Haojie Shi
Online Time-Informed Kinodynamic Motion Planning of Nonlinear Systems
Jul 03, 2024



Abstract:Sampling-based kinodynamic motion planners (SKMPs) are powerful in finding collision-free trajectories for high-dimensional systems under differential constraints. Time-informed set (TIS) can provide the heuristic search domain to accelerate their convergence to the time-optimal solution. However, existing TIS approximation methods suffer from the curse of dimensionality, computational burden, and limited system applicable scope, e.g., linear and polynomial nonlinear systems. To overcome these problems, we propose a method by leveraging deep learning technology, Koopman operator theory, and random set theory. Specifically, we propose a Deep Invertible Koopman operator with control U model named DIKU to predict states forward and backward over a long horizon by modifying the auxiliary network with an invertible neural network. A sampling-based approach, ASKU, performing reachability analysis for the DIKU is developed to approximate the TIS of nonlinear control systems online. Furthermore, we design an online time-informed SKMP using a direct sampling technique to draw uniform random samples in the TIS. Simulation experiment results demonstrate that our method outperforms other existing works, approximating TIS in near real-time and achieving superior planning performance in several time-optimal kinodynamic motion planning problems.
An Efficient Model-Based Approach on Learning Agile Motor Skills without Reinforcement
Mar 04, 2024
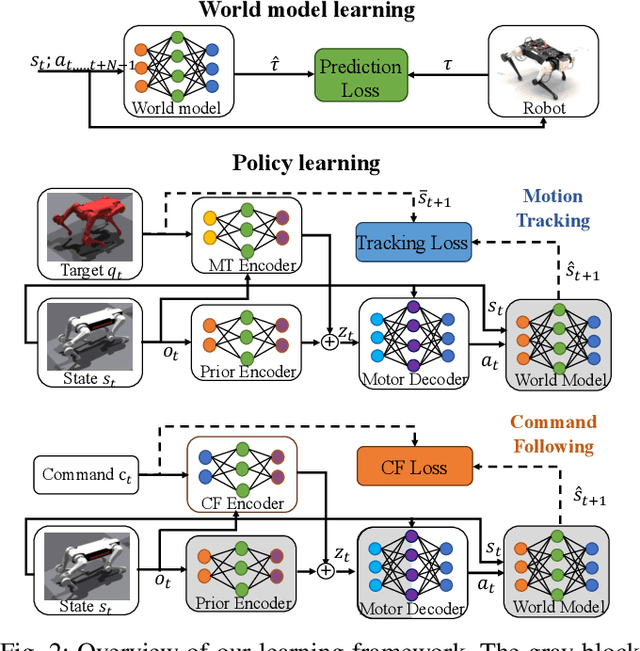
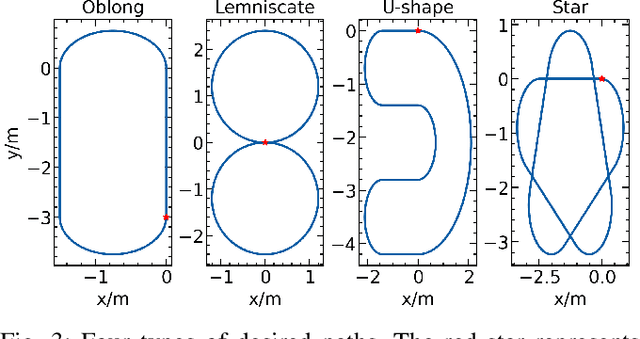
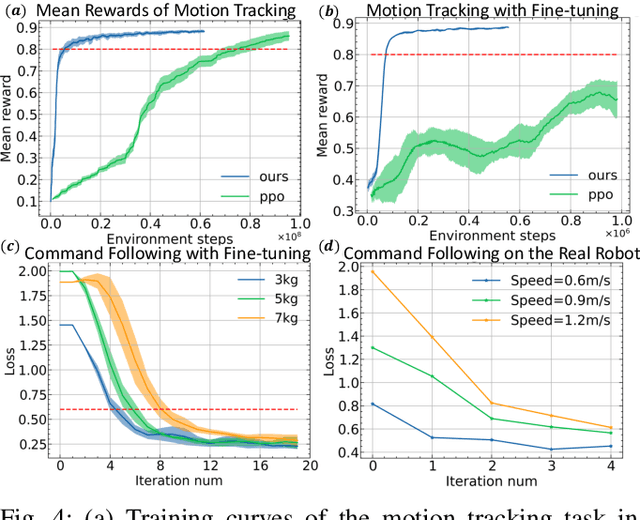
Abstract:Learning-based methods have improved locomotion skills of quadruped robots through deep reinforcement learning. However, the sim-to-real gap and low sample efficiency still limit the skill transfer. To address this issue, we propose an efficient model-based learning framework that combines a world model with a policy network. We train a differentiable world model to predict future states and use it to directly supervise a Variational Autoencoder (VAE)-based policy network to imitate real animal behaviors. This significantly reduces the need for real interaction data and allows for rapid policy updates. We also develop a high-level network to track diverse commands and trajectories. Our simulated results show a tenfold sample efficiency increase compared to reinforcement learning methods such as PPO. In real-world testing, our policy achieves proficient command-following performance with only a two-minute data collection period and generalizes well to new speeds and paths.
Terrain-Aware Quadrupedal Locomotion via Reinforcement Learning
Oct 11, 2023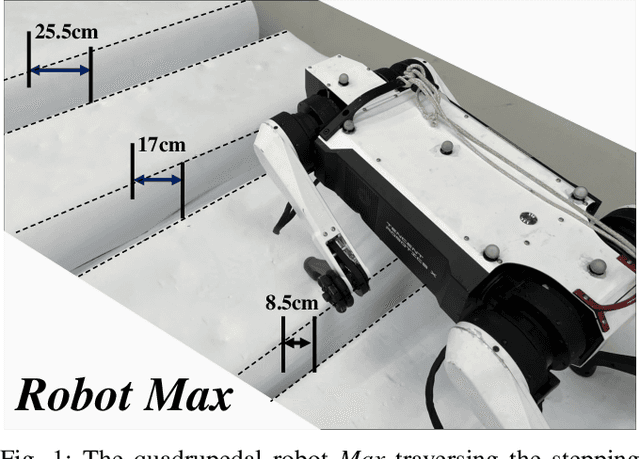
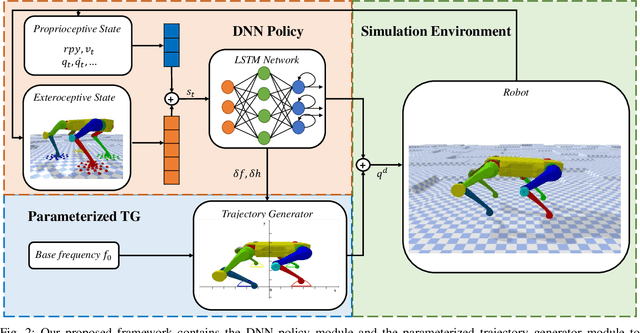
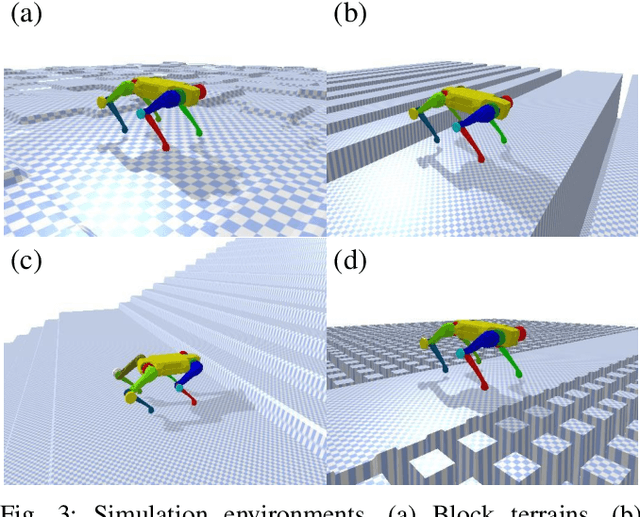
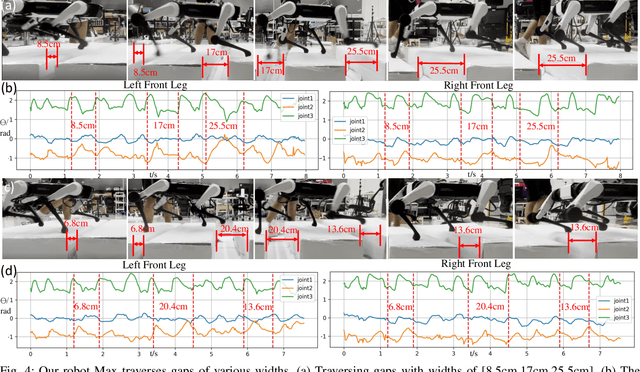
Abstract:In nature, legged animals have developed the ability to adapt to challenging terrains through perception, allowing them to plan safe body and foot trajectories in advance, which leads to safe and energy-efficient locomotion. Inspired by this observation, we present a novel approach to train a Deep Neural Network (DNN) policy that integrates proprioceptive and exteroceptive states with a parameterized trajectory generator for quadruped robots to traverse rough terrains. Our key idea is to use a DNN policy that can modify the parameters of the trajectory generator, such as foot height and frequency, to adapt to different terrains. To encourage the robot to step on safe regions and save energy consumption, we propose foot terrain reward and lifting foot height reward, respectively. By incorporating these rewards, our method can learn a safer and more efficient terrain-aware locomotion policy that can move a quadruped robot flexibly in any direction. To evaluate the effectiveness of our approach, we conduct simulation experiments on challenging terrains, including stairs, stepping stones, and poles. The simulation results demonstrate that our approach can successfully direct the robot to traverse such tough terrains in any direction. Furthermore, we validate our method on a real legged robot, which learns to traverse stepping stones with gaps over 25.5cm.
Deep Koopman Operator with Control for Nonlinear Systems
Feb 16, 2022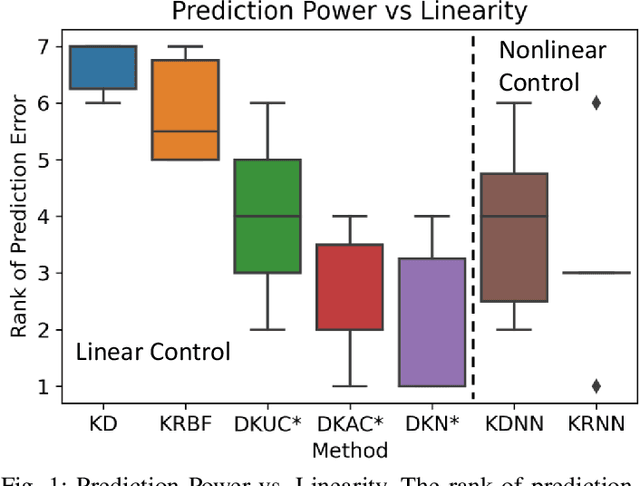
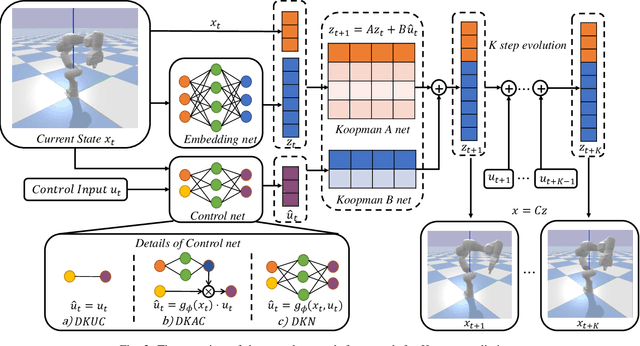
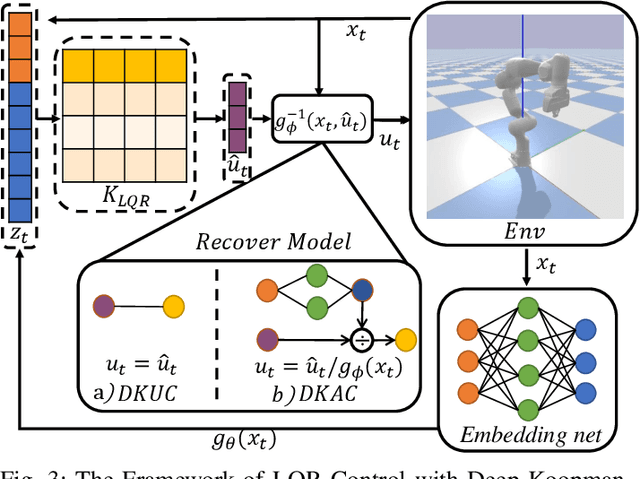
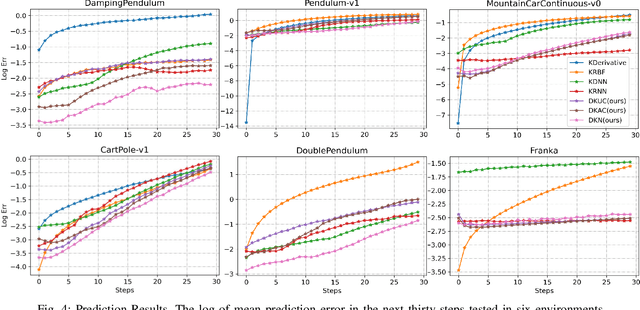
Abstract:Recently Koopman operator has become a promising data-driven tool to facilitate real-time control for unknown nonlinear systems. It maps nonlinear systems into equivalent linear systems in embedding space, ready for real-time linear control methods. However, designing an appropriate Koopman embedding function remains a challenging task. Furthermore, most Koopman-based algorithms only consider nonlinear systems with linear control input, resulting in lousy prediction and control performance when the system is fully nonlinear with the control input. In this work, we propose an end-to-end deep learning framework to learn the Koopman embedding function and Koopman Operator together to alleviate such difficulties. We first parameterize the embedding function and Koopman Operator with the neural network and train them end-to-end with the K-steps loss function. We then design an auxiliary control network to encode the nonlinear state-dependent control term to model the nonlinearity in control input. For linear control, this encoded term is considered the new control variable instead, ensuring the linearity of the embedding space. Then we deploy Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR) on the linear embedding space to derive the optimal control policy and decode the actual control input from the control net. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach outperforms other existing methods, reducing the prediction error by order-of-magnitude and achieving superior control performance in several nonlinear dynamic systems like damping pendulum, CartPole, and 7 Dof robotic manipulator.
Reinforcement Learning with Evolutionary Trajectory Generator: A General Approach for Quadrupedal Locomotion
Sep 16, 2021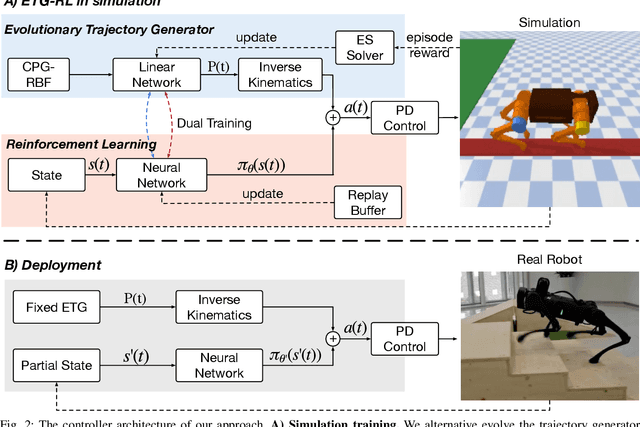
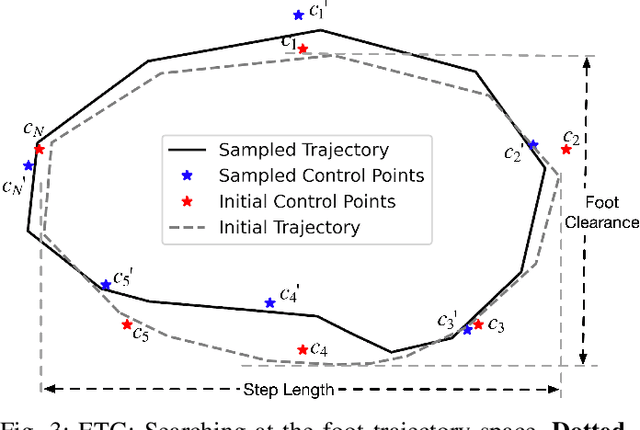
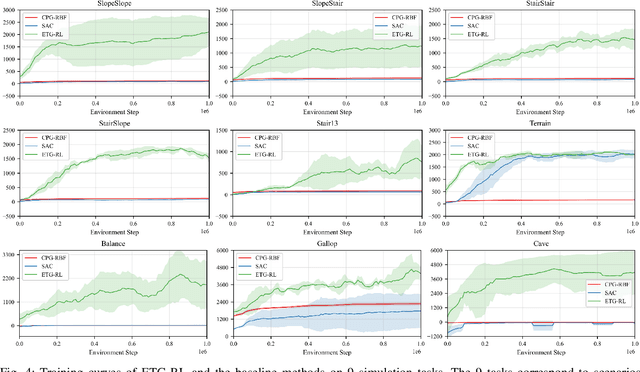
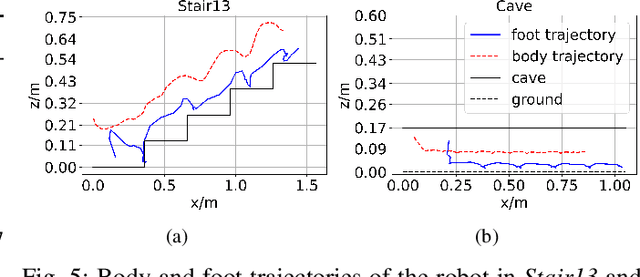
Abstract:Recently reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as a promising approach for quadrupedal locomotion, which can save the manual effort in conventional approaches such as designing skill-specific controllers. However, due to the complex nonlinear dynamics in quadrupedal robots and reward sparsity, it is still difficult for RL to learn effective gaits from scratch, especially in challenging tasks such as walking over the balance beam. To alleviate such difficulty, we propose a novel RL-based approach that contains an evolutionary foot trajectory generator. Unlike prior methods that use a fixed trajectory generator, the generator continually optimizes the shape of the output trajectory for the given task, providing diversified motion priors to guide the policy learning. The policy is trained with reinforcement learning to output residual control signals that fit different gaits. We then optimize the trajectory generator and policy network alternatively to stabilize the training and share the exploratory data to improve sample efficiency. As a result, our approach can solve a range of challenging tasks in simulation by learning from scratch, including walking on a balance beam and crawling through the cave. To further verify the effectiveness of our approach, we deploy the controller learned in the simulation on a 12-DoF quadrupedal robot, and it can successfully traverse challenging scenarios with efficient gaits.
INTERACTION Dataset: An INTERnational, Adversarial and Cooperative moTION Dataset in Interactive Driving Scenarios with Semantic Maps
Sep 30, 2019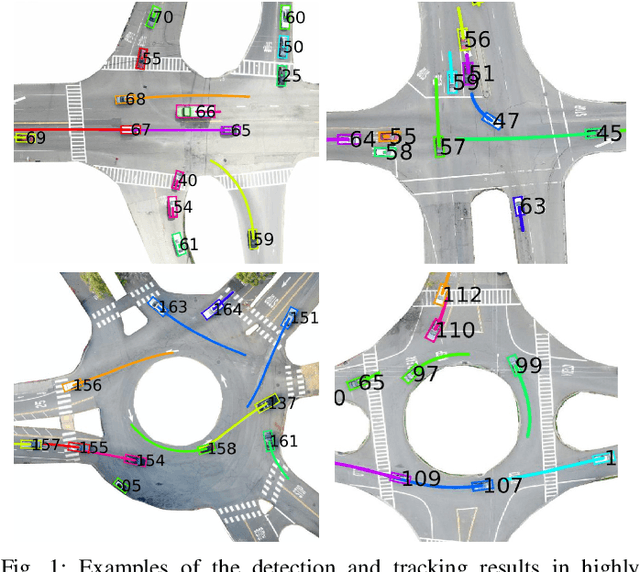
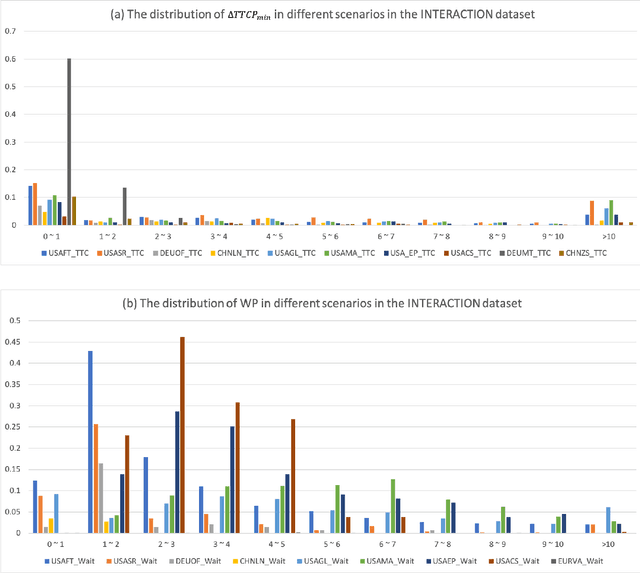
Abstract:Behavior-related research areas such as motion prediction/planning, representation/imitation learning, behavior modeling/generation, and algorithm testing, require support from high-quality motion datasets containing interactive driving scenarios with different driving cultures. In this paper, we present an INTERnational, Adversarial and Cooperative moTION dataset (INTERACTION dataset) in interactive driving scenarios with semantic maps. Five features of the dataset are highlighted. 1) The interactive driving scenarios are diverse, including urban/highway/ramp merging and lane changes, roundabouts with yield/stop signs, signalized intersections, intersections with one/two/all-way stops, etc. 2) Motion data from different countries and different continents are collected so that driving preferences and styles in different cultures are naturally included. 3) The driving behavior is highly interactive and complex with adversarial and cooperative motions of various traffic participants. Highly complex behavior such as negotiations, aggressive/irrational decisions and traffic rule violations are densely contained in the dataset, while regular behavior can also be found from cautious car-following, stop, left/right/U-turn to rational lane-change and cycling and pedestrian crossing, etc. 4) The levels of criticality span wide, from regular safe operations to dangerous, near-collision maneuvers. Real collision, although relatively slight, is also included. 5) Maps with complete semantic information are provided with physical layers, reference lines, lanelet connections and traffic rules. The data is recorded from drones and traffic cameras. Statistics of the dataset in terms of number of entities and interaction density are also provided, along with some utilization examples in a variety of behavior-related research areas. The dataset can be downloaded via https://interaction-dataset.com.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge