Guangyuan Li
MagicTryOn: Harnessing Diffusion Transformer for Garment-Preserving Video Virtual Try-on
May 28, 2025Abstract:Video Virtual Try-On (VVT) aims to simulate the natural appearance of garments across consecutive video frames, capturing their dynamic variations and interactions with human body motion. However, current VVT methods still face challenges in terms of spatiotemporal consistency and garment content preservation. First, they use diffusion models based on the U-Net, which are limited in their expressive capability and struggle to reconstruct complex details. Second, they adopt a separative modeling approach for spatial and temporal attention, which hinders the effective capture of structural relationships and dynamic consistency across frames. Third, their expression of garment details remains insufficient, affecting the realism and stability of the overall synthesized results, especially during human motion. To address the above challenges, we propose MagicTryOn, a video virtual try-on framework built upon the large-scale video diffusion Transformer. We replace the U-Net architecture with a diffusion Transformer and combine full self-attention to jointly model the spatiotemporal consistency of videos. We design a coarse-to-fine garment preservation strategy. The coarse strategy integrates garment tokens during the embedding stage, while the fine strategy incorporates multiple garment-based conditions, such as semantics, textures, and contour lines during the denoising stage. Moreover, we introduce a mask-aware loss to further optimize garment region fidelity. Extensive experiments on both image and video try-on datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms existing SOTA methods in comprehensive evaluations and generalizes to in-the-wild scenarios.
DyArtbank: Diverse Artistic Style Transfer via Pre-trained Stable Diffusion and Dynamic Style Prompt Artbank
Mar 11, 2025



Abstract:Artistic style transfer aims to transfer the learned style onto an arbitrary content image. However, most existing style transfer methods can only render consistent artistic stylized images, making it difficult for users to get enough stylized images to enjoy. To solve this issue, we propose a novel artistic style transfer framework called DyArtbank, which can generate diverse and highly realistic artistic stylized images. Specifically, we introduce a Dynamic Style Prompt ArtBank (DSPA), a set of learnable parameters. It can learn and store the style information from the collection of artworks, dynamically guiding pre-trained stable diffusion to generate diverse and highly realistic artistic stylized images. DSPA can also generate random artistic image samples with the learned style information, providing a new idea for data augmentation. Besides, a Key Content Feature Prompt (KCFP) module is proposed to provide sufficient content prompts for pre-trained stable diffusion to preserve the detailed structure of the input content image. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments verify the effectiveness of our proposed method. Code is available: https://github.com/Jamie-Cheung/DyArtbank
MC-VTON: Minimal Control Virtual Try-On Diffusion Transformer
Jan 07, 2025


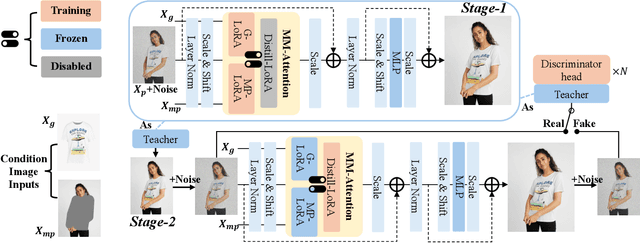
Abstract:Virtual try-on methods based on diffusion models achieve realistic try-on effects. They use an extra reference network or an additional image encoder to process multiple conditional image inputs, which results in high training costs. Besides, they require more than 25 inference steps, bringing a long inference time. In this work, with the development of diffusion transformer (DiT), we rethink the necessity of reference network or image encoder, then propose MC-VTON, enabling DiT to integrate minimal conditional try-on inputs by utilizing its intrinsic backbone. Compared to existing methods, the superiority of MC-VTON is demonstrated in four aspects: (1)Superior detail fidelity. Our DiT-based MC-VTON exhibits superior fidelity in preserving fine-grained details. (2)Simplified network and inputs. We remove any extra reference network or image encoder. We also remove unnecessary conditions like the long prompt, pose estimation, human parsing, and depth map. We require only the masked person image and the garment image. (3)Parameter-efficient training. To process the try-on task, we fine-tune the FLUX.1-dev with only 39.7M additional parameters 0.33% of the backbone parameters). (4)Less inference steps. We apply distillation diffusion on MC-VTON and only need 8 steps to generate a realistic try-on image, with only 86.8M additional parameters (0.72% of the backbone parameters). Experiments show that MC-VTON achieves superior qualitative and quantitative results with fewer condition inputs, fewer inference steps, and fewer trainable parameters than baseline methods.
Rethinking Video Deblurring with Wavelet-Aware Dynamic Transformer and Diffusion Model
Aug 24, 2024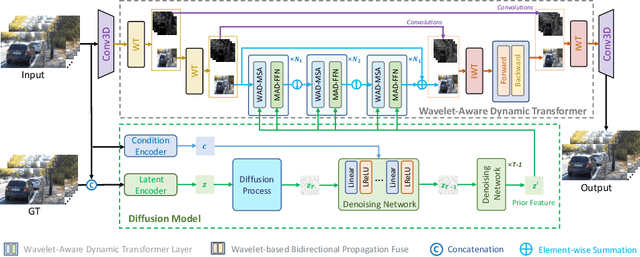
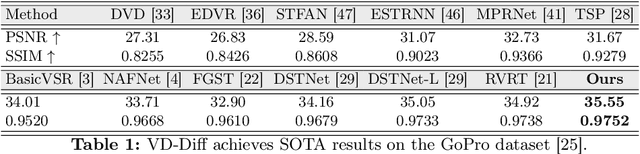
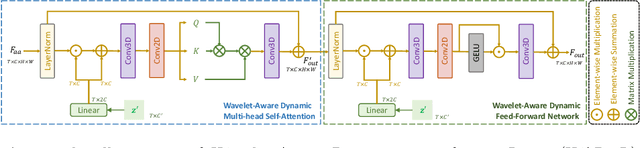
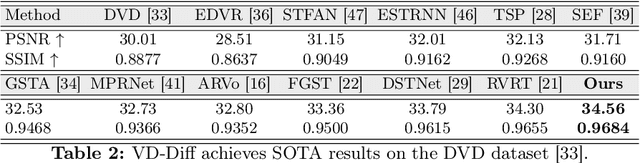
Abstract:Current video deblurring methods have limitations in recovering high-frequency information since the regression losses are conservative with high-frequency details. Since Diffusion Models (DMs) have strong capabilities in generating high-frequency details, we consider introducing DMs into the video deblurring task. However, we found that directly applying DMs to the video deblurring task has the following problems: (1) DMs require many iteration steps to generate videos from Gaussian noise, which consumes many computational resources. (2) DMs are easily misled by the blurry artifacts in the video, resulting in irrational content and distortion of the deblurred video. To address the above issues, we propose a novel video deblurring framework VD-Diff that integrates the diffusion model into the Wavelet-Aware Dynamic Transformer (WADT). Specifically, we perform the diffusion model in a highly compact latent space to generate prior features containing high-frequency information that conforms to the ground truth distribution. We design the WADT to preserve and recover the low-frequency information in the video while utilizing the high-frequency information generated by the diffusion model. Extensive experiments show that our proposed VD-Diff outperforms SOTA methods on GoPro, DVD, BSD, and Real-World Video datasets.
Rethink Arbitrary Style Transfer with Transformer and Contrastive Learning
Apr 21, 2024



Abstract:Arbitrary style transfer holds widespread attention in research and boasts numerous practical applications. The existing methods, which either employ cross-attention to incorporate deep style attributes into content attributes or use adaptive normalization to adjust content features, fail to generate high-quality stylized images. In this paper, we introduce an innovative technique to improve the quality of stylized images. Firstly, we propose Style Consistency Instance Normalization (SCIN), a method to refine the alignment between content and style features. In addition, we have developed an Instance-based Contrastive Learning (ICL) approach designed to understand the relationships among various styles, thereby enhancing the quality of the resulting stylized images. Recognizing that VGG networks are more adept at extracting classification features and need to be better suited for capturing style features, we have also introduced the Perception Encoder (PE) to capture style features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method generates high-quality stylized images and effectively prevents artifacts compared with the existing state-of-the-art methods.
Towards Highly Realistic Artistic Style Transfer via Stable Diffusion with Step-aware and Layer-aware Prompt
Apr 17, 2024
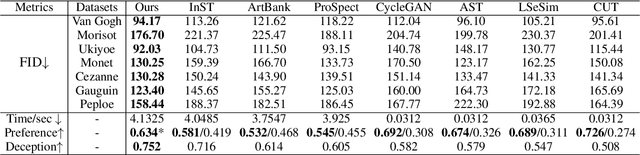
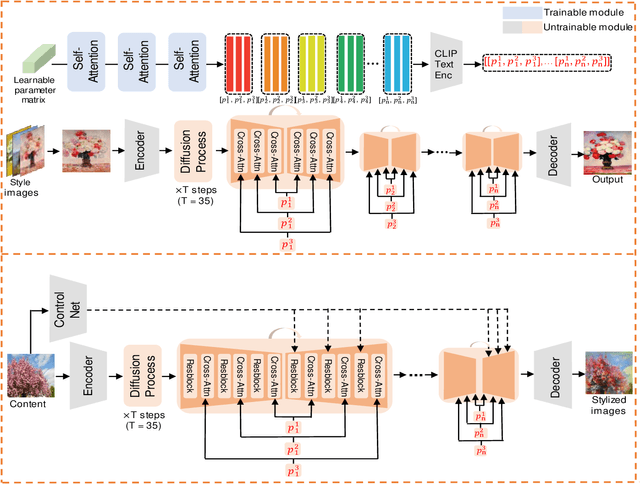
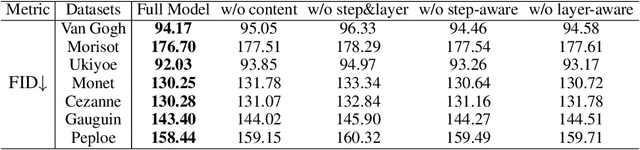
Abstract:Artistic style transfer aims to transfer the learned artistic style onto an arbitrary content image, generating artistic stylized images. Existing generative adversarial network-based methods fail to generate highly realistic stylized images and always introduce obvious artifacts and disharmonious patterns. Recently, large-scale pre-trained diffusion models opened up a new way for generating highly realistic artistic stylized images. However, diffusion model-based methods generally fail to preserve the content structure of input content images well, introducing some undesired content structure and style patterns. To address the above problems, we propose a novel pre-trained diffusion-based artistic style transfer method, called LSAST, which can generate highly realistic artistic stylized images while preserving the content structure of input content images well, without bringing obvious artifacts and disharmonious style patterns. Specifically, we introduce a Step-aware and Layer-aware Prompt Space, a set of learnable prompts, which can learn the style information from the collection of artworks and dynamically adjusts the input images' content structure and style pattern. To train our prompt space, we propose a novel inversion method, called Step-ware and Layer-aware Prompt Inversion, which allows the prompt space to learn the style information of the artworks collection. In addition, we inject a pre-trained conditional branch of ControlNet into our LSAST, which further improved our framework's ability to maintain content structure. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method can generate more highly realistic artistic stylized images than the state-of-the-art artistic style transfer methods.
Rethinking Diffusion Model for Multi-Contrast MRI Super-Resolution
Apr 07, 2024Abstract:Recently, diffusion models (DM) have been applied in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) super-resolution (SR) reconstruction, exhibiting impressive performance, especially with regard to detailed reconstruction. However, the current DM-based SR reconstruction methods still face the following issues: (1) They require a large number of iterations to reconstruct the final image, which is inefficient and consumes a significant amount of computational resources. (2) The results reconstructed by these methods are often misaligned with the real high-resolution images, leading to remarkable distortion in the reconstructed MR images. To address the aforementioned issues, we propose an efficient diffusion model for multi-contrast MRI SR, named as DiffMSR. Specifically, we apply DM in a highly compact low-dimensional latent space to generate prior knowledge with high-frequency detail information. The highly compact latent space ensures that DM requires only a few simple iterations to produce accurate prior knowledge. In addition, we design the Prior-Guide Large Window Transformer (PLWformer) as the decoder for DM, which can extend the receptive field while fully utilizing the prior knowledge generated by DM to ensure that the reconstructed MR image remains undistorted. Extensive experiments on public and clinical datasets demonstrate that our DiffMSR outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
3DGStream: On-the-Fly Training of 3D Gaussians for Efficient Streaming of Photo-Realistic Free-Viewpoint Videos
Mar 05, 2024Abstract:Constructing photo-realistic Free-Viewpoint Videos (FVVs) of dynamic scenes from multi-view videos remains a challenging endeavor. Despite the remarkable advancements achieved by current neural rendering techniques, these methods generally require complete video sequences for offline training and are not capable of real-time rendering. To address these constraints, we introduce 3DGStream, a method designed for efficient FVV streaming of real-world dynamic scenes. Our method achieves fast on-the-fly per-frame reconstruction within 12 seconds and real-time rendering at 200 FPS. Specifically, we utilize 3D Gaussians (3DGs) to represent the scene. Instead of the na\"ive approach of directly optimizing 3DGs per-frame, we employ a compact Neural Transformation Cache (NTC) to model the translations and rotations of 3DGs, markedly reducing the training time and storage required for each FVV frame. Furthermore, we propose an adaptive 3DG addition strategy to handle emerging objects in dynamic scenes. Experiments demonstrate that 3DGStream achieves competitive performance in terms of rendering speed, image quality, training time, and model storage when compared with state-of-the-art methods.
ArtBank: Artistic Style Transfer with Pre-trained Diffusion Model and Implicit Style Prompt Bank
Dec 11, 2023



Abstract:Artistic style transfer aims to repaint the content image with the learned artistic style. Existing artistic style transfer methods can be divided into two categories: small model-based approaches and pre-trained large-scale model-based approaches. Small model-based approaches can preserve the content strucuture, but fail to produce highly realistic stylized images and introduce artifacts and disharmonious patterns; Pre-trained large-scale model-based approaches can generate highly realistic stylized images but struggle with preserving the content structure. To address the above issues, we propose ArtBank, a novel artistic style transfer framework, to generate highly realistic stylized images while preserving the content structure of the content images. Specifically, to sufficiently dig out the knowledge embedded in pre-trained large-scale models, an Implicit Style Prompt Bank (ISPB), a set of trainable parameter matrices, is designed to learn and store knowledge from the collection of artworks and behave as a visual prompt to guide pre-trained large-scale models to generate highly realistic stylized images while preserving content structure. Besides, to accelerate training the above ISPB, we propose a novel Spatial-Statistical-based self-Attention Module (SSAM). The qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method over state-of-the-art artistic style transfer methods.
VGOS: Voxel Grid Optimization for View Synthesis from Sparse Inputs
Apr 26, 2023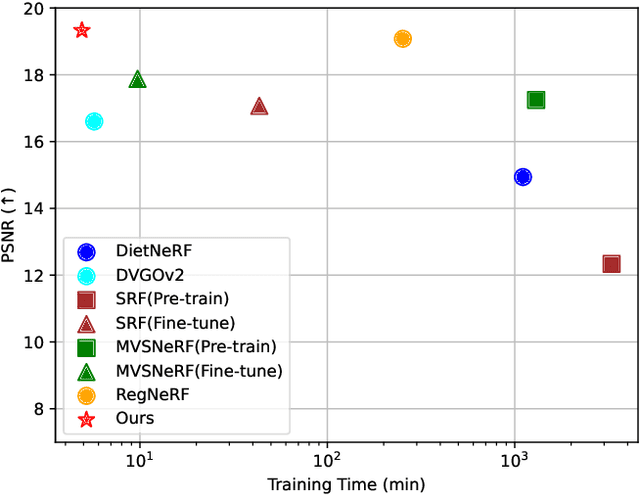
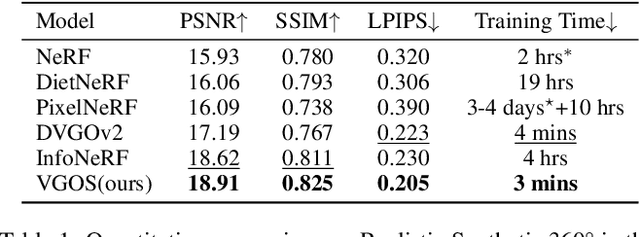
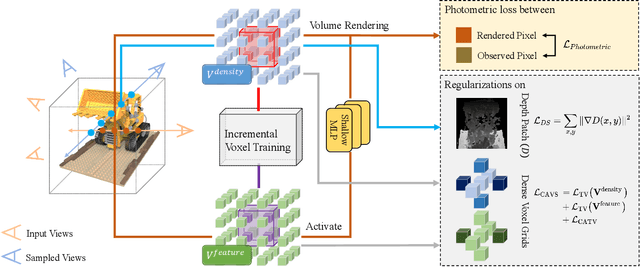
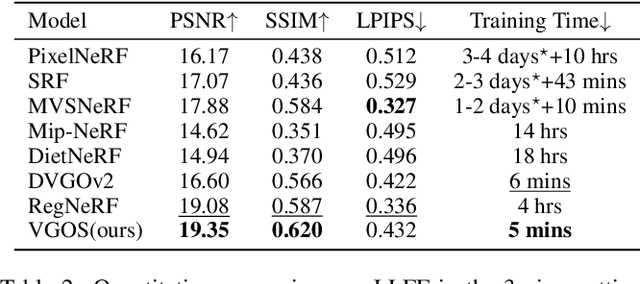
Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) has shown great success in novel view synthesis due to its state-of-the-art quality and flexibility. However, NeRF requires dense input views (tens to hundreds) and a long training time (hours to days) for a single scene to generate high-fidelity images. Although using the voxel grids to represent the radiance field can significantly accelerate the optimization process, we observe that for sparse inputs, the voxel grids are more prone to overfitting to the training views and will have holes and floaters, which leads to artifacts. In this paper, we propose VGOS, an approach for fast (3-5 minutes) radiance field reconstruction from sparse inputs (3-10 views) to address these issues. To improve the performance of voxel-based radiance field in sparse input scenarios, we propose two methods: (a) We introduce an incremental voxel training strategy, which prevents overfitting by suppressing the optimization of peripheral voxels in the early stage of reconstruction. (b) We use several regularization techniques to smooth the voxels, which avoids degenerate solutions. Experiments demonstrate that VGOS achieves state-of-the-art performance for sparse inputs with super-fast convergence. Code will be available at https://github.com/SJoJoK/VGOS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge