Inwoo Hwang
Locality-aware Concept Bottleneck Model
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Concept bottleneck models (CBMs) are inherently interpretable models that make predictions based on human-understandable visual cues, referred to as concepts. As obtaining dense concept annotations with human labeling is demanding and costly, recent approaches utilize foundation models to determine the concepts existing in the images. However, such label-free CBMs often fail to localize concepts in relevant regions, attending to visually unrelated regions when predicting concept presence. To this end, we propose a framework, coined Locality-aware Concept Bottleneck Model (LCBM), which utilizes rich information from foundation models and adopts prototype learning to ensure accurate spatial localization of the concepts. Specifically, we assign one prototype to each concept, promoted to represent a prototypical image feature of that concept. These prototypes are learned by encouraging them to encode similar local regions, leveraging foundation models to assure the relevance of each prototype to its associated concept. Then we use the prototypes to facilitate the learning process of identifying the proper local region from which each concept should be predicted. Experimental results demonstrate that LCBM effectively identifies present concepts in the images and exhibits improved localization while maintaining comparable classification performance.
Towards Spatially Consistent Image Generation: On Incorporating Intrinsic Scene Properties into Diffusion Models
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Image generation models trained on large datasets can synthesize high-quality images but often produce spatially inconsistent and distorted images due to limited information about the underlying structures and spatial layouts. In this work, we leverage intrinsic scene properties (e.g., depth, segmentation maps) that provide rich information about the underlying scene, unlike prior approaches that solely rely on image-text pairs or use intrinsics as conditional inputs. Our approach aims to co-generate both images and their corresponding intrinsics, enabling the model to implicitly capture the underlying scene structure and generate more spatially consistent and realistic images. Specifically, we first extract rich intrinsic scene properties from a large image dataset with pre-trained estimators, eliminating the need for additional scene information or explicit 3D representations. We then aggregate various intrinsic scene properties into a single latent variable using an autoencoder. Building upon pre-trained large-scale Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs), our method simultaneously denoises the image and intrinsic domains by carefully sharing mutual information so that the image and intrinsic reflect each other without degrading image quality. Experimental results demonstrate that our method corrects spatial inconsistencies and produces a more natural layout of scenes while maintaining the fidelity and textual alignment of the base model (e.g., Stable Diffusion).
PEER pressure: Model-to-Model Regularization for Single Source Domain Generalization
May 19, 2025Abstract:Data augmentation is a popular tool for single source domain generalization, which expands the source domain by generating simulated ones, improving generalization on unseen target domains. In this work, we show that the performance of such augmentation-based methods in the target domains universally fluctuates during training, posing challenges in model selection under realistic scenarios. We argue that the fluctuation stems from the inability of the model to accumulate the knowledge learned from diverse augmentations, exacerbating feature distortion during training. Based on this observation, we propose a novel generalization method, coined Parameter-Space Ensemble with Entropy Regularization (PEER), that uses a proxy model to learn the augmented data on behalf of the main model. The main model is updated by averaging its parameters with the proxy model, progressively accumulating knowledge over the training steps. Maximizing the mutual information between the output representations of the two models guides the learning process of the proxy model, mitigating feature distortion during training. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of PEER in reducing the OOD performance fluctuation and enhancing generalization across various datasets, including PACS, Digits, Office-Home, and VLCS. Notably, our method with simple random augmentation achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing prior approaches on sDG that utilize complex data augmentation strategies.
SceneMI: Motion In-betweening for Modeling Human-Scene Interactions
Mar 20, 2025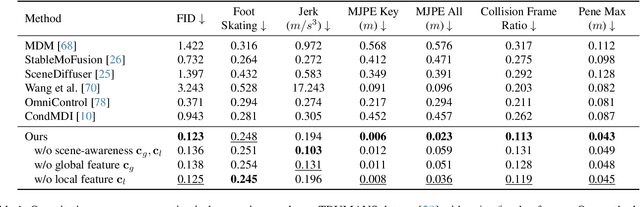
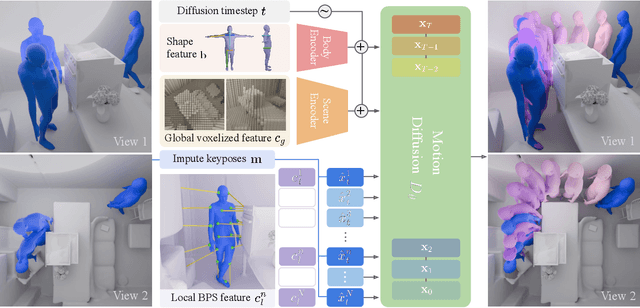
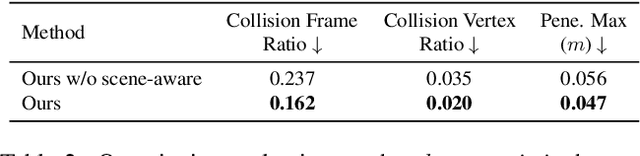
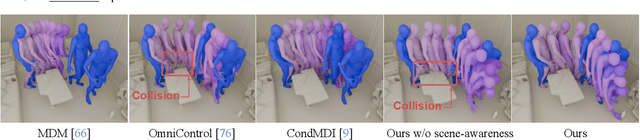
Abstract:Modeling human-scene interactions (HSI) is essential for understanding and simulating everyday human behaviors. Recent approaches utilizing generative modeling have made progress in this domain; however, they are limited in controllability and flexibility for real-world applications. To address these challenges, we propose reformulating the HSI modeling problem as Scene-aware Motion In-betweening -- a more tractable and practical task. We introduce SceneMI, a framework that supports several practical applications, including keyframe-guided character animation in 3D scenes and enhancing the motion quality of imperfect HSI data. SceneMI employs dual scene descriptors to comprehensively encode global and local scene context. Furthermore, our framework leverages the inherent denoising nature of diffusion models to generalize on noisy keyframes. Experimental results demonstrate SceneMI's effectiveness in scene-aware keyframe in-betweening and generalization to the real-world GIMO dataset, where motions and scenes are acquired by noisy IMU sensors and smartphones. We further showcase SceneMI's applicability in HSI reconstruction from monocular videos.
Motion Synthesis with Sparse and Flexible Keyjoint Control
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Creating expressive character animations is labor-intensive, requiring intricate manual adjustment of animators across space and time. Previous works on controllable motion generation often rely on a predefined set of dense spatio-temporal specifications (e.g., dense pelvis trajectories with exact per-frame timing), limiting practicality for animators. To process high-level intent and intuitive control in diverse scenarios, we propose a practical controllable motions synthesis framework that respects sparse and flexible keyjoint signals. Our approach employs a decomposed diffusion-based motion synthesis framework that first synthesizes keyjoint movements from sparse input control signals and then synthesizes full-body motion based on the completed keyjoint trajectories. The low-dimensional keyjoint movements can easily adapt to various control signal types, such as end-effector position for diverse goal-driven motion synthesis, or incorporate functional constraints on a subset of keyjoints. Additionally, we introduce a time-agnostic control formulation, eliminating the need for frame-specific timing annotations and enhancing control flexibility. Then, the shared second stage can synthesize a natural whole-body motion that precisely satisfies the task requirement from dense keyjoint movements. We demonstrate the effectiveness of sparse and flexible keyjoint control through comprehensive experiments on diverse datasets and scenarios.
Less is More: Improving Motion Diffusion Models with Sparse Keyframes
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in motion diffusion models have led to remarkable progress in diverse motion generation tasks, including text-to-motion synthesis. However, existing approaches represent motions as dense frame sequences, requiring the model to process redundant or less informative frames. The processing of dense animation frames imposes significant training complexity, especially when learning intricate distributions of large motion datasets even with modern neural architectures. This severely limits the performance of generative motion models for downstream tasks. Inspired by professional animators who mainly focus on sparse keyframes, we propose a novel diffusion framework explicitly designed around sparse and geometrically meaningful keyframes. Our method reduces computation by masking non-keyframes and efficiently interpolating missing frames. We dynamically refine the keyframe mask during inference to prioritize informative frames in later diffusion steps. Extensive experiments show that our approach consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in text alignment and motion realism, while also effectively maintaining high performance at significantly fewer diffusion steps. We further validate the robustness of our framework by using it as a generative prior and adapting it to different downstream tasks. Source code and pre-trained models will be released upon acceptance.
A Survey on Human Interaction Motion Generation
Mar 17, 2025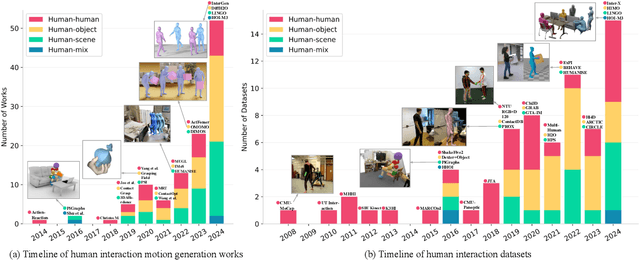
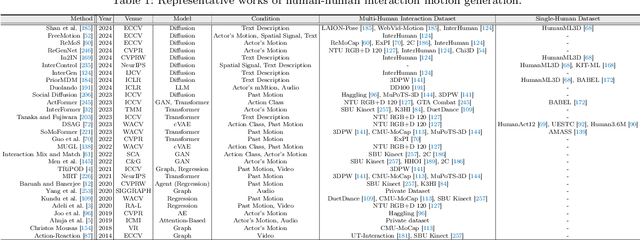

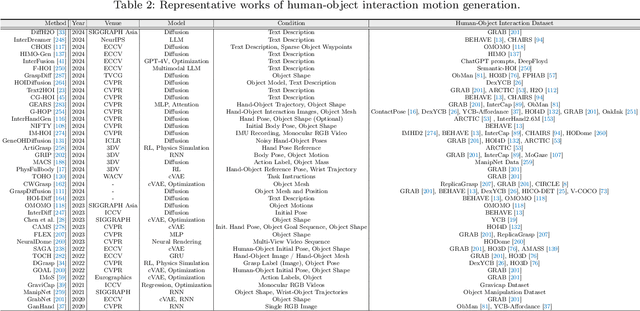
Abstract:Humans inhabit a world defined by interactions -- with other humans, objects, and environments. These interactive movements not only convey our relationships with our surroundings but also demonstrate how we perceive and communicate with the real world. Therefore, replicating these interaction behaviors in digital systems has emerged as an important topic for applications in robotics, virtual reality, and animation. While recent advances in deep generative models and new datasets have accelerated progress in this field, significant challenges remain in modeling the intricate human dynamics and their interactions with entities in the external world. In this survey, we present, for the first time, a comprehensive overview of the literature in human interaction motion generation. We begin by establishing foundational concepts essential for understanding the research background. We then systematically review existing solutions and datasets across three primary interaction tasks -- human-human, human-object, and human-scene interactions -- followed by evaluation metrics. Finally, we discuss open research directions and future opportunities.
Versatile Physics-based Character Control with Hybrid Latent Representation
Mar 17, 2025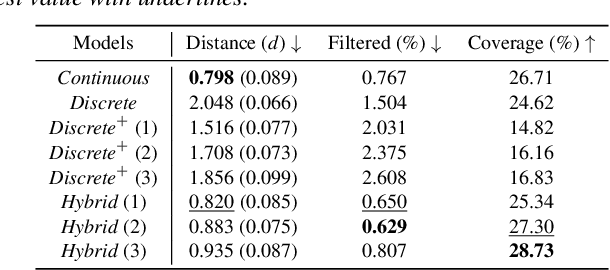
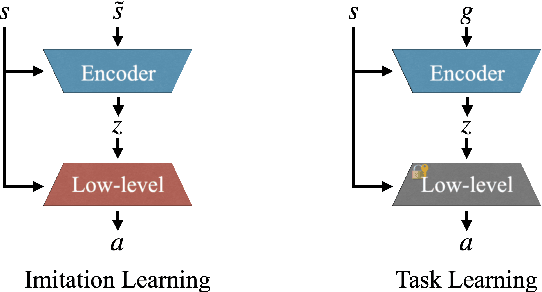

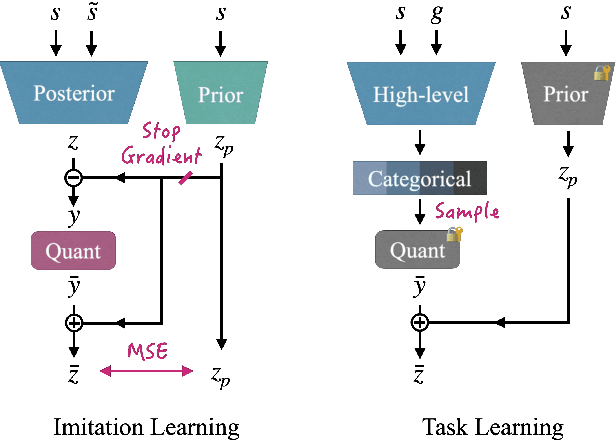
Abstract:We present a versatile latent representation that enables physically simulated character to efficiently utilize motion priors. To build a powerful motion embedding that is shared across multiple tasks, the physics controller should employ rich latent space that is easily explored and capable of generating high-quality motion. We propose integrating continuous and discrete latent representations to build a versatile motion prior that can be adapted to a wide range of challenging control tasks. Specifically, we build a discrete latent model to capture distinctive posterior distribution without collapse, and simultaneously augment the sampled vector with the continuous residuals to generate high-quality, smooth motion without jittering. We further incorporate Residual Vector Quantization, which not only maximizes the capacity of the discrete motion prior, but also efficiently abstracts the action space during the task learning phase. We demonstrate that our agent can produce diverse yet smooth motions simply by traversing the learned motion prior through unconditional motion generation. Furthermore, our model robustly satisfies sparse goal conditions with highly expressive natural motions, including head-mounted device tracking and motion in-betweening at irregular intervals, which could not be achieved with existing latent representations.
Fine-Grained Causal Dynamics Learning with Quantization for Improving Robustness in Reinforcement Learning
Jun 05, 2024Abstract:Causal dynamics learning has recently emerged as a promising approach to enhancing robustness in reinforcement learning (RL). Typically, the goal is to build a dynamics model that makes predictions based on the causal relationships among the entities. Despite the fact that causal connections often manifest only under certain contexts, existing approaches overlook such fine-grained relationships and lack a detailed understanding of the dynamics. In this work, we propose a novel dynamics model that infers fine-grained causal structures and employs them for prediction, leading to improved robustness in RL. The key idea is to jointly learn the dynamics model with a discrete latent variable that quantizes the state-action space into subgroups. This leads to recognizing meaningful context that displays sparse dependencies, where causal structures are learned for each subgroup throughout the training. Experimental results demonstrate the robustness of our method to unseen states and locally spurious correlations in downstream tasks where fine-grained causal reasoning is crucial. We further illustrate the effectiveness of our subgroup-based approach with quantization in discovering fine-grained causal relationships compared to prior methods.
Efficient Monte Carlo Tree Search via On-the-Fly State-Conditioned Action Abstraction
Jun 02, 2024Abstract:Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) has showcased its efficacy across a broad spectrum of decision-making problems. However, its performance often degrades under vast combinatorial action space, especially where an action is composed of multiple sub-actions. In this work, we propose an action abstraction based on the compositional structure between a state and sub-actions for improving the efficiency of MCTS under a factored action space. Our method learns a latent dynamics model with an auxiliary network that captures sub-actions relevant to the transition on the current state, which we call state-conditioned action abstraction. Notably, it infers such compositional relationships from high-dimensional observations without the known environment model. During the tree traversal, our method constructs the state-conditioned action abstraction for each node on-the-fly, reducing the search space by discarding the exploration of redundant sub-actions. Experimental results demonstrate the superior sample efficiency of our method compared to vanilla MuZero, which suffers from expansive action space.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge