Eric A. Hoffman
Multi-View Transformers for Airway-To-Lung Ratio Inference on Cardiac CT Scans: The C4R Study
Jan 15, 2025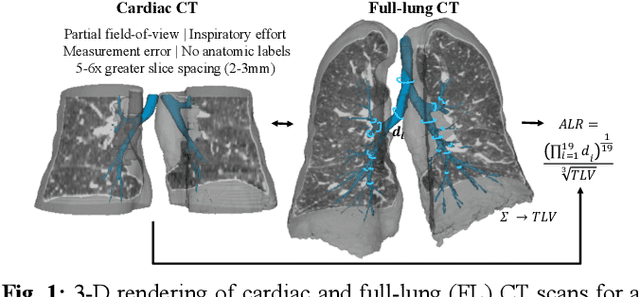
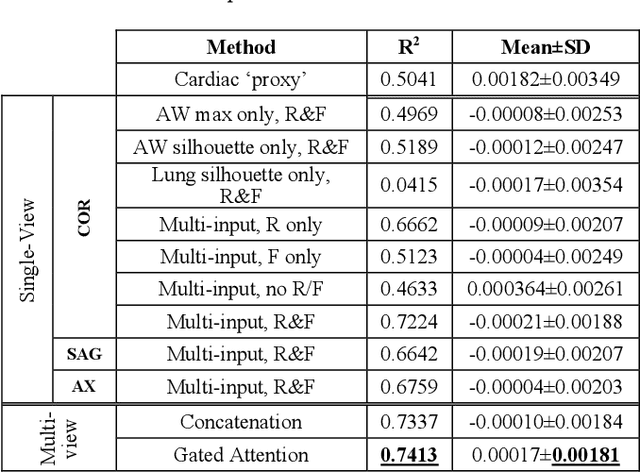
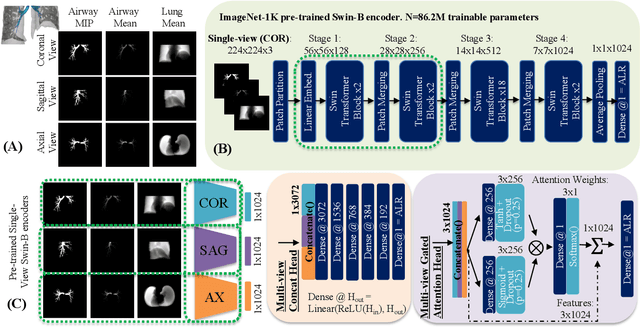
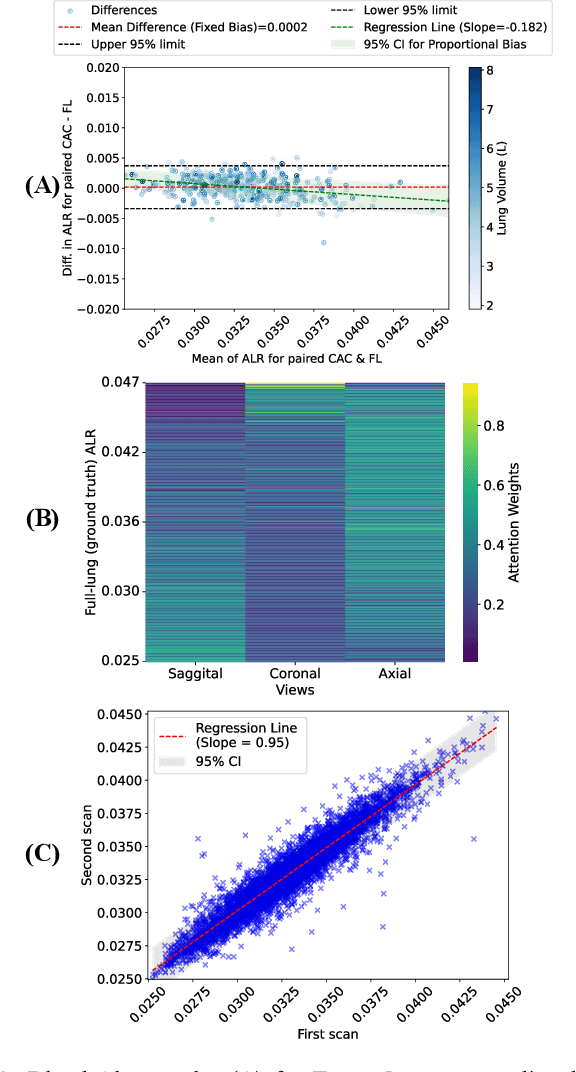
Abstract:The ratio of airway tree lumen to lung size (ALR), assessed at full inspiration on high resolution full-lung computed tomography (CT), is a major risk factor for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). There is growing interest to infer ALR from cardiac CT images, which are widely available in epidemiological cohorts, to investigate the relationship of ALR to severe COVID-19 and post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC). Previously, cardiac scans included approximately 2/3 of the total lung volume with 5-6x greater slice thickness than high-resolution (HR) full-lung (FL) CT. In this study, we present a novel attention-based Multi-view Swin Transformer to infer FL ALR values from segmented cardiac CT scans. For the supervised training we exploit paired full-lung and cardiac CTs acquired in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Our network significantly outperforms a proxy direct ALR inference on segmented cardiac CT scans and achieves accuracy and reproducibility comparable with a scan-rescan reproducibility of the FL ALR ground-truth.
Robust Quantification of Percent Emphysema on CT via Domain Attention: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) Lung Study
Mar 06, 2024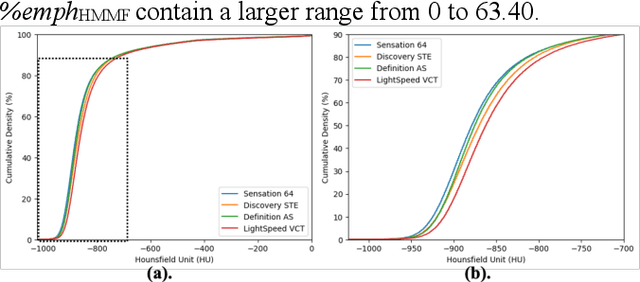
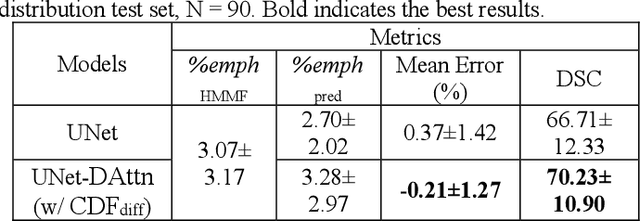
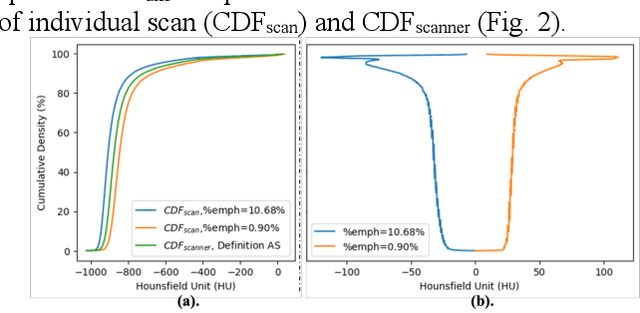
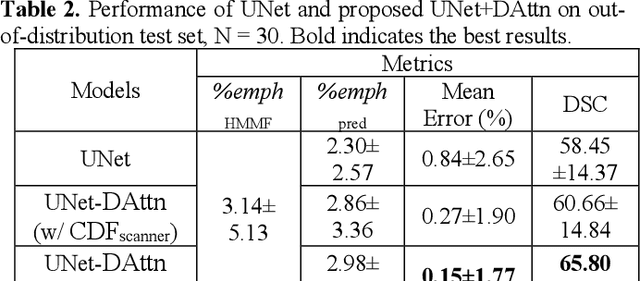
Abstract:Robust quantification of pulmonary emphysema on computed tomography (CT) remains challenging for large-scale research studies that involve scans from different scanner types and for translation to clinical scans. Existing studies have explored several directions to tackle this challenge, including density correction, noise filtering, regression, hidden Markov measure field (HMMF) model-based segmentation, and volume-adjusted lung density. Despite some promising results, previous studies either required a tedious workflow or limited opportunities for downstream emphysema subtyping, limiting efficient adaptation on a large-scale study. To alleviate this dilemma, we developed an end-to-end deep learning framework based on an existing HMMF segmentation framework. We first demonstrate that a regular UNet cannot replicate the existing HMMF results because of the lack of scanner priors. We then design a novel domain attention block to fuse image feature with quantitative scanner priors which significantly improves the results.
Robust deep labeling of radiological emphysema subtypes using squeeze and excitation convolutional neural networks: The MESA Lung and SPIROMICS Studies
Mar 01, 2024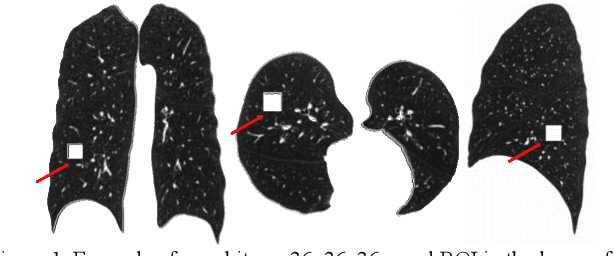
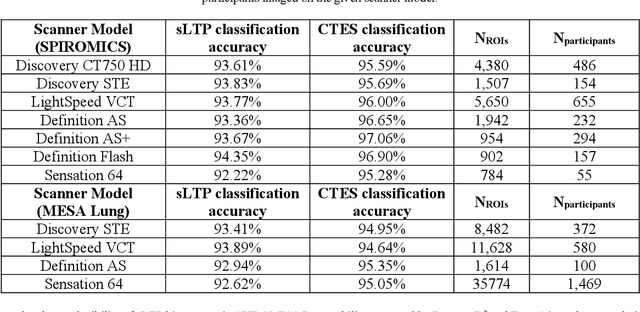
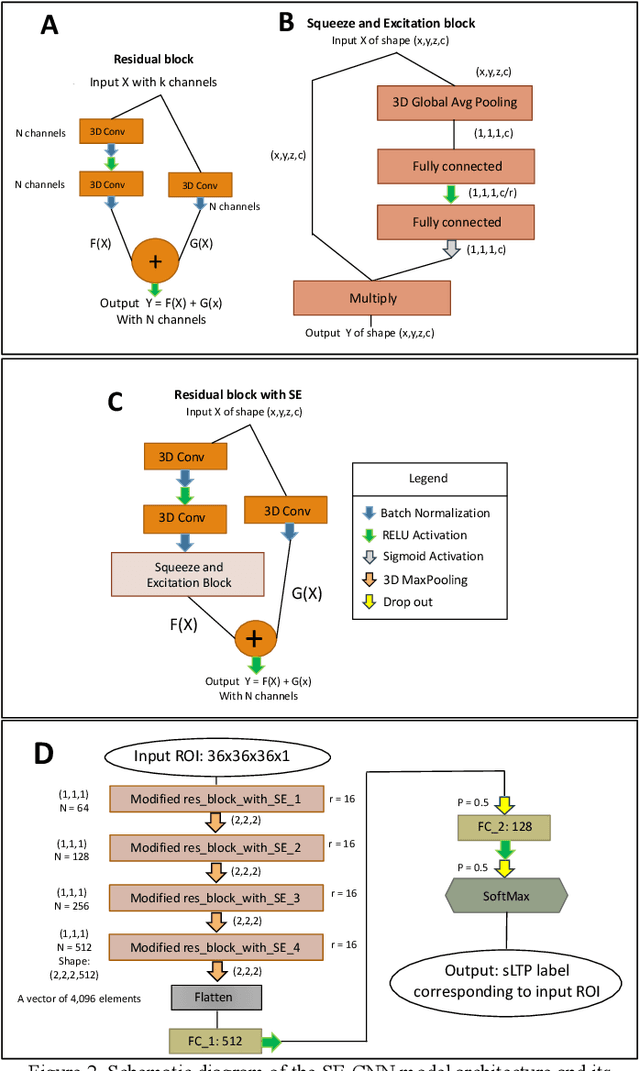
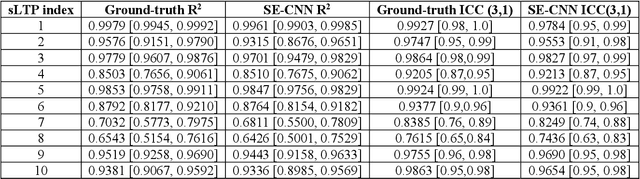
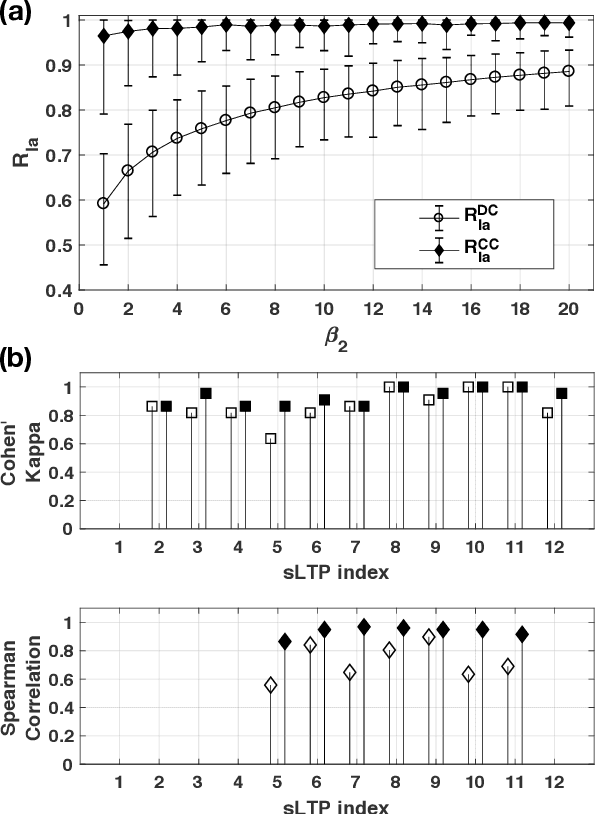
Abstract:Pulmonary emphysema, the progressive, irreversible loss of lung tissue, is conventionally categorized into three subtypes identifiable on pathology and on lung computed tomography (CT) images. Recent work has led to the unsupervised learning of ten spatially-informed lung texture patterns (sLTPs) on lung CT, representing distinct patterns of emphysematous lung parenchyma based on both textural appearance and spatial location within the lung, and which aggregate into 6 robust and reproducible CT Emphysema Subtypes (CTES). Existing methods for sLTP segmentation, however, are slow and highly sensitive to changes in CT acquisition protocol. In this work, we present a robust 3-D squeeze-and-excitation CNN for supervised classification of sLTPs and CTES on lung CT. Our results demonstrate that this model achieves accurate and reproducible sLTP segmentation on lung CTscans, across two independent cohorts and independently of scanner manufacturer and model.
Unsupervised Airway Tree Clustering with Deep Learning: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) Lung Study
Feb 28, 2024


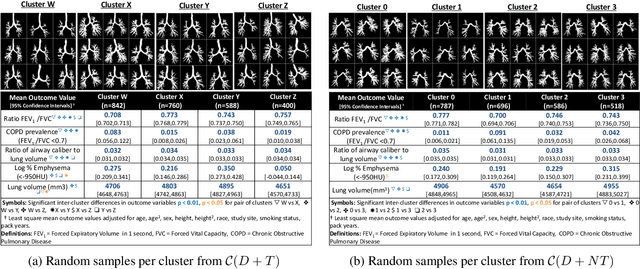
Abstract:High-resolution full lung CT scans now enable the detailed segmentation of airway trees up to the 6th branching generation. The airway binary masks display very complex tree structures that may encode biological information relevant to disease risk and yet remain challenging to exploit via traditional methods such as meshing or skeletonization. Recent clinical studies suggest that some variations in shape patterns and caliber of the human airway tree are highly associated with adverse health outcomes, including all-cause mortality and incident COPD. However, quantitative characterization of variations observed on CT segmented airway tree remain incomplete, as does our understanding of the clinical and developmental implications of such. In this work, we present an unsupervised deep-learning pipeline for feature extraction and clustering of human airway trees, learned directly from projections of 3D airway segmentations. We identify four reproducible and clinically distinct airway sub-types in the MESA Lung CT cohort.
Lung2Lung: Volumetric Style Transfer with Self-Ensembling for High-Resolution Cross-Volume Computed Tomography
Oct 06, 2022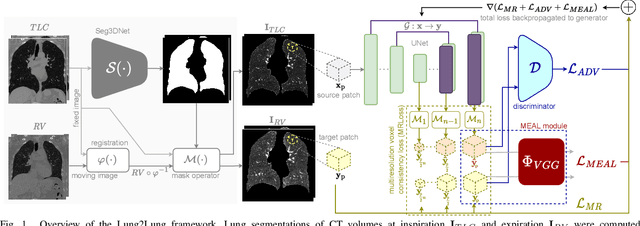
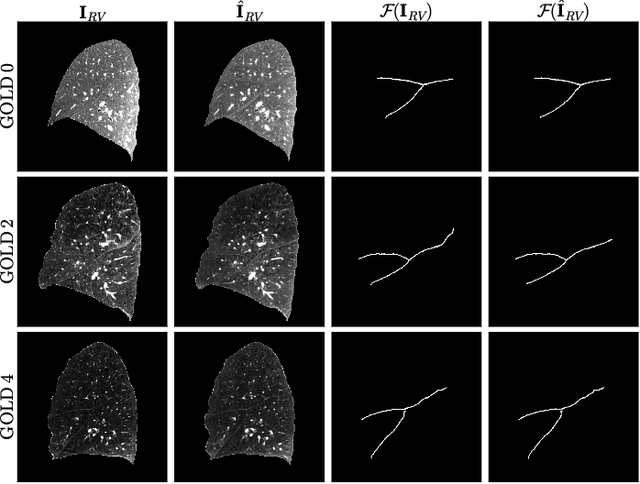
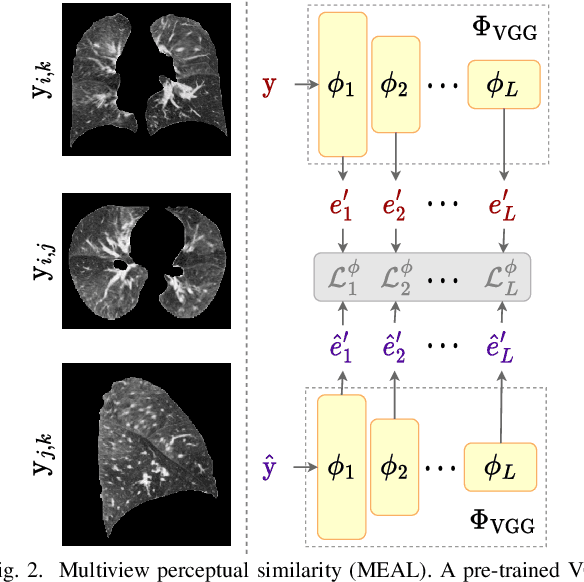
Abstract:Chest computed tomography (CT) at inspiration is often complemented by an expiratory CT for identifying peripheral airways disease in the form of air trapping. Additionally, co-registered inspiratory-expiratory volumes are used to derive several clinically relevant measures of local lung function. Acquiring CT at different volumes, however, increases radiation dosage, acquisition time, and may not be achievable due to various complications, limiting the utility of registration-based measures, To address this, we propose Lung2Lung - a style-based generative adversarial approach for translating CT images from end-inspiratory to end-expiratory volume. Lung2Lung addresses several limitations of the traditional generative models including slicewise discontinuities, limited size of generated volumes, and their inability to model neural style at a volumetric level. We introduce multiview perceptual similarity (MEAL) to capture neural styles in 3D. To incorporate global information into the training process and refine the output of our model, we also propose self-ensembling (SE). Lung2Lung, with MEAL and SE, is able to generate large 3D volumes of size 320 x 320 x 320 that are validated using a diverse cohort of 1500 subjects with varying disease severity. The model shows superior performance against several state-of-the-art 2D and 3D generative models with a peak-signal-to-noise ratio of 24.53 dB and structural similarity of 0.904. Clinical validation shows that the synthetic volumes can be used to reliably extract several clinical endpoints of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
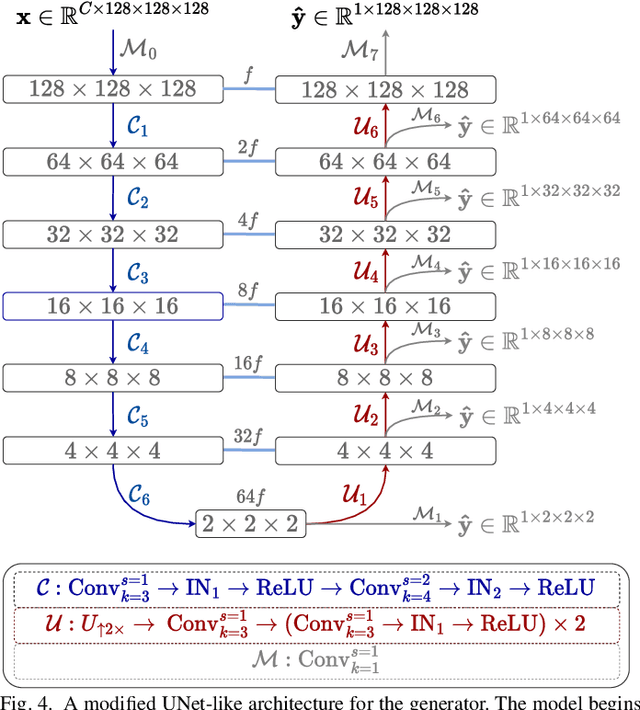
Single volume lung biomechanics from chest computed tomography using a mode preserving generative adversarial network
Oct 15, 2021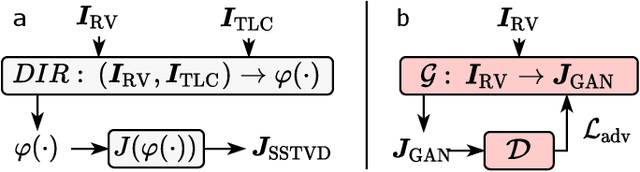
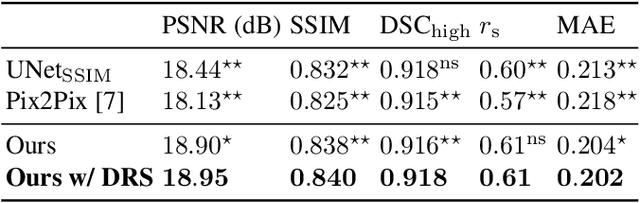
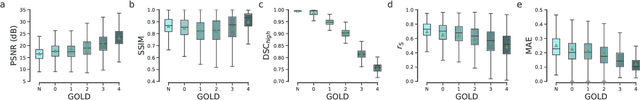
Abstract:Local tissue expansion of the lungs is typically derived by registering computed tomography (CT) scans acquired at multiple lung volumes. However, acquiring multiple scans incurs increased radiation dose, time, and cost, and may not be possible in many cases, thus restricting the applicability of registration-based biomechanics. We propose a generative adversarial learning approach for estimating local tissue expansion directly from a single CT scan. The proposed framework was trained and evaluated on 2500 subjects from the SPIROMICS cohort. Once trained, the framework can be used as a registration-free method for predicting local tissue expansion. We evaluated model performance across varying degrees of disease severity and compared its performance with two image-to-image translation frameworks - UNet and Pix2Pix. Our model achieved an overall PSNR of 18.95 decibels, SSIM of 0.840, and Spearman's correlation of 0.61 at a high spatial resolution of 1 mm3.
CT Image Segmentation for Inflamed and Fibrotic Lungs Using a Multi-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network
Oct 16, 2020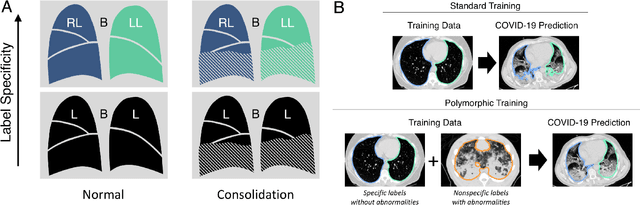
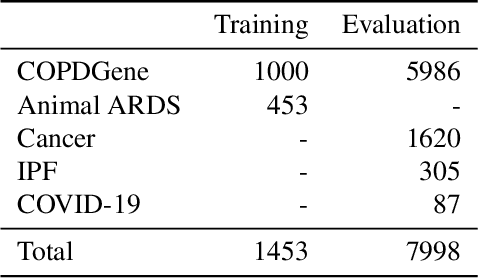
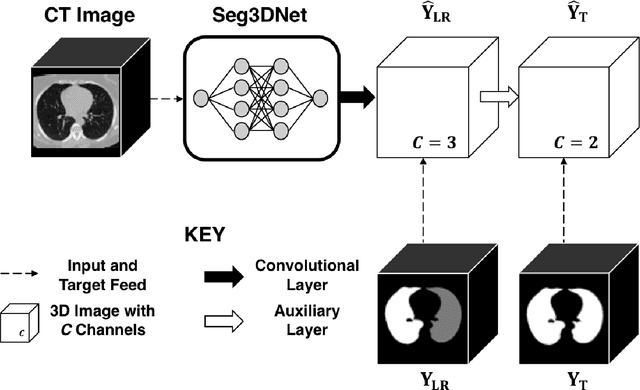
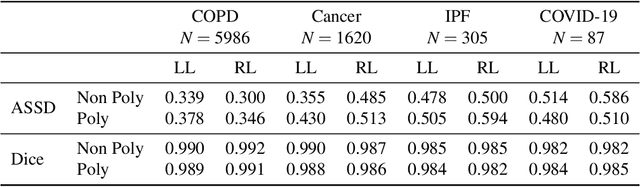
Abstract:The purpose of this study was to develop a fully-automated segmentation algorithm, robust to various density enhancing lung abnormalities, to facilitate rapid quantitative analysis of computed tomography images. A polymorphic training approach is proposed, in which both specifically labeled left and right lungs of humans with COPD, and nonspecifically labeled lungs of animals with acute lung injury, were incorporated into training a single neural network. The resulting network is intended for predicting left and right lung regions in humans with or without diffuse opacification and consolidation. Performance of the proposed lung segmentation algorithm was extensively evaluated on CT scans of subjects with COPD, confirmed COVID-19, lung cancer, and IPF, despite no labeled training data of the latter three diseases. Lobar segmentations were obtained using the left and right lung segmentation as input to the LobeNet algorithm. Regional lobar analysis was performed using hierarchical clustering to identify radiographic subtypes of COVID-19. The proposed lung segmentation algorithm was quantitatively evaluated using semi-automated and manually-corrected segmentations in 87 COVID-19 CT images, achieving an average symmetric surface distance of $0.495 \pm 0.309$ mm and Dice coefficient of $0.985 \pm 0.011$. Hierarchical clustering identified four radiographical phenotypes of COVID-19 based on lobar fractions of consolidated and poorly aerated tissue. Lower left and lower right lobes were consistently more afflicted with poor aeration and consolidation. However, the most severe cases demonstrated involvement of all lobes. The polymorphic training approach was able to accurately segment COVID-19 cases with diffuse consolidation without requiring COVID-19 cases for training.
Novel Subtypes of Pulmonary Emphysema Based on Spatially-Informed Lung Texture Learning
Jul 09, 2020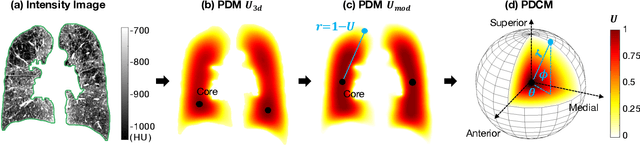
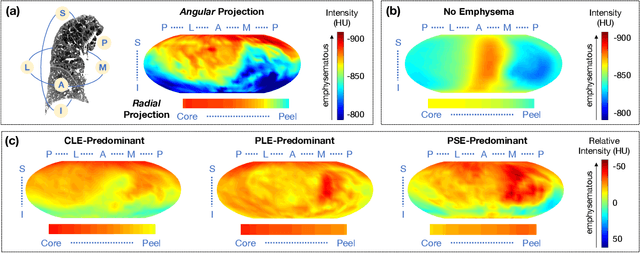
Abstract:Pulmonary emphysema overlaps considerably with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and is traditionally subcategorized into three subtypes previously identified on autopsy. Unsupervised learning of emphysema subtypes on computed tomography (CT) opens the way to new definitions of emphysema subtypes and eliminates the need of thorough manual labeling. However, CT-based emphysema subtypes have been limited to texture-based patterns without considering spatial location. In this work, we introduce a standardized spatial mapping of the lung for quantitative study of lung texture location, and propose a novel framework for combining spatial and texture information to discover spatially-informed lung texture patterns (sLTPs) that represent novel emphysema subtypes. Exploiting two cohorts of full-lung CT scans from the MESA COPD and EMCAP studies, we first show that our spatial mapping enables population-wide study of emphysema spatial location. We then evaluate the characteristics of the sLTPs discovered on MESA COPD, and show that they are reproducible, able to encode standard emphysema subtypes, and associated with physiological symptoms.
Explaining Radiological Emphysema Subtypes with Unsupervised Texture Prototypes: MESA COPD Study
Dec 05, 2016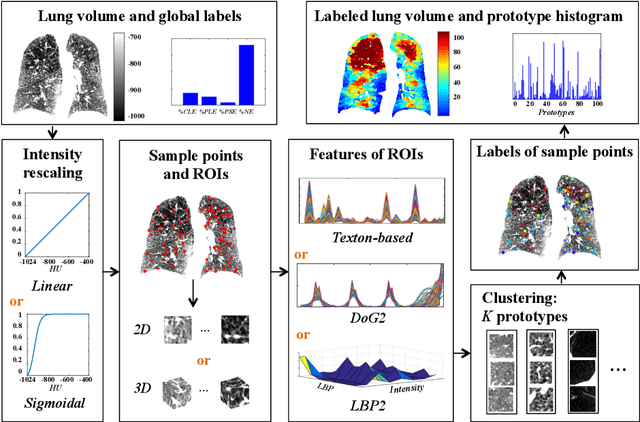
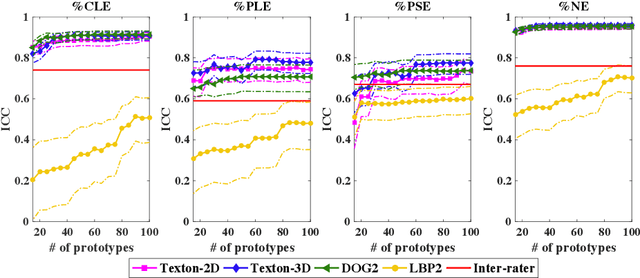
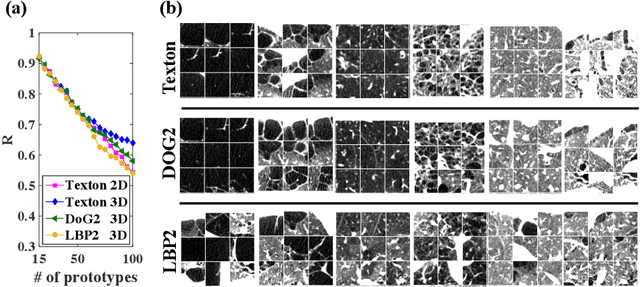

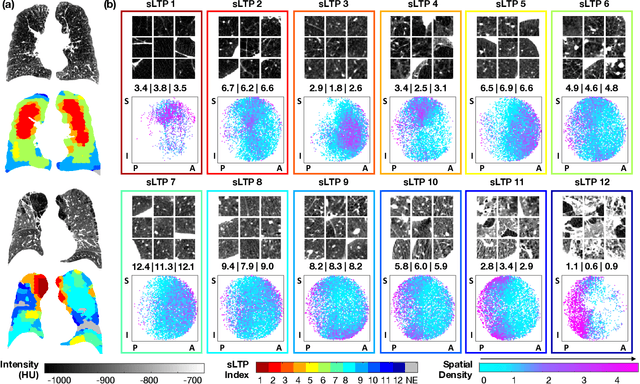
Abstract:Pulmonary emphysema is traditionally subcategorized into three subtypes, which have distinct radiological appearances on computed tomography (CT) and can help with the diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Automated texture-based quantification of emphysema subtypes has been successfully implemented via supervised learning of these three emphysema subtypes. In this work, we demonstrate that unsupervised learning on a large heterogeneous database of CT scans can generate texture prototypes that are visually homogeneous and distinct, reproducible across subjects, and capable of predicting accurately the three standard radiological subtypes. These texture prototypes enable automated labeling of lung volumes, and open the way to new interpretations of lung CT scans with finer subtyping of emphysema.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge