Goce Trajcevski
Root Cause Analysis of Hydrogen Bond Separation in Spatio-Temporal Molecular Dynamics using Causal Models
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:Molecular dynamics simulations (MDS) face challenges, including resource-heavy computations and the need to manually scan outputs to detect "interesting events," such as the formation and persistence of hydrogen bonds between atoms of different molecules. A critical research gap lies in identifying the underlying causes of hydrogen bond formation and separation -understanding which interactions or prior events contribute to their emergence over time. With this challenge in mind, we propose leveraging spatio-temporal data analytics and machine learning models to enhance the detection of these phenomena. In this paper, our approach is inspired by causal modeling and aims to identify the root cause variables of hydrogen bond formation and separation events. Specifically, we treat the separation of hydrogen bonds as an "intervention" occurring and represent the causal structure of the bonding and separation events in the MDS as graphical causal models. These causal models are built using a variational autoencoder-inspired architecture that enables us to infer causal relationships across samples with diverse underlying causal graphs while leveraging shared dynamic information. We further include a step to infer the root causes of changes in the joint distribution of the causal models. By constructing causal models that capture shifts in the conditional distributions of molecular interactions during bond formation or separation, this framework provides a novel perspective on root cause analysis in molecular dynamic systems. We validate the efficacy of our model empirically on the atomic trajectories that used MDS for chiral separation, demonstrating that we can predict many steps in the future and also find the variables driving the observed changes in the system.
Motif-Consistent Counterfactuals with Adversarial Refinement for Graph-Level Anomaly Detection
Jul 18, 2024Abstract:Graph-level anomaly detection is significant in diverse domains. To improve detection performance, counterfactual graphs have been exploited to benefit the generalization capacity by learning causal relations. Most existing studies directly introduce perturbations (e.g., flipping edges) to generate counterfactual graphs, which are prone to alter the semantics of generated examples and make them off the data manifold, resulting in sub-optimal performance. To address these issues, we propose a novel approach, Motif-consistent Counterfactuals with Adversarial Refinement (MotifCAR), for graph-level anomaly detection. The model combines the motif of one graph, the core subgraph containing the identification (category) information, and the contextual subgraph (non-motif) of another graph to produce a raw counterfactual graph. However, the produced raw graph might be distorted and cannot satisfy the important counterfactual properties: Realism, Validity, Proximity and Sparsity. Towards that, we present a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based graph optimizer to refine the raw counterfactual graphs. It adopts the discriminator to guide the generator to generate graphs close to realistic data, i.e., meet the property Realism. Further, we design the motif consistency to force the motif of the generated graphs to be consistent with the realistic graphs, meeting the property Validity. Also, we devise the contextual loss and connection loss to control the contextual subgraph and the newly added links to meet the properties Proximity and Sparsity. As a result, the model can generate high-quality counterfactual graphs. Experiments demonstrate the superiority of MotifCAR.
Predicting Human Mobility via Self-supervised Disentanglement Learning
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:Deep neural networks have recently achieved considerable improvements in learning human behavioral patterns and individual preferences from massive spatial-temporal trajectories data. However, most of the existing research concentrates on fusing different semantics underlying sequential trajectories for mobility pattern learning which, in turn, yields a narrow perspective on comprehending human intrinsic motions. In addition, the inherent sparsity and under-explored heterogeneous collaborative items pertaining to human check-ins hinder the potential exploitation of human diverse periodic regularities as well as common interests. Motivated by recent advances in disentanglement learning, in this study we propose a novel disentangled solution called SSDL for tackling the next POI prediction problem. SSDL primarily seeks to disentangle the potential time-invariant and time-varying factors into different latent spaces from massive trajectories data, providing an interpretable view to understand the intricate semantics underlying human diverse mobility representations. To address the data sparsity issue, we present two realistic trajectory augmentation approaches to enhance the understanding of both the human intrinsic periodicity and constantly-changing intents. In addition, we devise a POI-centric graph structure to explore heterogeneous collaborative signals underlying historical check-ins. Extensive experiments conducted on four real-world datasets demonstrate that our proposed SSDL significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches -- for example, it yields up to 8.57% improvements on ACC@1.
A Survey of Information Cascade Analysis: Models, Predictions and Recent Advances
May 25, 2020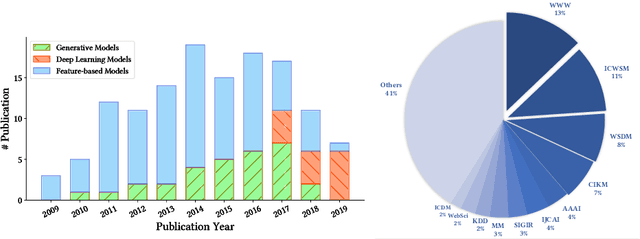
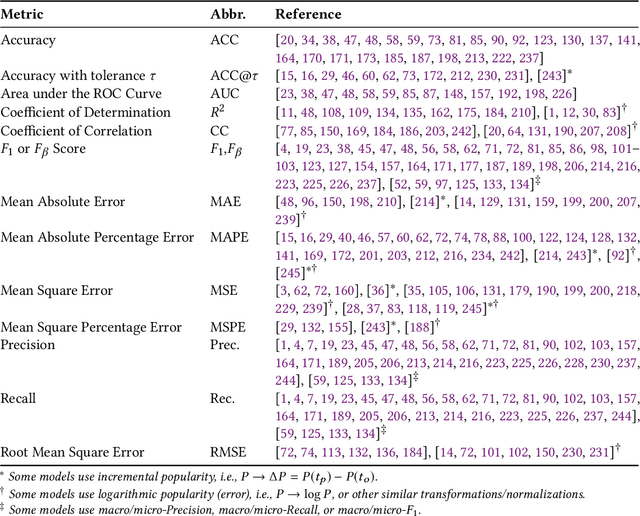
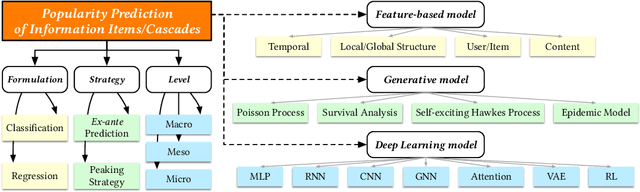
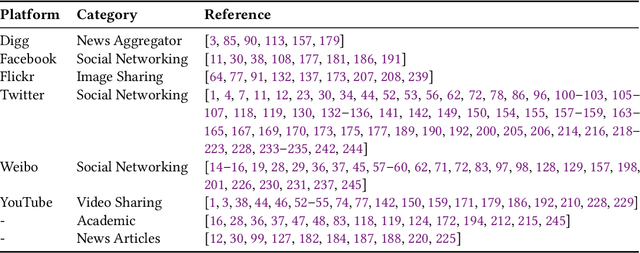
Abstract:The deluge of digital information in our daily life -- from user-generated content such as microblogs and scientific papers, to online business such as viral marketing and advertising -- offers unprecedented opportunities to explore and exploit the trajectories and structures of the evolution of information cascades. Abundant research efforts, both academic and industrial, have aimed to reach a better understanding of the mechanisms driving the spread of information and quantifying the outcome of information diffusion. This article presents a comprehensive review and categorization of information popularity prediction methods, from feature engineering and stochastic processes, through graph representation, to deep learning-based approaches. Specifically, we first formally define different types of information cascades and summarize the perspectives of existing studies. We then present a taxonomy that categorizes existing works into the aforementioned three main groups as well as the main subclasses in each group, and we systematically review cutting-edge research work. Finally, we summarize the pros and cons of existing research efforts and outline the open challenges and opportunities in this field.
A Heterogeneous Dynamical Graph Neural Networks Approach to Quantify Scientific Impact
Mar 26, 2020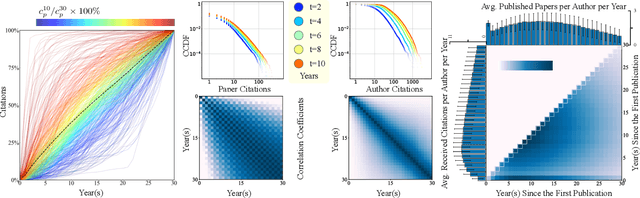
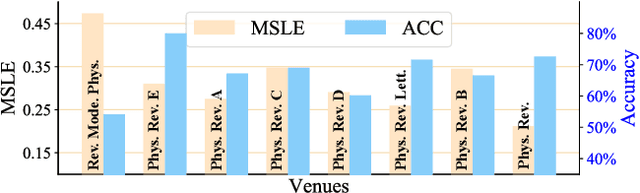
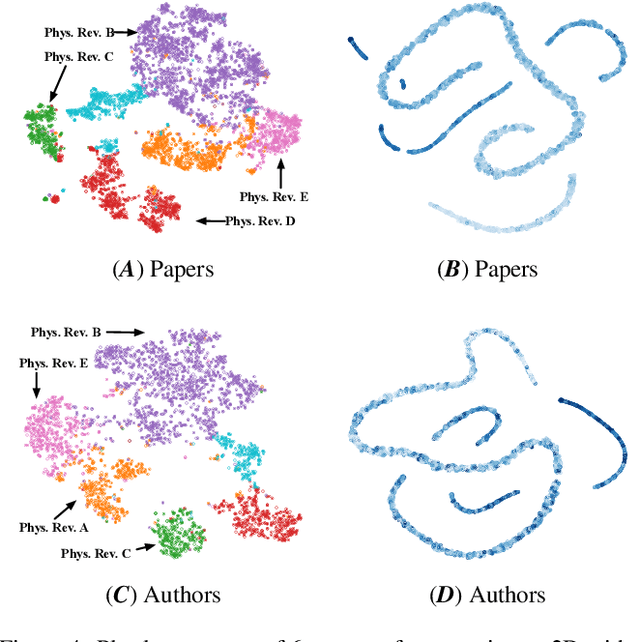
Abstract:Quantifying and predicting the long-term impact of scientific writings or individual scholars has important implications for many policy decisions, such as funding proposal evaluation and identifying emerging research fields. In this work, we propose an approach based on Heterogeneous Dynamical Graph Neural Network (HDGNN) to explicitly model and predict the cumulative impact of papers and authors. HDGNN extends heterogeneous GNNs by incorporating temporally evolving characteristics and capturing both structural properties of attributed graph and the growing sequence of citation behavior. HDGNN is significantly different from previous models in its capability of modeling the node impact in a dynamic manner while taking into account the complex relations among nodes. Experiments conducted on a real citation dataset demonstrate its superior performance of predicting the impact of both papers and authors.
Continual Graph Learning
Mar 22, 2020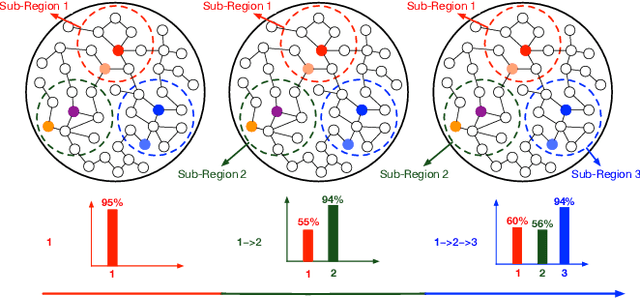
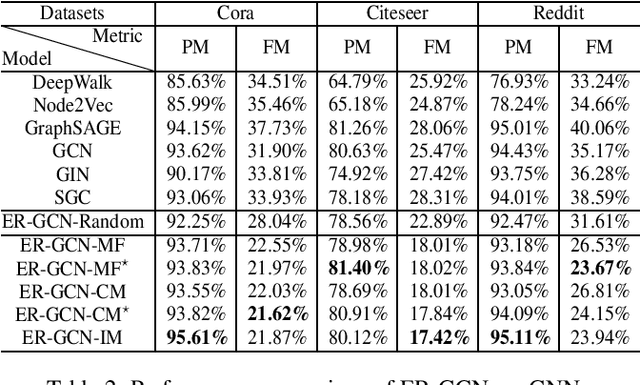
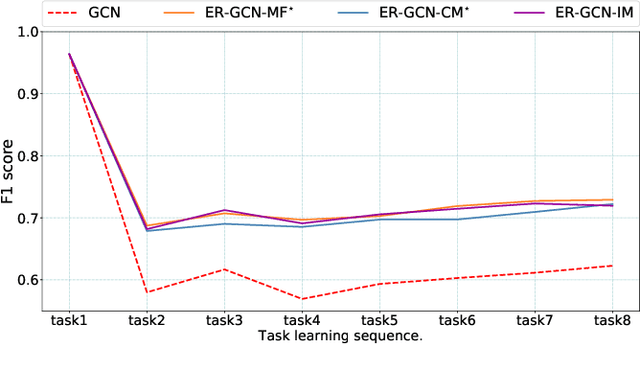
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have recently received significant research attention due to their prominent performance on a variety of graph-related learning tasks. Most of the existing works focus on either static or dynamic graph settings, addressing a particular task, e.g., node/graph classification, link prediction. In this work, we investigate the question: can GNNs be applied to continuously learning a sequence of tasks? Towards that, we explore the Continual Graph Learning (CGL) paradigm and we present the Experience Replay based framework ER-GNN for CGL to address the catastrophic forgetting problem in existing GNNs. ER-GNN stores knowledge from previous tasks as experiences and replays them when learning new tasks to mitigate the forgetting issue. We propose three experience node selection strategies: mean of features, coverage maximization and influence maximization, to guide the process of selecting experience nodes. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of ER-GNN and shed light on the incremental (non-Euclidean) graph structure learning.
Frosting Weights for Better Continual Training
Jan 07, 2020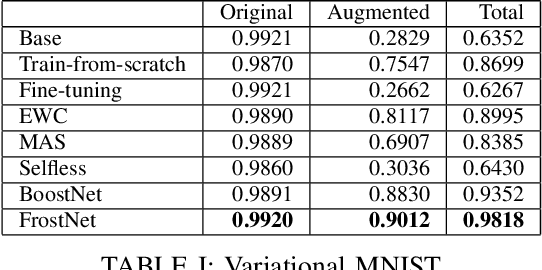
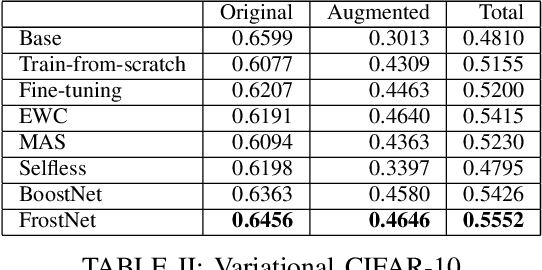
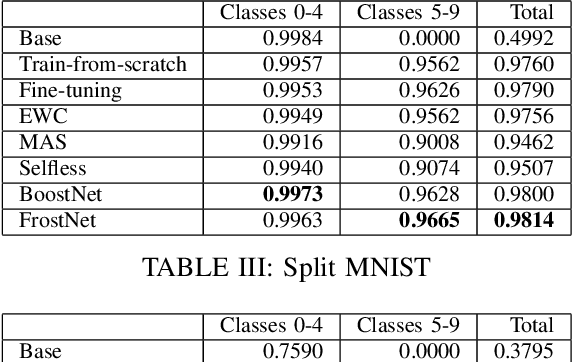
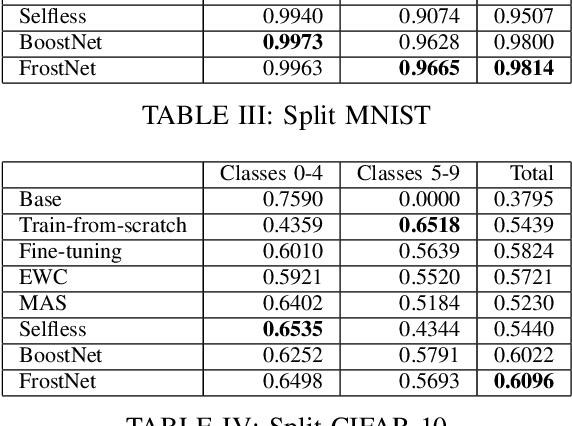
Abstract:Training a neural network model can be a lifelong learning process and is a computationally intensive one. A severe adverse effect that may occur in deep neural network models is that they can suffer from catastrophic forgetting during retraining on new data. To avoid such disruptions in the continuous learning, one appealing property is the additive nature of ensemble models. In this paper, we propose two generic ensemble approaches, gradient boosting and meta-learning, to solve the catastrophic forgetting problem in tuning pre-trained neural network models.
Meta-GNN: On Few-shot Node Classification in Graph Meta-learning
May 23, 2019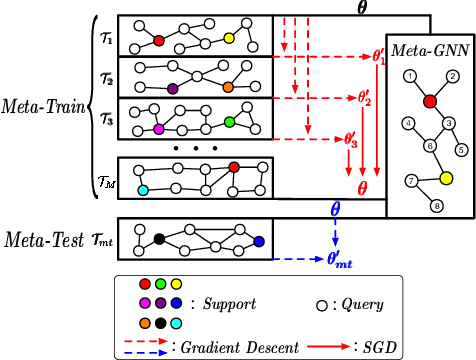
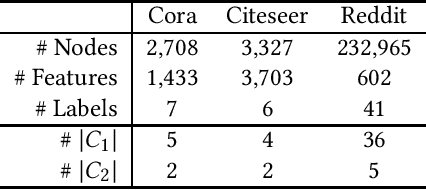
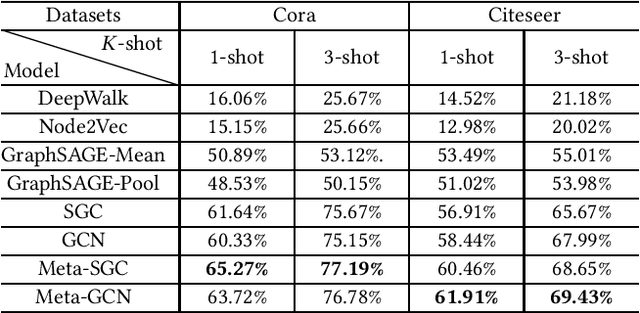
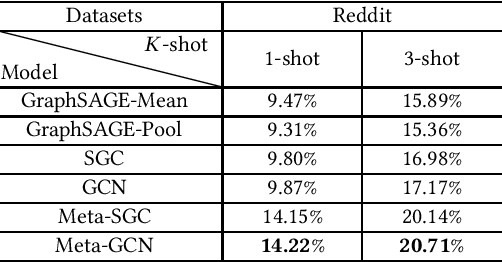
Abstract:Meta-learning has received a tremendous recent attention as a possible approach for mimicking human intelligence, i.e., acquiring new knowledge and skills with little or even no demonstration. Most of the existing meta-learning methods are proposed to tackle few-shot learning problems such as image and text, in rather Euclidean domain. However, there are very few works applying meta-learning to non-Euclidean domains, and the recently proposed graph neural networks (GNNs) models do not perform effectively on graph few-shot learning problems. Towards this, we propose a novel graph meta-learning framework -- Meta-GNN -- to tackle the few-shot node classification problem in graph meta-learning settings. It obtains the prior knowledge of classifiers by training on many similar few-shot learning tasks and then classifies the nodes from new classes with only few labeled samples. Additionally, Meta-GNN is a general model that can be straightforwardly incorporated into any existing state-of-the-art GNN. Our experiments conducted on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that our proposed approach not only improves the node classification performance by a large margin on few-shot learning problems in meta-learning paradigm, but also learns a more general and flexible model for task adaption.
Experimental Comparison of Representation Methods and Distance Measures for Time Series Data
Dec 09, 2010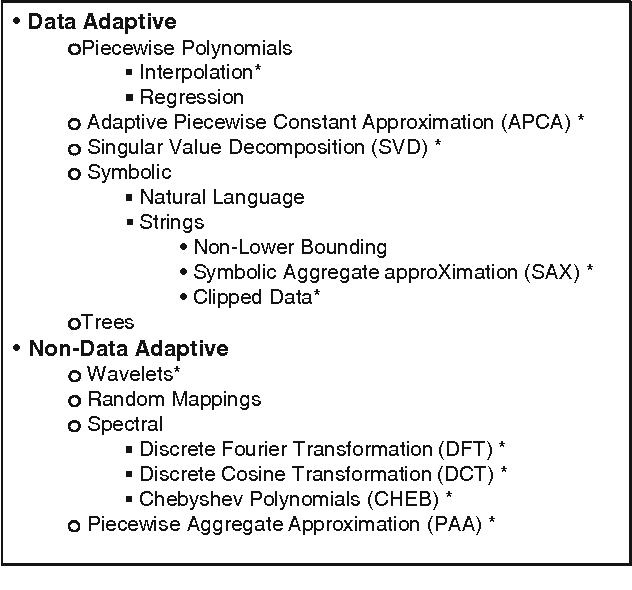
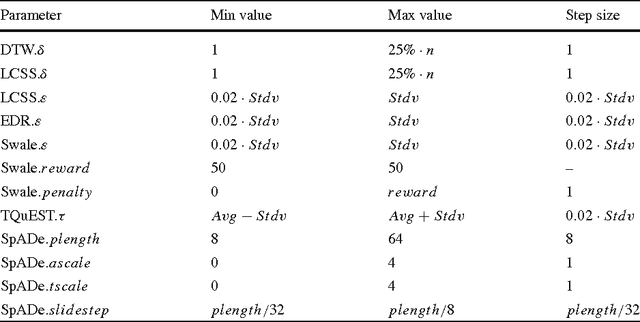
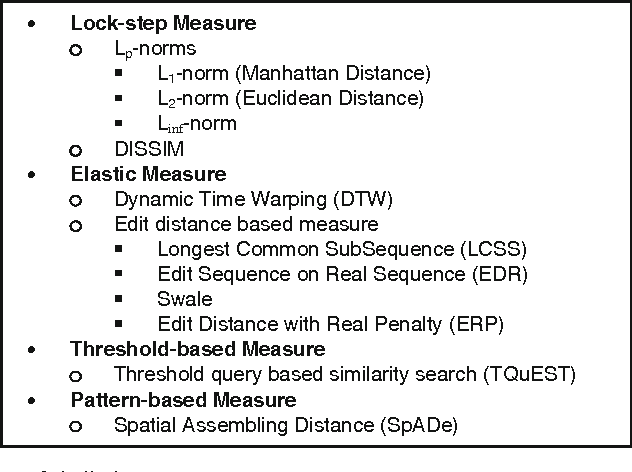
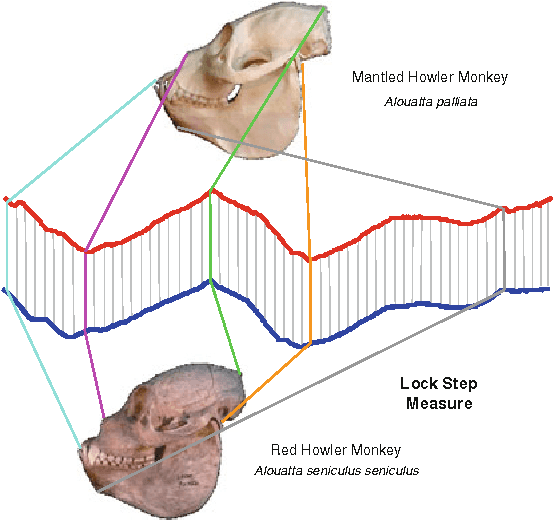
Abstract:The previous decade has brought a remarkable increase of the interest in applications that deal with querying and mining of time series data. Many of the research efforts in this context have focused on introducing new representation methods for dimensionality reduction or novel similarity measures for the underlying data. In the vast majority of cases, each individual work introducing a particular method has made specific claims and, aside from the occasional theoretical justifications, provided quantitative experimental observations. However, for the most part, the comparative aspects of these experiments were too narrowly focused on demonstrating the benefits of the proposed methods over some of the previously introduced ones. In order to provide a comprehensive validation, we conducted an extensive experimental study re-implementing eight different time series representations and nine similarity measures and their variants, and testing their effectiveness on thirty-eight time series data sets from a wide variety of application domains. In this paper, we give an overview of these different techniques and present our comparative experimental findings regarding their effectiveness. In addition to providing a unified validation of some of the existing achievements, our experiments also indicate that, in some cases, certain claims in the literature may be unduly optimistic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge