Fengpeng Yue
TRIP-Bench: A Benchmark for Long-Horizon Interactive Agents in Real-World Scenarios
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:As LLM-based agents are deployed in increasingly complex real-world settings, existing benchmarks underrepresent key challenges such as enforcing global constraints, coordinating multi-tool reasoning, and adapting to evolving user behavior over long, multi-turn interactions. To bridge this gap, we introduce \textbf{TRIP-Bench}, a long-horizon benchmark grounded in realistic travel-planning scenarios. TRIP-Bench leverages real-world data, offers 18 curated tools and 40+ travel requirements, and supports automated evaluation. It includes splits of varying difficulty; the hard split emphasizes long and ambiguous interactions, style shifts, feasibility changes, and iterative version revision. Dialogues span up to 15 user turns, can involve 150+ tool calls, and may exceed 200k tokens of context. Experiments show that even advanced models achieve at most 50\% success on the easy split, with performance dropping below 10\% on hard subsets. We further propose \textbf{GTPO}, an online multi-turn reinforcement learning method with specialized reward normalization and reward differencing. Applied to Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct, GTPO improves constraint satisfaction and interaction robustness, outperforming Gemini-3-Pro in our evaluation. We expect TRIP-Bench to advance practical long-horizon interactive agents, and GTPO to provide an effective online RL recipe for robust long-horizon training.
PolyVoice: Language Models for Speech to Speech Translation
Jun 13, 2023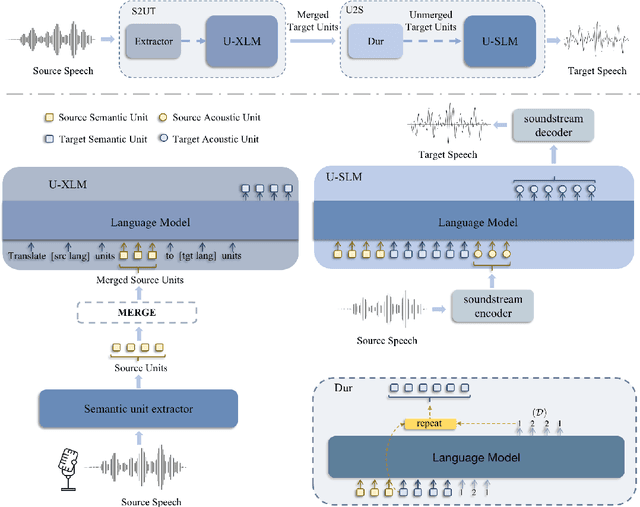

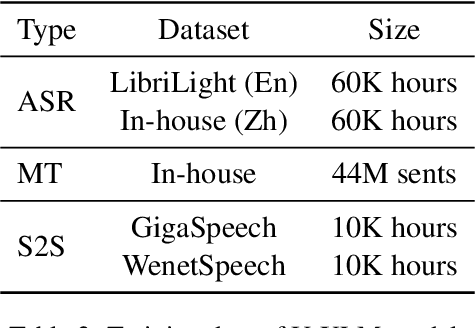
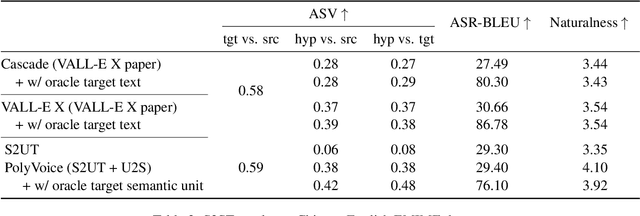
Abstract:We propose PolyVoice, a language model-based framework for speech-to-speech translation (S2ST) system. Our framework consists of two language models: a translation language model and a speech synthesis language model. We use discretized speech units, which are generated in a fully unsupervised way, and thus our framework can be used for unwritten languages. For the speech synthesis part, we adopt the existing VALL-E X approach and build a unit-based audio language model. This grants our framework the ability to preserve the voice characteristics and the speaking style of the original speech. We examine our system on Chinese $\rightarrow$ English and English $\rightarrow$ Spanish pairs. Experimental results show that our system can generate speech with high translation quality and audio quality. Speech samples are available at https://speechtranslation.github.io/polyvoice.
M3ST: Mix at Three Levels for Speech Translation
Dec 07, 2022Abstract:How to solve the data scarcity problem for end-to-end speech-to-text translation (ST)? It's well known that data augmentation is an efficient method to improve performance for many tasks by enlarging the dataset. In this paper, we propose Mix at three levels for Speech Translation (M^3ST) method to increase the diversity of the augmented training corpus. Specifically, we conduct two phases of fine-tuning based on a pre-trained model using external machine translation (MT) data. In the first stage of fine-tuning, we mix the training corpus at three levels, including word level, sentence level and frame level, and fine-tune the entire model with mixed data. At the second stage of fine-tuning, we take both original speech sequences and original text sequences in parallel into the model to fine-tune the network, and use Jensen-Shannon divergence to regularize their outputs. Experiments on MuST-C speech translation benchmark and analysis show that M^3ST outperforms current strong baselines and achieves state-of-the-art results on eight directions with an average BLEU of 29.9.
Leveraging Pseudo-labeled Data to Improve Direct Speech-to-Speech Translation
May 18, 2022



Abstract:Direct Speech-to-speech translation (S2ST) has drawn more and more attention recently. The task is very challenging due to data scarcity and complex speech-to-speech mapping. In this paper, we report our recent achievements in S2ST. Firstly, we build a S2ST Transformer baseline which outperforms the original Translatotron. Secondly, we utilize the external data by pseudo-labeling and obtain a new state-of-the-art result on the Fisher English-to-Spanish test set. Indeed, we exploit the pseudo data with a combination of popular techniques which are not trivial when applied to S2ST. Moreover, we evaluate our approach on both syntactically similar (Spanish-English) and distant (English-Chinese) language pairs. Our implementation is available at https://github.com/fengpeng-yue/speech-to-speech-translation.
Exploring Machine Speech Chain for Domain Adaptation and Few-Shot Speaker Adaptation
Apr 08, 2021



Abstract:Machine Speech Chain, which integrates both end-to-end (E2E) automatic speech recognition (ASR) and text-to-speech (TTS) into one circle for joint training, has been proven to be effective in data augmentation by leveraging large amounts of unpaired data. In this paper, we explore the TTS->ASR pipeline in speech chain to do domain adaptation for both neural TTS and E2E ASR models, with only text data from target domain. We conduct experiments by adapting from audiobook domain (LibriSpeech) to presentation domain (TED-LIUM), there is a relative word error rate (WER) reduction of 10% for the E2E ASR model on the TED-LIUM test set, and a relative WER reduction of 51.5% in synthetic speech generated by neural TTS in the presentation domain. Further, we apply few-shot speaker adaptation for the E2E ASR by using a few utterances from target speakers in an unsupervised way, results in additional gains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge