Gilles Puy
DANTE
Driving on Registers
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We present DrivoR, a simple and efficient transformer-based architecture for end-to-end autonomous driving. Our approach builds on pretrained Vision Transformers (ViTs) and introduces camera-aware register tokens that compress multi-camera features into a compact scene representation, significantly reducing downstream computation without sacrificing accuracy. These tokens drive two lightweight transformer decoders that generate and then score candidate trajectories. The scoring decoder learns to mimic an oracle and predicts interpretable sub-scores representing aspects such as safety, comfort, and efficiency, enabling behavior-conditioned driving at inference. Despite its minimal design, DrivoR outperforms or matches strong contemporary baselines across NAVSIM-v1, NAVSIM-v2, and the photorealistic closed-loop HUGSIM benchmark. Our results show that a pure-transformer architecture, combined with targeted token compression, is sufficient for accurate, efficient, and adaptive end-to-end driving. Code and checkpoints will be made available via the project page.
3D sans 3D Scans: Scalable Pre-training from Video-Generated Point Clouds
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Despite recent progress in 3D self-supervised learning, collecting large-scale 3D scene scans remains expensive and labor-intensive. In this work, we investigate whether 3D representations can be learned from unlabeled videos recorded without any real 3D sensors. We present Laplacian-Aware Multi-level 3D Clustering with Sinkhorn-Knopp (LAM3C), a self-supervised framework that learns from video-generated point clouds from unlabeled videos. We first introduce RoomTours, a video-generated point cloud dataset constructed by collecting room-walkthrough videos from the web (e.g., real-estate tours) and generating 49,219 scenes using an off-the-shelf feed-forward reconstruction model. We also propose a noise-regularized loss that stabilizes representation learning by enforcing local geometric smoothness and ensuring feature stability under noisy point clouds. Remarkably, without using any real 3D scans, LAM3C achieves higher performance than the previous self-supervised methods on indoor semantic and instance segmentation. These results suggest that unlabeled videos represent an abundant source of data for 3D self-supervised learning.
LOSC: LiDAR Open-voc Segmentation Consolidator
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:We study the use of image-based Vision-Language Models (VLMs) for open-vocabulary segmentation of lidar scans in driving settings. Classically, image semantics can be back-projected onto 3D point clouds. Yet, resulting point labels are noisy and sparse. We consolidate these labels to enforce both spatio-temporal consistency and robustness to image-level augmentations. We then train a 3D network based on these refined labels. This simple method, called LOSC, outperforms the SOTA of zero-shot open-vocabulary semantic and panoptic segmentation on both nuScenes and SemanticKITTI, with significant margins.
LiDPM: Rethinking Point Diffusion for Lidar Scene Completion
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Training diffusion models that work directly on lidar points at the scale of outdoor scenes is challenging due to the difficulty of generating fine-grained details from white noise over a broad field of view. The latest works addressing scene completion with diffusion models tackle this problem by reformulating the original DDPM as a local diffusion process. It contrasts with the common practice of operating at the level of objects, where vanilla DDPMs are currently used. In this work, we close the gap between these two lines of work. We identify approximations in the local diffusion formulation, show that they are not required to operate at the scene level, and that a vanilla DDPM with a well-chosen starting point is enough for completion. Finally, we demonstrate that our method, LiDPM, leads to better results in scene completion on SemanticKITTI. The project page is https://astra-vision.github.io/LiDPM .
Clustering is back: Reaching state-of-the-art LiDAR instance segmentation without training
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Panoptic segmentation of LiDAR point clouds is fundamental to outdoor scene understanding, with autonomous driving being a primary application. While state-of-the-art approaches typically rely on end-to-end deep learning architectures and extensive manual annotations of instances, the significant cost and time investment required for labeling large-scale point cloud datasets remains a major bottleneck in this field. In this work, we demonstrate that competitive panoptic segmentation can be achieved using only semantic labels, with instances predicted without any training or annotations. Our method achieves performance comparable to current state-of-the-art supervised methods on standard benchmarks including SemanticKITTI and nuScenes, and outperforms every publicly available method on SemanticKITTI as a drop-in instance head replacement, while running in real-time on a single-threaded CPU and requiring no instance labels. Our method is fully explainable, and requires no learning or parameter tuning. Code is available at https://github.com/valeoai/Alpine/
UNIT: Unsupervised Online Instance Segmentation through Time
Sep 12, 2024Abstract:Online object segmentation and tracking in Lidar point clouds enables autonomous agents to understand their surroundings and make safe decisions. Unfortunately, manual annotations for these tasks are prohibitively costly. We tackle this problem with the task of class-agnostic unsupervised online instance segmentation and tracking. To that end, we leverage an instance segmentation backbone and propose a new training recipe that enables the online tracking of objects. Our network is trained on pseudo-labels, eliminating the need for manual annotations. We conduct an evaluation using metrics adapted for temporal instance segmentation. Computing these metrics requires temporally-consistent instance labels. When unavailable, we construct these labels using the available 3D bounding boxes and semantic labels in the dataset. We compare our method against strong baselines and demonstrate its superiority across two different outdoor Lidar datasets.
Train Till You Drop: Towards Stable and Robust Source-free Unsupervised 3D Domain Adaptation
Sep 06, 2024Abstract:We tackle the challenging problem of source-free unsupervised domain adaptation (SFUDA) for 3D semantic segmentation. It amounts to performing domain adaptation on an unlabeled target domain without any access to source data; the available information is a model trained to achieve good performance on the source domain. A common issue with existing SFUDA approaches is that performance degrades after some training time, which is a by product of an under-constrained and ill-posed problem. We discuss two strategies to alleviate this issue. First, we propose a sensible way to regularize the learning problem. Second, we introduce a novel criterion based on agreement with a reference model. It is used (1) to stop the training when appropriate and (2) as validator to select hyperparameters without any knowledge on the target domain. Our contributions are easy to implement and readily amenable for all SFUDA methods, ensuring stable improvements over all baselines. We validate our findings on various 3D lidar settings, achieving state-of-the-art performance. The project repository (with code) is: github.com/valeoai/TTYD.
MILAN: Milli-Annotations for Lidar Semantic Segmentation
Jul 22, 2024



Abstract:Annotating lidar point clouds for autonomous driving is a notoriously expensive and time-consuming task. In this work, we show that the quality of recent self-supervised lidar scan representations allows a great reduction of the annotation cost. Our method has two main steps. First, we show that self-supervised representations allow a simple and direct selection of highly informative lidar scans to annotate: training a network on these selected scans leads to much better results than a random selection of scans and, more interestingly, to results on par with selections made by SOTA active learning methods. In a second step, we leverage the same self-supervised representations to cluster points in our selected scans. Asking the annotator to classify each cluster, with a single click per cluster, then permits us to close the gap with fully-annotated training sets, while only requiring one thousandth of the point labels.
Valeo4Cast: A Modular Approach to End-to-End Forecasting
Jun 12, 2024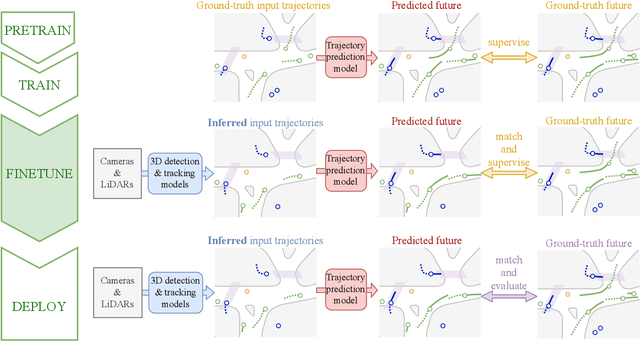
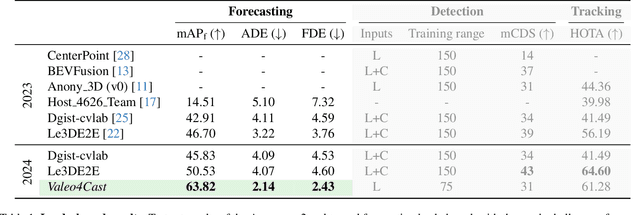
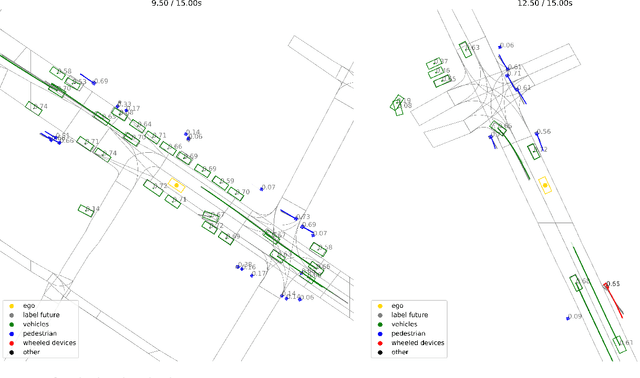
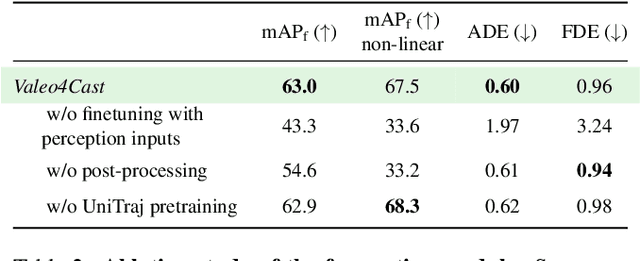
Abstract:Motion forecasting is crucial in autonomous driving systems to anticipate the future trajectories of surrounding agents such as pedestrians, vehicles, and traffic signals. In end-to-end forecasting, the model must jointly detect from sensor data (cameras or LiDARs) the position and past trajectories of the different elements of the scene and predict their future location. We depart from the current trend of tackling this task via end-to-end training from perception to forecasting and we use a modular approach instead. Following a recent study, we individually build and train detection, tracking, and forecasting modules. We then only use consecutive finetuning steps to integrate the modules better and alleviate compounding errors. Our study reveals that this simple yet effective approach significantly improves performance on the end-to-end forecasting benchmark. Consequently, our solution ranks first in the Argoverse 2 end-to-end Forecasting Challenge held at CVPR 2024 Workshop on Autonomous Driving (WAD), with 63.82 mAPf. We surpass forecasting results by +17.1 points over last year's winner and by +13.3 points over this year's runner-up. This remarkable performance in forecasting can be explained by our modular paradigm, which integrates finetuning strategies and significantly outperforms the end-to-end-trained counterparts.
BEVContrast: Self-Supervision in BEV Space for Automotive Lidar Point Clouds
Oct 26, 2023Abstract:We present a surprisingly simple and efficient method for self-supervision of 3D backbone on automotive Lidar point clouds. We design a contrastive loss between features of Lidar scans captured in the same scene. Several such approaches have been proposed in the literature from PointConstrast, which uses a contrast at the level of points, to the state-of-the-art TARL, which uses a contrast at the level of segments, roughly corresponding to objects. While the former enjoys a great simplicity of implementation, it is surpassed by the latter, which however requires a costly pre-processing. In BEVContrast, we define our contrast at the level of 2D cells in the Bird's Eye View plane. Resulting cell-level representations offer a good trade-off between the point-level representations exploited in PointContrast and segment-level representations exploited in TARL: we retain the simplicity of PointContrast (cell representations are cheap to compute) while surpassing the performance of TARL in downstream semantic segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge