Gaurav Manek
Projected Off-Policy Q-Learning (POP-QL) for Stabilizing Offline Reinforcement Learning
Nov 25, 2023Abstract:A key problem in off-policy Reinforcement Learning (RL) is the mismatch, or distribution shift, between the dataset and the distribution over states and actions visited by the learned policy. This problem is exacerbated in the fully offline setting. The main approach to correct this shift has been through importance sampling, which leads to high-variance gradients. Other approaches, such as conservatism or behavior-regularization, regularize the policy at the cost of performance. In this paper, we propose a new approach for stable off-policy Q-Learning. Our method, Projected Off-Policy Q-Learning (POP-QL), is a novel actor-critic algorithm that simultaneously reweights off-policy samples and constrains the policy to prevent divergence and reduce value-approximation error. In our experiments, POP-QL not only shows competitive performance on standard benchmarks, but also out-performs competing methods in tasks where the data-collection policy is significantly sub-optimal.
Learning Stable Deep Dynamics Models
Jan 17, 2020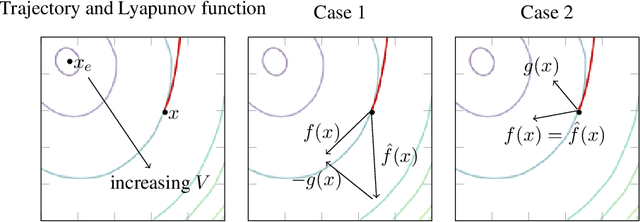
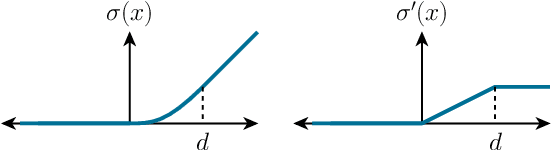
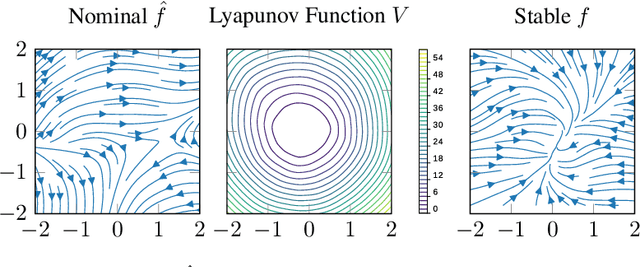
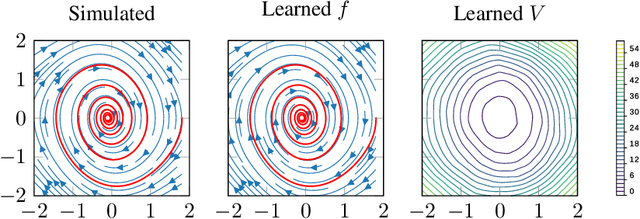
Abstract:Deep networks are commonly used to model dynamical systems, predicting how the state of a system will evolve over time (either autonomously or in response to control inputs). Despite the predictive power of these systems, it has been difficult to make formal claims about the basic properties of the learned systems. In this paper, we propose an approach for learning dynamical systems that are guaranteed to be stable over the entire state space. The approach works by jointly learning a dynamics model and Lyapunov function that guarantees non-expansiveness of the dynamics under the learned Lyapunov function. We show that such learning systems are able to model simple dynamical systems and can be combined with additional deep generative models to learn complex dynamics, such as video textures, in a fully end-to-end fashion.
Efficient GAN-Based Anomaly Detection
Feb 17, 2018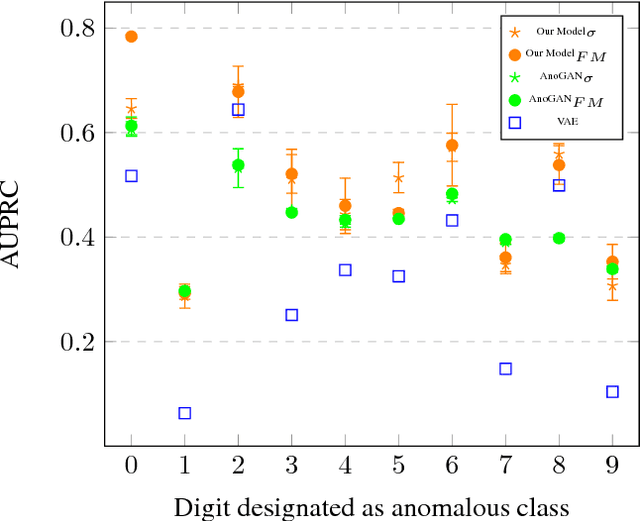
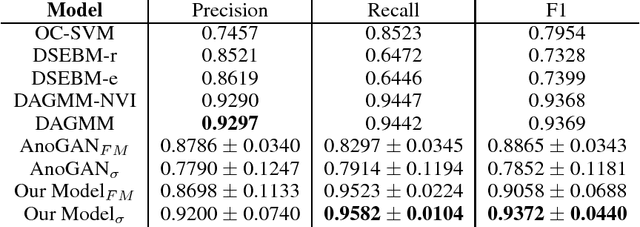
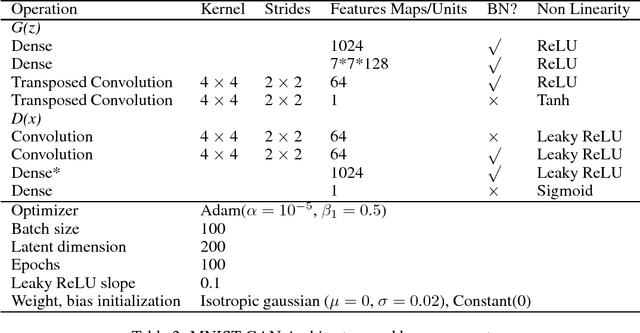
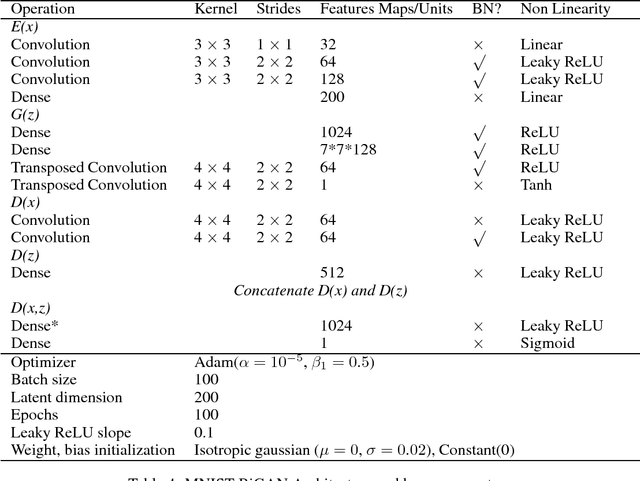
Abstract:Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are able to model the complex highdimensional distributions of real-world data, which suggests they could be effective for anomaly detection. However, few works have explored the use of GANs for the anomaly detection task. We leverage recently developed GAN models for anomaly detection, and achieve state-of-the-art performance on image and network intrusion datasets, while being several hundred-fold faster at test time than the only published GAN-based method.
Pruning Convolutional Neural Networks for Image Instance Retrieval
Jul 18, 2017
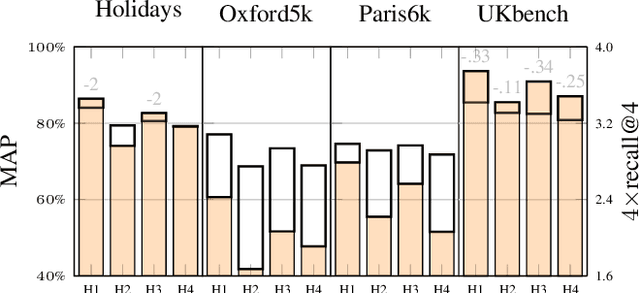
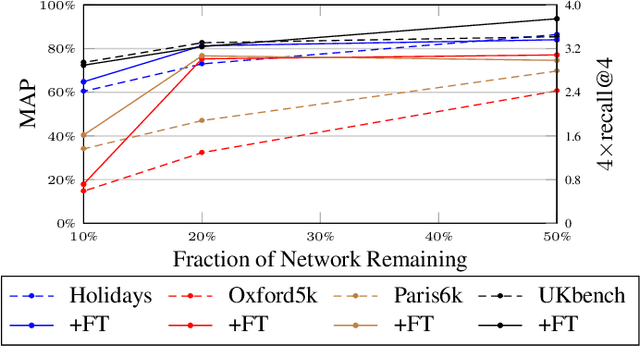
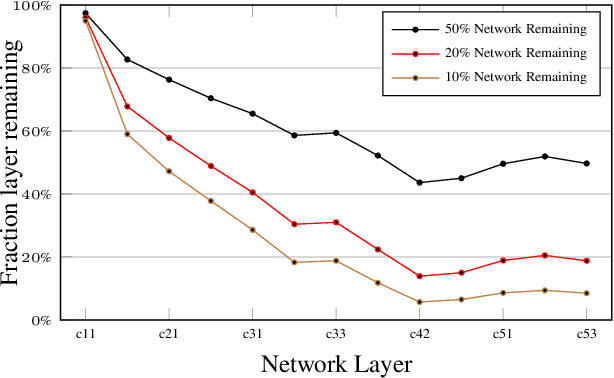
Abstract:In this work, we focus on the problem of image instance retrieval with deep descriptors extracted from pruned Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN). The objective is to heavily prune convolutional edges while maintaining retrieval performance. To this end, we introduce both data-independent and data-dependent heuristics to prune convolutional edges, and evaluate their performance across various compression rates with different deep descriptors over several benchmark datasets. Further, we present an end-to-end framework to fine-tune the pruned network, with a triplet loss function specially designed for the retrieval task. We show that the combination of heuristic pruning and fine-tuning offers 5x compression rate without considerable loss in retrieval performance.
Truly Multi-modal YouTube-8M Video Classification with Video, Audio, and Text
Jul 10, 2017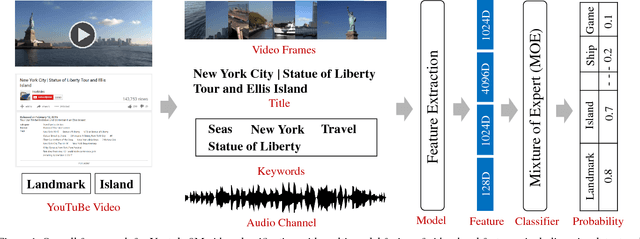
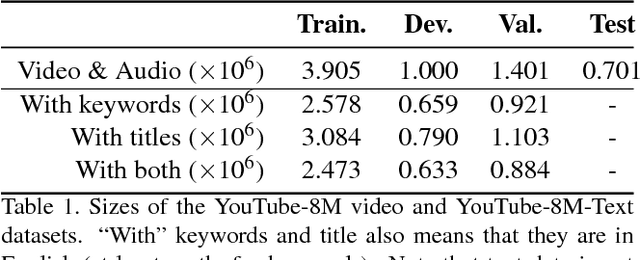
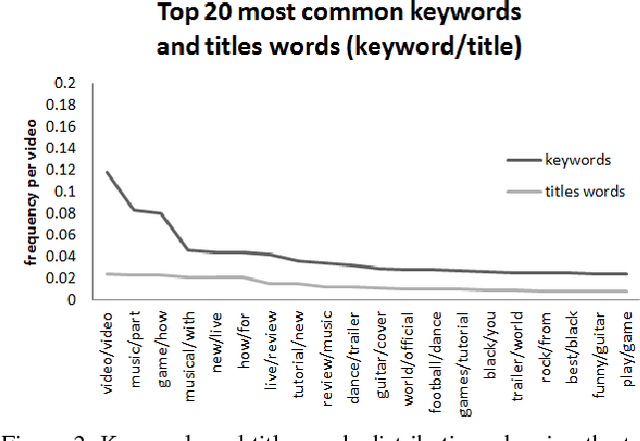
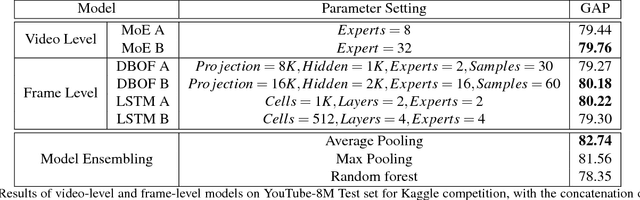
Abstract:The YouTube-8M video classification challenge requires teams to classify 0.7 million videos into one or more of 4,716 classes. In this Kaggle competition, we placed in the top 3% out of 650 participants using released video and audio features. Beyond that, we extend the original competition by including text information in the classification, making this a truly multi-modal approach with vision, audio and text. The newly introduced text data is termed as YouTube-8M-Text. We present a classification framework for the joint use of text, visual and audio features, and conduct an extensive set of experiments to quantify the benefit that this additional mode brings. The inclusion of text yields state-of-the-art results, e.g. 86.7% GAP on the YouTube-8M-Text validation dataset.
Deep Learning for Lung Cancer Detection: Tackling the Kaggle Data Science Bowl 2017 Challenge
May 26, 2017
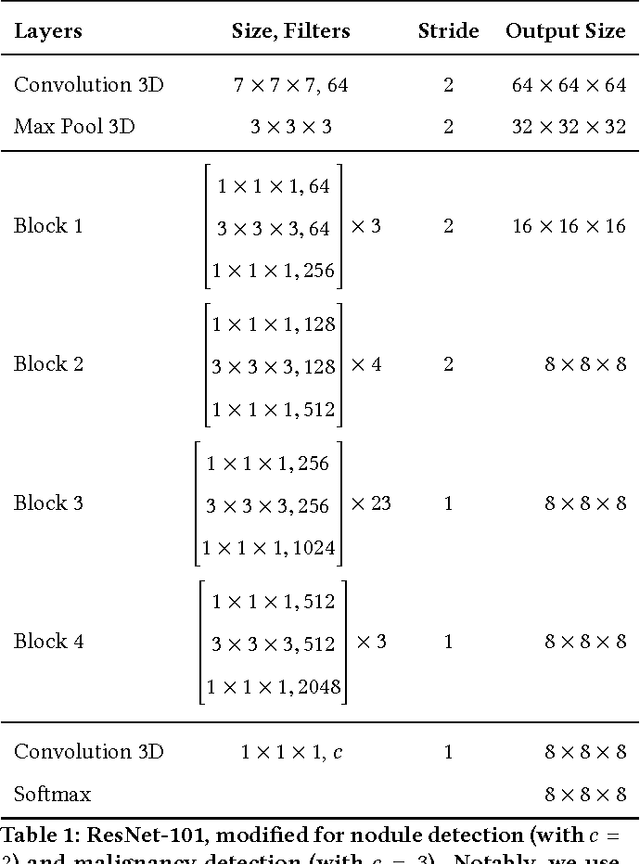
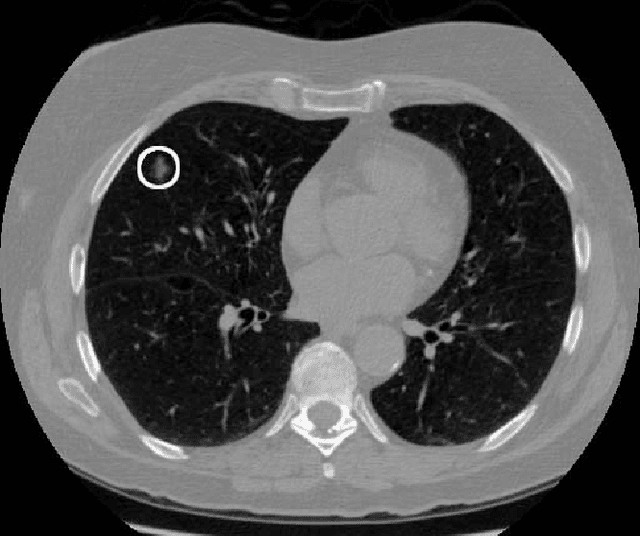
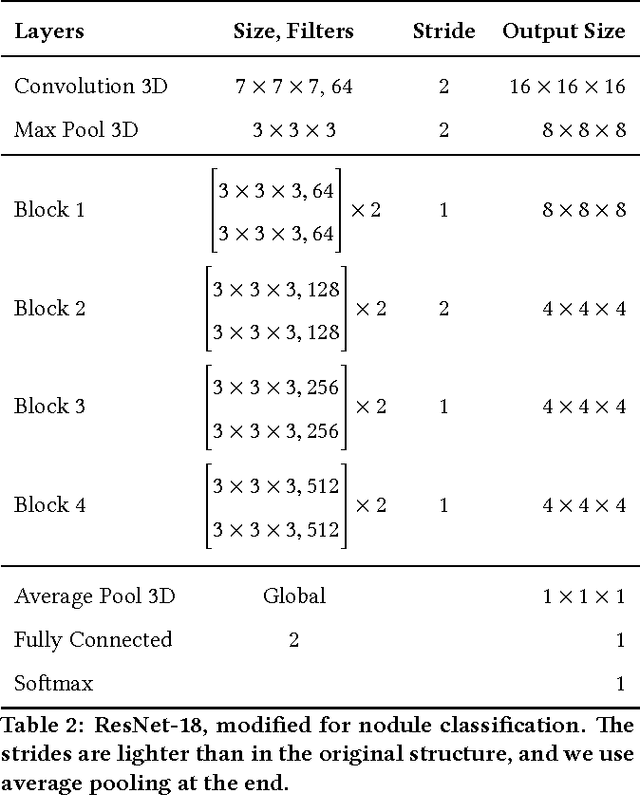
Abstract:We present a deep learning framework for computer-aided lung cancer diagnosis. Our multi-stage framework detects nodules in 3D lung CAT scans, determines if each nodule is malignant, and finally assigns a cancer probability based on these results. We discuss the challenges and advantages of our framework. In the Kaggle Data Science Bowl 2017, our framework ranked 41st out of 1972 teams.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge