Kangning Yang
OpenRR-1k: A Scalable Dataset for Real-World Reflection Removal
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Reflection removal technology plays a crucial role in photography and computer vision applications. However, existing techniques are hindered by the lack of high-quality in-the-wild datasets. In this paper, we propose a novel paradigm for collecting reflection datasets from a fresh perspective. Our approach is convenient, cost-effective, and scalable, while ensuring that the collected data pairs are of high quality, perfectly aligned, and represent natural and diverse scenarios. Following this paradigm, we collect a Real-world, Diverse, and Pixel-aligned dataset (named OpenRR-1k dataset), which contains 1,000 high-quality transmission-reflection image pairs collected in the wild. Through the analysis of several reflection removal methods and benchmark evaluation experiments on our dataset, we demonstrate its effectiveness in improving robustness in challenging real-world environments. Our dataset is available at https://github.com/caijie0620/OpenRR-1k.
OpenRR-5k: A Large-Scale Benchmark for Reflection Removal in the Wild
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Removing reflections is a crucial task in computer vision, with significant applications in photography and image enhancement. Nevertheless, existing methods are constrained by the absence of large-scale, high-quality, and diverse datasets. In this paper, we present a novel benchmark for Single Image Reflection Removal (SIRR). We have developed a large-scale dataset containing 5,300 high-quality, pixel-aligned image pairs, each consisting of a reflection image and its corresponding clean version. Specifically, the dataset is divided into two parts: 5,000 images are used for training, and 300 images are used for validation. Additionally, we have included 100 real-world testing images without ground truth (GT) to further evaluate the practical performance of reflection removal methods. All image pairs are precisely aligned at the pixel level to guarantee accurate supervision. The dataset encompasses a broad spectrum of real-world scenarios, featuring various lighting conditions, object types, and reflection patterns, and is segmented into training, validation, and test sets to facilitate thorough evaluation. To validate the usefulness of our dataset, we train a U-Net-based model and evaluate it using five widely-used metrics, including PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS, DISTS, and NIQE. We will release both the dataset and the code on https://github.com/caijie0620/OpenRR-5k to facilitate future research in this field.
Degradation-Aware Image Enhancement via Vision-Language Classification
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Image degradation is a prevalent issue in various real-world applications, affecting visual quality and downstream processing tasks. In this study, we propose a novel framework that employs a Vision-Language Model (VLM) to automatically classify degraded images into predefined categories. The VLM categorizes an input image into one of four degradation types: (A) super-resolution degradation (including noise, blur, and JPEG compression), (B) reflection artifacts, (C) motion blur, or (D) no visible degradation (high-quality image). Once classified, images assigned to categories A, B, or C undergo targeted restoration using dedicated models tailored for each specific degradation type. The final output is a restored image with improved visual quality. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in accurately classifying image degradations and enhancing image quality through specialized restoration models. Our method presents a scalable and automated solution for real-world image enhancement tasks, leveraging the capabilities of VLMs in conjunction with state-of-the-art restoration techniques.
F2T2-HiT: A U-Shaped FFT Transformer and Hierarchical Transformer for Reflection Removal
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Single Image Reflection Removal (SIRR) technique plays a crucial role in image processing by eliminating unwanted reflections from the background. These reflections, often caused by photographs taken through glass surfaces, can significantly degrade image quality. SIRR remains a challenging problem due to the complex and varied reflections encountered in real-world scenarios. These reflections vary significantly in intensity, shapes, light sources, sizes, and coverage areas across the image, posing challenges for most existing methods to effectively handle all cases. To address these challenges, this paper introduces a U-shaped Fast Fourier Transform Transformer and Hierarchical Transformer (F2T2-HiT) architecture, an innovative Transformer-based design for SIRR. Our approach uniquely combines Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) Transformer blocks and Hierarchical Transformer blocks within a UNet framework. The FFT Transformer blocks leverage the global frequency domain information to effectively capture and separate reflection patterns, while the Hierarchical Transformer blocks utilize multi-scale feature extraction to handle reflections of varying sizes and complexities. Extensive experiments conducted on three publicly available testing datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art performance, validating the effectiveness of our approach.
Survey on Single-Image Reflection Removal using Deep Learning Techniques
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:The phenomenon of reflection is quite common in digital images, posing significant challenges for various applications such as computer vision, photography, and image processing. Traditional methods for reflection removal often struggle to achieve clean results while maintaining high fidelity and robustness, particularly in real-world scenarios. Over the past few decades, numerous deep learning-based approaches for reflection removal have emerged, yielding impressive results. In this survey, we conduct a comprehensive review of the current literature by focusing on key venues such as ICCV, ECCV, CVPR, NeurIPS, etc., as these conferences and journals have been central to advances in the field. Our review follows a structured paper selection process, and we critically assess both single-stage and two-stage deep learning methods for reflection removal. The contribution of this survey is three-fold: first, we provide a comprehensive summary of the most recent work on single-image reflection removal; second, we outline task hypotheses, current deep learning techniques, publicly available datasets, and relevant evaluation metrics; and third, we identify key challenges and opportunities in deep learning-based reflection removal, highlighting the potential of this rapidly evolving research area.
Multimodal Affective Analysis Using Hierarchical Attention Strategy with Word-Level Alignment
May 22, 2018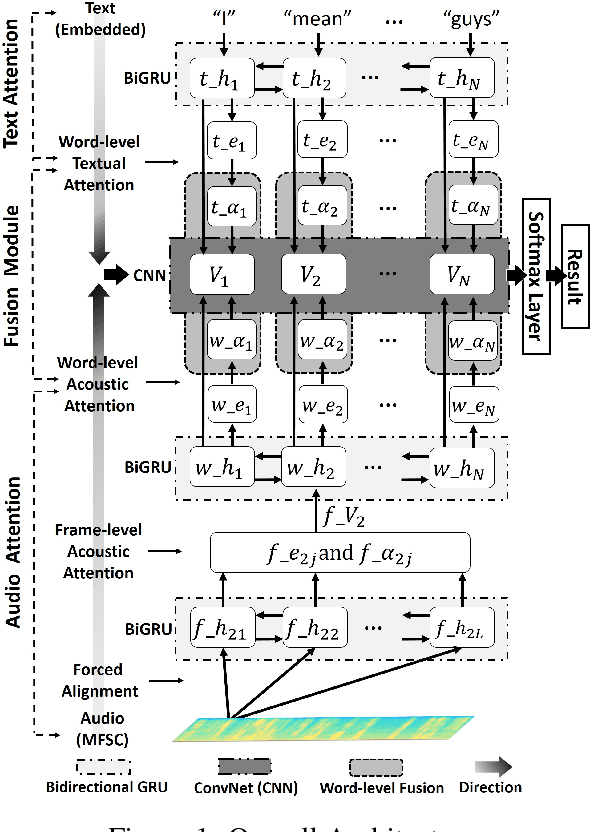
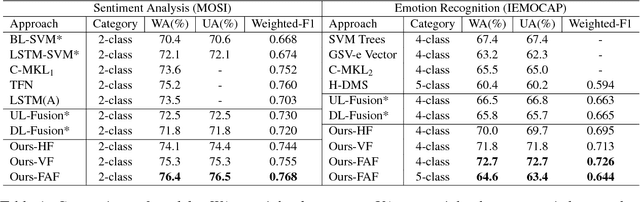
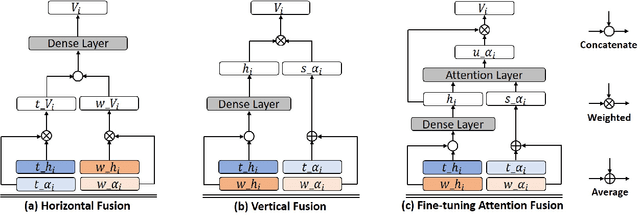
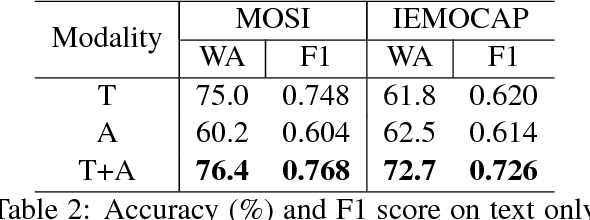
Abstract:Multimodal affective computing, learning to recognize and interpret human affects and subjective information from multiple data sources, is still challenging because: (i) it is hard to extract informative features to represent human affects from heterogeneous inputs; (ii) current fusion strategies only fuse different modalities at abstract level, ignoring time-dependent interactions between modalities. Addressing such issues, we introduce a hierarchical multimodal architecture with attention and word-level fusion to classify utter-ance-level sentiment and emotion from text and audio data. Our introduced model outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches on published datasets and we demonstrated that our model is able to visualize and interpret the synchronized attention over modalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge