Huijie Zhang
AlphaFlow: Understanding and Improving MeanFlow Models
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:MeanFlow has recently emerged as a powerful framework for few-step generative modeling trained from scratch, but its success is not yet fully understood. In this work, we show that the MeanFlow objective naturally decomposes into two parts: trajectory flow matching and trajectory consistency. Through gradient analysis, we find that these terms are strongly negatively correlated, causing optimization conflict and slow convergence. Motivated by these insights, we introduce $\alpha$-Flow, a broad family of objectives that unifies trajectory flow matching, Shortcut Model, and MeanFlow under one formulation. By adopting a curriculum strategy that smoothly anneals from trajectory flow matching to MeanFlow, $\alpha$-Flow disentangles the conflicting objectives, and achieves better convergence. When trained from scratch on class-conditional ImageNet-1K 256x256 with vanilla DiT backbones, $\alpha$-Flow consistently outperforms MeanFlow across scales and settings. Our largest $\alpha$-Flow-XL/2+ model achieves new state-of-the-art results using vanilla DiT backbones, with FID scores of 2.58 (1-NFE) and 2.15 (2-NFE).
Understanding Generalization in Diffusion Models via Probability Flow Distance
May 26, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have emerged as a powerful class of generative models, capable of producing high-quality samples that generalize beyond the training data. However, evaluating this generalization remains challenging: theoretical metrics are often impractical for high-dimensional data, while no practical metrics rigorously measure generalization. In this work, we bridge this gap by introducing probability flow distance ($\texttt{PFD}$), a theoretically grounded and computationally efficient metric to measure distributional generalization. Specifically, $\texttt{PFD}$ quantifies the distance between distributions by comparing their noise-to-data mappings induced by the probability flow ODE. Moreover, by using $\texttt{PFD}$ under a teacher-student evaluation protocol, we empirically uncover several key generalization behaviors in diffusion models, including: (1) scaling behavior from memorization to generalization, (2) early learning and double descent training dynamics, and (3) bias-variance decomposition. Beyond these insights, our work lays a foundation for future empirical and theoretical studies on generalization in diffusion models.
Shallow Diffuse: Robust and Invisible Watermarking through Low-Dimensional Subspaces in Diffusion Models
Oct 28, 2024Abstract:The widespread use of AI-generated content from diffusion models has raised significant concerns regarding misinformation and copyright infringement. Watermarking is a crucial technique for identifying these AI-generated images and preventing their misuse. In this paper, we introduce Shallow Diffuse, a new watermarking technique that embeds robust and invisible watermarks into diffusion model outputs. Unlike existing approaches that integrate watermarking throughout the entire diffusion sampling process, Shallow Diffuse decouples these steps by leveraging the presence of a low-dimensional subspace in the image generation process. This method ensures that a substantial portion of the watermark lies in the null space of this subspace, effectively separating it from the image generation process. Our theoretical and empirical analyses show that this decoupling strategy greatly enhances the consistency of data generation and the detectability of the watermark. Extensive experiments further validate that our Shallow Diffuse outperforms existing watermarking methods in terms of robustness and consistency. The codes will be released at https://github.com/liwd190019/Shallow-Diffuse.
Exploring Low-Dimensional Subspaces in Diffusion Models for Controllable Image Editing
Sep 04, 2024
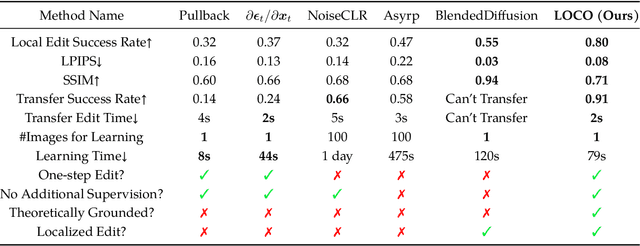
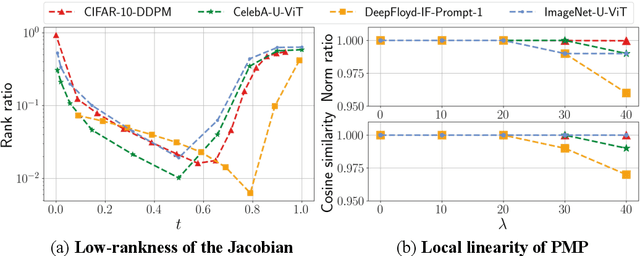
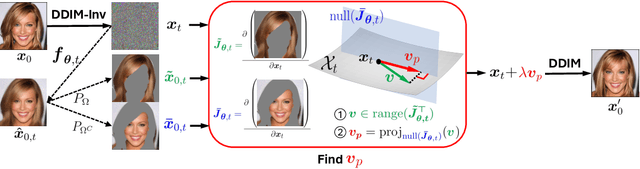
Abstract:Recently, diffusion models have emerged as a powerful class of generative models. Despite their success, there is still limited understanding of their semantic spaces. This makes it challenging to achieve precise and disentangled image generation without additional training, especially in an unsupervised way. In this work, we improve the understanding of their semantic spaces from intriguing observations: among a certain range of noise levels, (1) the learned posterior mean predictor (PMP) in the diffusion model is locally linear, and (2) the singular vectors of its Jacobian lie in low-dimensional semantic subspaces. We provide a solid theoretical basis to justify the linearity and low-rankness in the PMP. These insights allow us to propose an unsupervised, single-step, training-free LOw-rank COntrollable image editing (LOCO Edit) method for precise local editing in diffusion models. LOCO Edit identified editing directions with nice properties: homogeneity, transferability, composability, and linearity. These properties of LOCO Edit benefit greatly from the low-dimensional semantic subspace. Our method can further be extended to unsupervised or text-supervised editing in various text-to-image diffusion models (T-LOCO Edit). Finally, extensive empirical experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of LOCO Edit. The codes will be released at https://github.com/ChicyChen/LOCO-Edit.
Diffusion Models Learn Low-Dimensional Distributions via Subspace Clustering
Sep 04, 2024



Abstract:Recent empirical studies have demonstrated that diffusion models can effectively learn the image distribution and generate new samples. Remarkably, these models can achieve this even with a small number of training samples despite a large image dimension, circumventing the curse of dimensionality. In this work, we provide theoretical insights into this phenomenon by leveraging key empirical observations: (i) the low intrinsic dimensionality of image data, (ii) a union of manifold structure of image data, and (iii) the low-rank property of the denoising autoencoder in trained diffusion models. These observations motivate us to assume the underlying data distribution of image data as a mixture of low-rank Gaussians and to parameterize the denoising autoencoder as a low-rank model according to the score function of the assumed distribution. With these setups, we rigorously show that optimizing the training loss of diffusion models is equivalent to solving the canonical subspace clustering problem over the training samples. Based on this equivalence, we further show that the minimal number of samples required to learn the underlying distribution scales linearly with the intrinsic dimensions under the above data and model assumptions. This insight sheds light on why diffusion models can break the curse of dimensionality and exhibit the phase transition in learning distributions. Moreover, we empirically establish a correspondence between the subspaces and the semantic representations of image data, facilitating image editing. We validate these results with corroborated experimental results on both simulated distributions and image datasets.
Improving Efficiency of Diffusion Models via Multi-Stage Framework and Tailored Multi-Decoder Architectures
Dec 14, 2023



Abstract:Diffusion models, emerging as powerful deep generative tools, excel in various applications. They operate through a two-steps process: introducing noise into training samples and then employing a model to convert random noise into new samples (e.g., images). However, their remarkable generative performance is hindered by slow training and sampling. This is due to the necessity of tracking extensive forward and reverse diffusion trajectories, and employing a large model with numerous parameters across multiple timesteps (i.e., noise levels). To tackle these challenges, we present a multi-stage framework inspired by our empirical findings. These observations indicate the advantages of employing distinct parameters tailored to each timestep while retaining universal parameters shared across all time steps. Our approach involves segmenting the time interval into multiple stages where we employ custom multi-decoder U-net architecture that blends time-dependent models with a universally shared encoder. Our framework enables the efficient distribution of computational resources and mitigates inter-stage interference, which substantially improves training efficiency. Extensive numerical experiments affirm the effectiveness of our framework, showcasing significant training and sampling efficiency enhancements on three state-of-the-art diffusion models, including large-scale latent diffusion models. Furthermore, our ablation studies illustrate the impact of two important components in our framework: (i) a novel timestep clustering algorithm for stage division, and (ii) an innovative multi-decoder U-net architecture, seamlessly integrating universal and customized hyperparameters.
The Emergence of Reproducibility and Consistency in Diffusion Models
Oct 08, 2023



Abstract:Recently, diffusion models have emerged as powerful deep generative models, showcasing cutting-edge performance across various applications such as image generation, solving inverse problems, and text-to-image synthesis. These models generate new data (e.g., images) by transforming random noise inputs through a reverse diffusion process. In this work, we uncover a distinct and prevalent phenomenon within diffusion models in contrast to most other generative models, which we refer to as ``consistent model reproducibility''. To elaborate, our extensive experiments have consistently shown that when starting with the same initial noise input and sampling with a deterministic solver, diffusion models tend to produce nearly identical output content. This consistency holds true regardless of the choices of model architectures and training procedures. Additionally, our research has unveiled that this exceptional model reproducibility manifests in two distinct training regimes: (i) ``memorization regime,'' characterized by a significantly overparameterized model which attains reproducibility mainly by memorizing the training data; (ii) ``generalization regime,'' in which the model is trained on an extensive dataset, and its reproducibility emerges with the model's generalization capabilities. Our analysis provides theoretical justification for the model reproducibility in ``memorization regime''. Moreover, our research reveals that this valuable property generalizes to many variants of diffusion models, including conditional diffusion models, diffusion models for solving inverse problems, and fine-tuned diffusion models. A deeper understanding of this phenomenon has the potential to yield more interpretable and controllable data generative processes based on diffusion models.
TransNet: Transparent Object Manipulation Through Category-Level Pose Estimation
Jul 23, 2023



Abstract:Transparent objects present multiple distinct challenges to visual perception systems. First, their lack of distinguishing visual features makes transparent objects harder to detect and localize than opaque objects. Even humans find certain transparent surfaces with little specular reflection or refraction, like glass doors, difficult to perceive. A second challenge is that depth sensors typically used for opaque object perception cannot obtain accurate depth measurements on transparent surfaces due to their unique reflective properties. Stemming from these challenges, we observe that transparent object instances within the same category, such as cups, look more similar to each other than to ordinary opaque objects of that same category. Given this observation, the present paper explores the possibility of category-level transparent object pose estimation rather than instance-level pose estimation. We propose \textit{\textbf{TransNet}}, a two-stage pipeline that estimates category-level transparent object pose using localized depth completion and surface normal estimation. TransNet is evaluated in terms of pose estimation accuracy on a large-scale transparent object dataset and compared to a state-of-the-art category-level pose estimation approach. Results from this comparison demonstrate that TransNet achieves improved pose estimation accuracy on transparent objects. Moreover, we use TransNet to build an autonomous transparent object manipulation system for robotic pick-and-place and pouring tasks.
TransNet: Category-Level Transparent Object Pose Estimation
Aug 22, 2022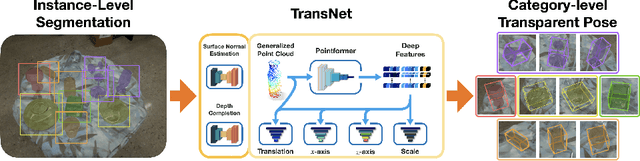

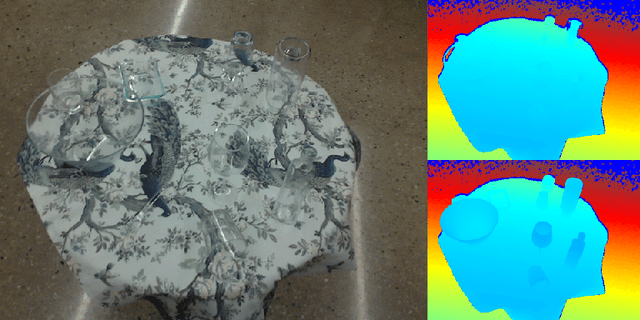
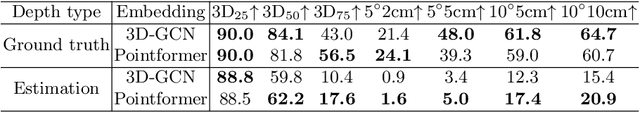
Abstract:Transparent objects present multiple distinct challenges to visual perception systems. First, their lack of distinguishing visual features makes transparent objects harder to detect and localize than opaque objects. Even humans find certain transparent surfaces with little specular reflection or refraction, e.g. glass doors, difficult to perceive. A second challenge is that common depth sensors typically used for opaque object perception cannot obtain accurate depth measurements on transparent objects due to their unique reflective properties. Stemming from these challenges, we observe that transparent object instances within the same category (e.g. cups) look more similar to each other than to ordinary opaque objects of that same category. Given this observation, the present paper sets out to explore the possibility of category-level transparent object pose estimation rather than instance-level pose estimation. We propose TransNet, a two-stage pipeline that learns to estimate category-level transparent object pose using localized depth completion and surface normal estimation. TransNet is evaluated in terms of pose estimation accuracy on a recent, large-scale transparent object dataset and compared to a state-of-the-art category-level pose estimation approach. Results from this comparison demonstrate that TransNet achieves improved pose estimation accuracy on transparent objects and key findings from the included ablation studies suggest future directions for performance improvements.
ClearPose: Large-scale Transparent Object Dataset and Benchmark
Mar 08, 2022
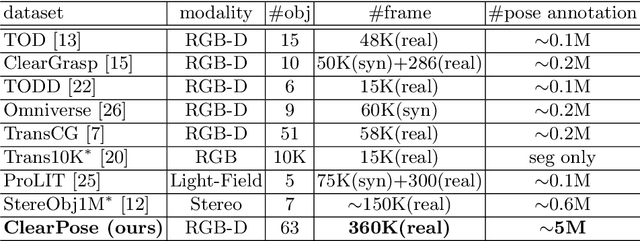

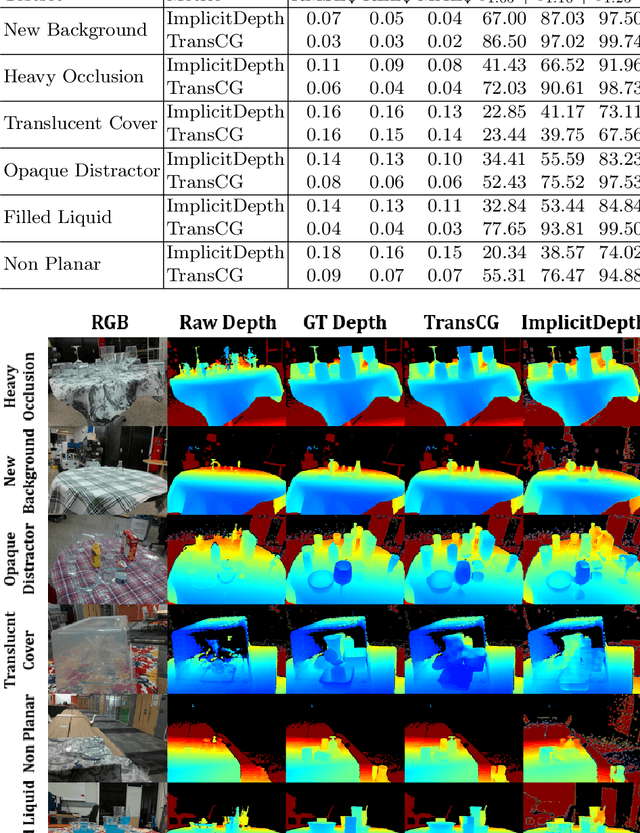
Abstract:Transparent objects are ubiquitous in household settings and pose distinct challenges for visual sensing and perception systems. The optical properties of transparent objects leave conventional 3D sensors alone unreliable for object depth and pose estimation. These challenges are highlighted by the shortage of large-scale RGB-Depth datasets focusing on transparent objects in real-world settings. In this work, we contribute a large-scale real-world RGB-Depth transparent object dataset named ClearPose to serve as a benchmark dataset for segmentation, scene-level depth completion and object-centric pose estimation tasks. The ClearPose dataset contains over 350K labeled real-world RGB-Depth frames and 4M instance annotations covering 63 household objects. The dataset includes object categories commonly used in daily life under various lighting and occluding conditions as well as challenging test scenarios such as cases of occlusion by opaque or translucent objects, non-planar orientations, presence of liquids, etc. We benchmark several state-of-the-art depth completion and object pose estimation deep neural networks on ClearPose.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge