Hongxiang Huang
Event-Based Eye Tracking. 2025 Event-based Vision Workshop
Apr 25, 2025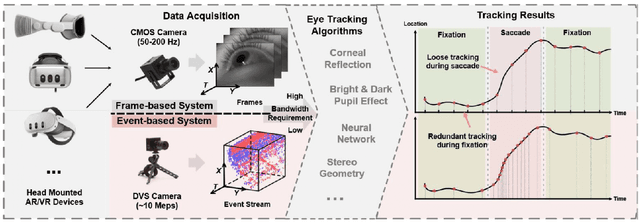
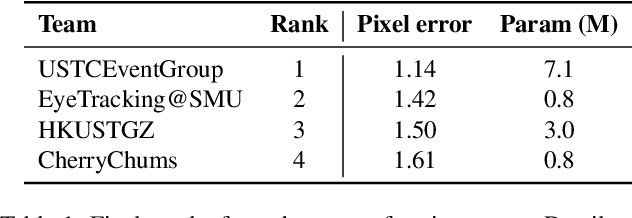
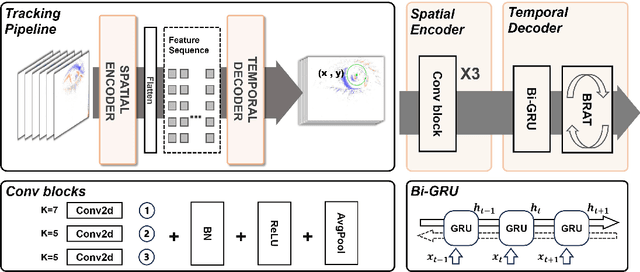
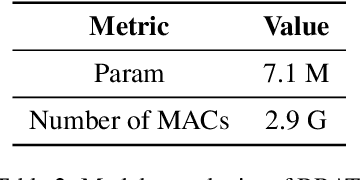
Abstract:This survey serves as a review for the 2025 Event-Based Eye Tracking Challenge organized as part of the 2025 CVPR event-based vision workshop. This challenge focuses on the task of predicting the pupil center by processing event camera recorded eye movement. We review and summarize the innovative methods from teams rank the top in the challenge to advance future event-based eye tracking research. In each method, accuracy, model size, and number of operations are reported. In this survey, we also discuss event-based eye tracking from the perspective of hardware design.
Exploring Temporal Dynamics in Event-based Eye Tracker
Mar 31, 2025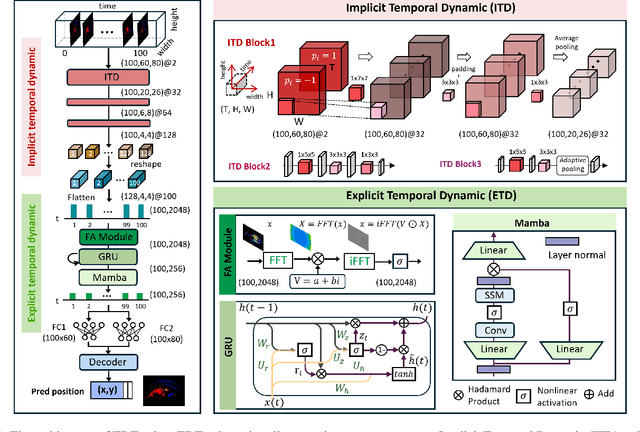
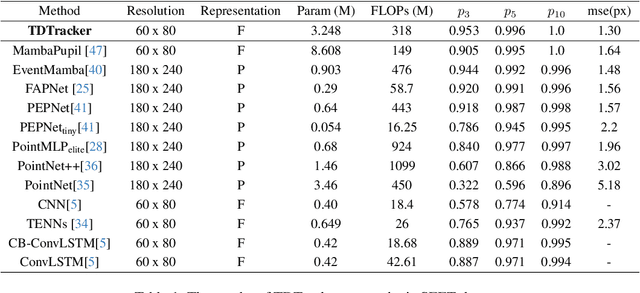
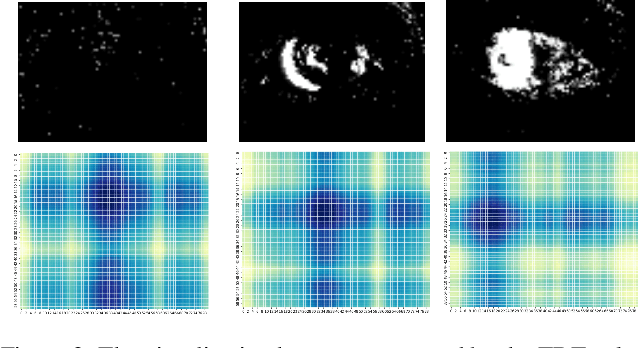
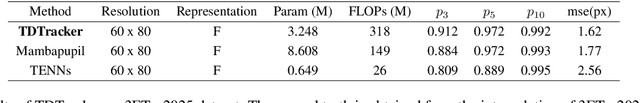
Abstract:Eye-tracking is a vital technology for human-computer interaction, especially in wearable devices such as AR, VR, and XR. The realization of high-speed and high-precision eye-tracking using frame-based image sensors is constrained by their limited temporal resolution, which impairs the accurate capture of rapid ocular dynamics, such as saccades and blinks. Event cameras, inspired by biological vision systems, are capable of perceiving eye movements with extremely low power consumption and ultra-high temporal resolution. This makes them a promising solution for achieving high-speed, high-precision tracking with rich temporal dynamics. In this paper, we propose TDTracker, an effective eye-tracking framework that captures rapid eye movements by thoroughly modeling temporal dynamics from both implicit and explicit perspectives. TDTracker utilizes 3D convolutional neural networks to capture implicit short-term temporal dynamics and employs a cascaded structure consisting of a Frequency-aware Module, GRU, and Mamba to extract explicit long-term temporal dynamics. Ultimately, a prediction heatmap is used for eye coordinate regression. Experimental results demonstrate that TDTracker achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on the synthetic SEET dataset and secured Third place in the CVPR event-based eye-tracking challenge 2025. Our code is available at https://github.com/rhwxmx/TDTracker.
Frequency-aware Event Cloud Network
Dec 30, 2024



Abstract:Event cameras are biologically inspired sensors that emit events asynchronously with remarkable temporal resolution, garnering significant attention from both industry and academia. Mainstream methods favor frame and voxel representations, which reach a satisfactory performance while introducing time-consuming transformation, bulky models, and sacrificing fine-grained temporal information. Alternatively, Point Cloud representation demonstrates promise in addressing the mentioned weaknesses, but it ignores the polarity information, and its models have limited proficiency in abstracting long-term events' features. In this paper, we propose a frequency-aware network named FECNet that leverages Event Cloud representations. FECNet fully utilizes 2S-1T-1P Event Cloud by innovating the event-based Group and Sampling module. To accommodate the long sequence events from Event Cloud, FECNet embraces feature extraction in the frequency domain via the Fourier transform. This approach substantially extinguishes the explosion of Multiply Accumulate Operations (MACs) while effectively abstracting spatial-temporal features. We conducted extensive experiments on event-based object classification, action recognition, and human pose estimation tasks, and the results substantiate the effectiveness and efficiency of FECNet.
Globally Correlation-Aware Hard Negative Generation
Nov 20, 2024Abstract:Hard negative generation aims to generate informative negative samples that help to determine the decision boundaries and thus facilitate advancing deep metric learning. Current works select pair/triplet samples, learn their correlations, and fuse them to generate hard negatives. However, these works merely consider the local correlations of selected samples, ignoring global sample correlations that would provide more significant information to generate more informative negatives. In this work, we propose a Globally Correlation-Aware Hard Negative Generation (GCA-HNG) framework, which first learns sample correlations from a global perspective and exploits these correlations to guide generating hardness-adaptive and diverse negatives. Specifically, this approach begins by constructing a structured graph to model sample correlations, where each node represents a specific sample and each edge represents the correlations between corresponding samples. Then, we introduce an iterative graph message propagation to propagate the messages of node and edge through the whole graph and thus learn the sample correlations globally. Finally, with the guidance of the learned global correlations, we propose a channel-adaptive manner to combine an anchor and multiple negatives for HNG. Compared to current methods, GCA-HNG allows perceiving sample correlations with numerous negatives from a global and comprehensive perspective and generates the negatives with better hardness and diversity. Extensive experiment results demonstrate that the proposed GCA-HNG is superior to related methods on four image retrieval benchmark datasets. Codes and trained models are available at \url{https://github.com/PWenJay/GCA-HNG}.
AGTGAN: Unpaired Image Translation for Photographic Ancient Character Generation
Mar 13, 2023



Abstract:The study of ancient writings has great value for archaeology and philology. Essential forms of material are photographic characters, but manual photographic character recognition is extremely time-consuming and expertise-dependent. Automatic classification is therefore greatly desired. However, the current performance is limited due to the lack of annotated data. Data generation is an inexpensive but useful solution for data scarcity. Nevertheless, the diverse glyph shapes and complex background textures of photographic ancient characters make the generation task difficult, leading to the unsatisfactory results of existing methods. In this paper, we propose an unsupervised generative adversarial network called AGTGAN. By the explicit global and local glyph shape style modeling followed by the stroke-aware texture transfer, as well as an associate adversarial learning mechanism, our method can generate characters with diverse glyphs and realistic textures. We evaluate our approach on the photographic ancient character datasets, e.g., OBC306 and CSDD. Our method outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches in various metrics and performs much better in terms of the diversity and authenticity of generated samples. With our generated images, experiments on the largest photographic oracle bone character dataset show that our method can achieve a significant increase in classification accuracy, up to 16.34%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge