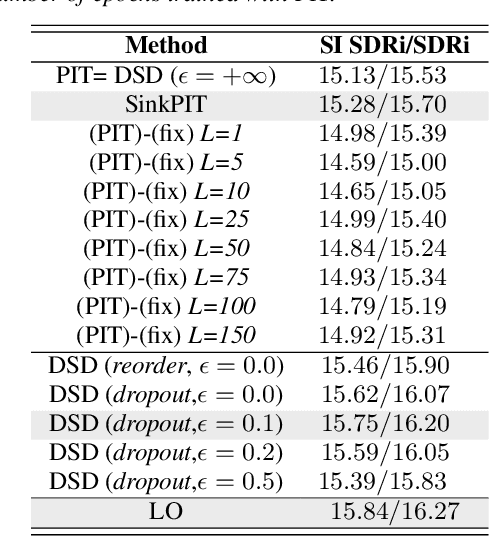
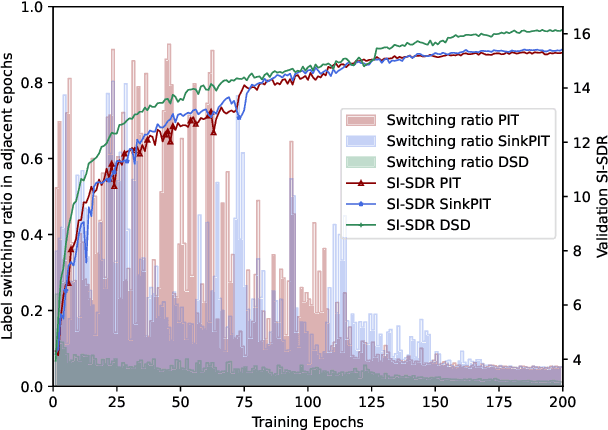
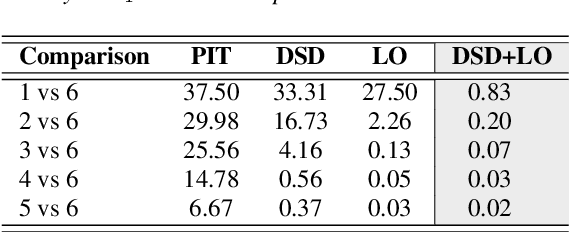
Abstract:In supervised speech separation, permutation invariant training (PIT) is widely used to handle label ambiguity by selecting the best permutation to update the model. Despite its success, previous studies showed that PIT is plagued by excessive label assignment switching in adjacent epochs, impeding the model to learn better label assignments. To address this issue, we propose a novel training strategy, dynamic sample dropout (DSD), which considers previous best label assignments and evaluation metrics to exclude the samples that may negatively impact the learned label assignments during training. Additionally, we include layer-wise optimization (LO) to improve the performance by solving layer-decoupling. Our experiments showed that combining DSD and LO outperforms the baseline and solves excessive label assignment switching and layer-decoupling issues. The proposed DSD and LO approach is easy to implement, requires no extra training sets or steps, and shows generality to various speech separation tasks.
Self-supervised speech representation learning for keyword-spotting with light-weight transformers
Mar 07, 2023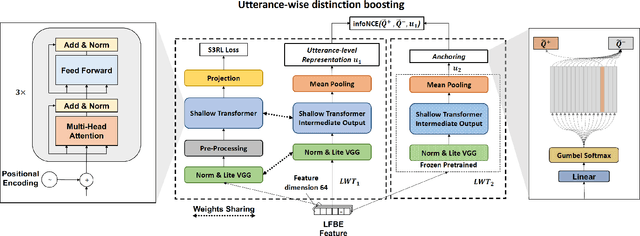
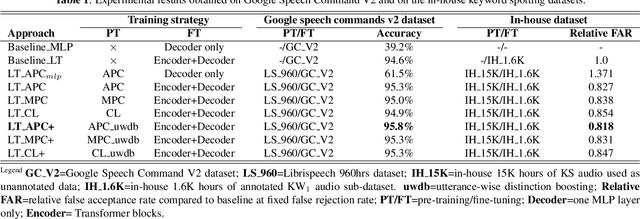
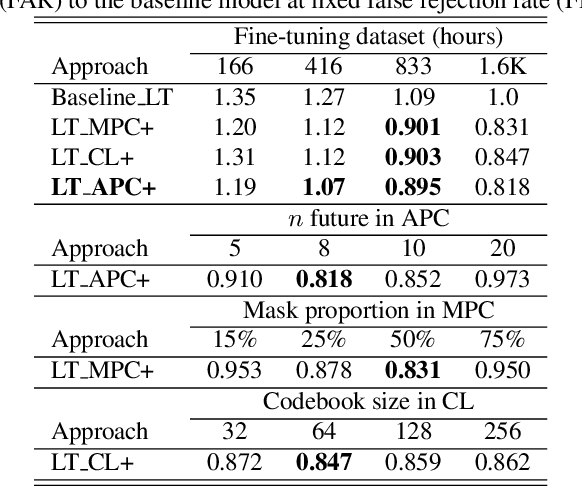
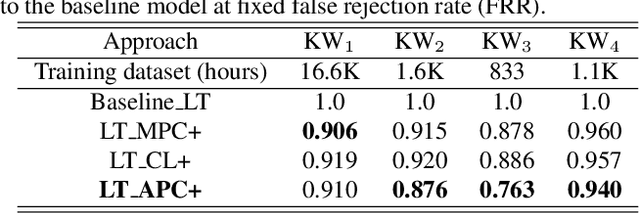
Abstract:Self-supervised speech representation learning (S3RL) is revolutionizing the way we leverage the ever-growing availability of data. While S3RL related studies typically use large models, we employ light-weight networks to comply with tight memory of compute-constrained devices. We demonstrate the effectiveness of S3RL on a keyword-spotting (KS) problem by using transformers with 330k parameters and propose a mechanism to enhance utterance-wise distinction, which proves crucial for improving performance on classification tasks. On the Google speech commands v2 dataset, the proposed method applied to the Auto-Regressive Predictive Coding S3RL led to a 1.2% accuracy improvement compared to training from scratch. On an in-house KS dataset with four different keywords, it provided 6% to 23.7% relative false accept improvement at fixed false reject rate. We argue this demonstrates the applicability of S3RL approaches to light-weight models for KS and confirms S3RL is a powerful alternative to traditional supervised learning for resource-constrained applications.
Time-Domain Mapping Based Single-Channel Speech Separation With Hierarchical Constraint Training
Oct 20, 2021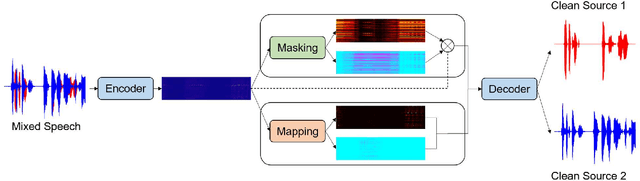
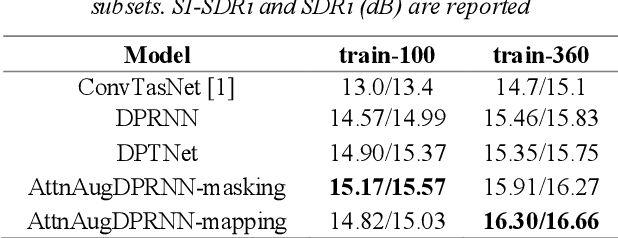
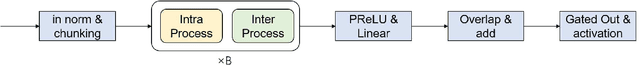
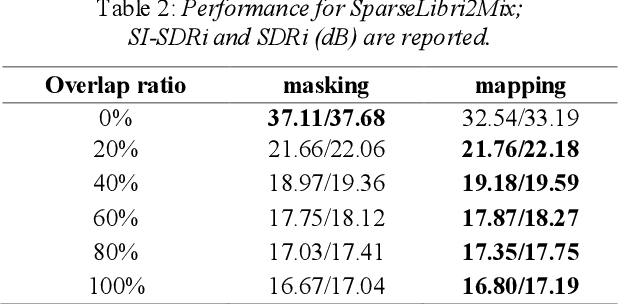
Abstract:Single-channel speech separation is required for multi-speaker speech recognition. Recent deep learning-based approaches focused on time-domain audio separation net (TasNet) because it has superior performance and lower latency compared to the conventional time-frequency-based (T-F-based) approaches. Most of these works rely on the masking-based method that estimates a linear mapping function (mask) for each speaker. However, the other commonly used method, the mapping-based method that is less sensitive to SNR variations, is inadequately studied in the time domain. We explore the potential of the mapping-based method by introducing attention augmented DPRNN (AttnAugDPRNN) which directly approximates the clean sources from the mixture for speech separation. Permutation Invariant Training (PIT) has been a paradigm to solve the label ambiguity problem for speech separation but usually leads to suboptimal performance. To solve this problem, we propose an efficient training strategy called Hierarchical Constraint Training (HCT) to regularize the training, which could effectively improve the model performance. When using PIT, our results showed that mapping-based AttnAugDPRNN outperformed masking-based AttnAugDPRNN when the training corpus is large. Mapping-based AttnAugDPRNN with HCT significantly improved the SI-SDR by 10.1% compared to the masking-based AttnAugDPRNN without HCT.
Contextual Non-Local Alignment over Full-Scale Representation for Text-Based Person Search
Jan 08, 2021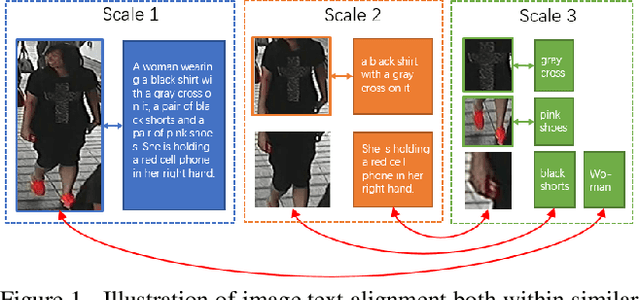
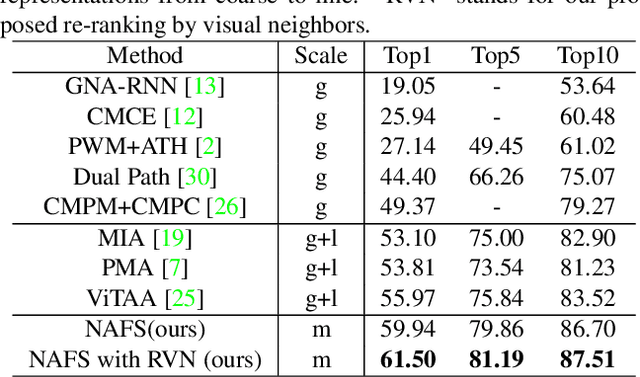
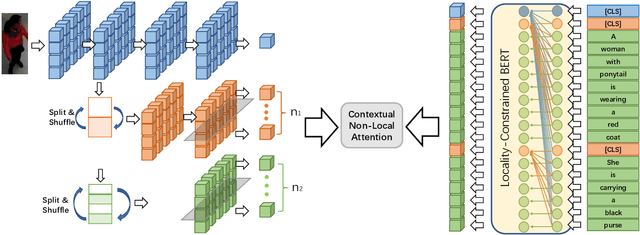
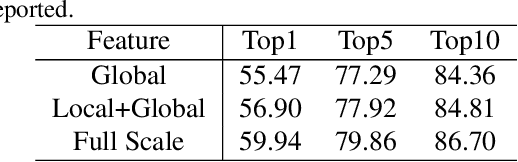
Abstract:Text-based person search aims at retrieving target person in an image gallery using a descriptive sentence of that person. It is very challenging since modal gap makes effectively extracting discriminative features more difficult. Moreover, the inter-class variance of both pedestrian images and descriptions is small. So comprehensive information is needed to align visual and textual clues across all scales. Most existing methods merely consider the local alignment between images and texts within a single scale (e.g. only global scale or only partial scale) then simply construct alignment at each scale separately. To address this problem, we propose a method that is able to adaptively align image and textual features across all scales, called NAFS (i.e.Non-local Alignment over Full-Scale representations). Firstly, a novel staircase network structure is proposed to extract full-scale image features with better locality. Secondly, a BERT with locality-constrained attention is proposed to obtain representations of descriptions at different scales. Then, instead of separately aligning features at each scale, a novel contextual non-local attention mechanism is applied to simultaneously discover latent alignments across all scales. The experimental results show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods by 5.53% in terms of top-1 and 5.35% in terms of top-5 on text-based person search dataset. The code is available at https://github.com/TencentYoutuResearch/PersonReID-NAFS
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge