Robust Quantification of Percent Emphysema on CT via Domain Attention: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) Lung Study
Paper and Code
Mar 06, 2024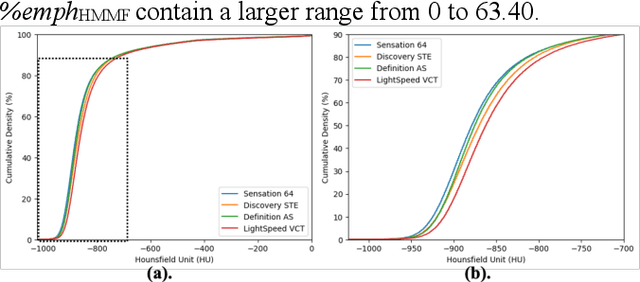
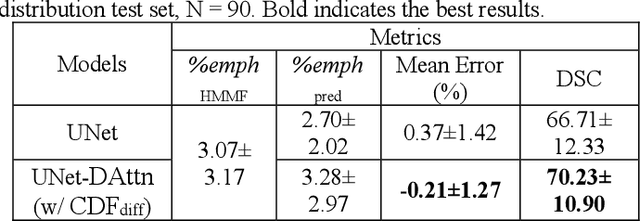
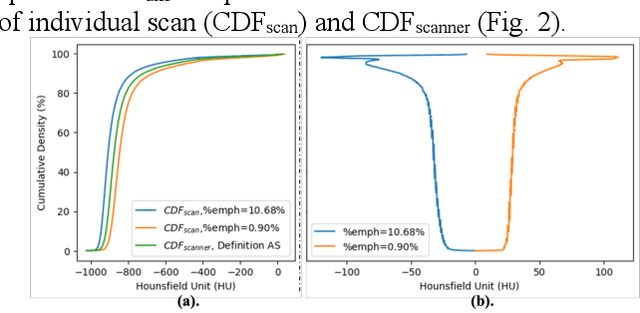
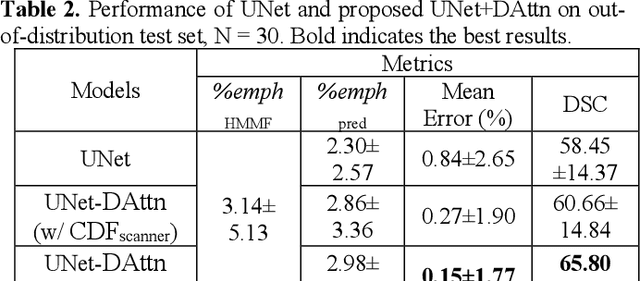
Robust quantification of pulmonary emphysema on computed tomography (CT) remains challenging for large-scale research studies that involve scans from different scanner types and for translation to clinical scans. Existing studies have explored several directions to tackle this challenge, including density correction, noise filtering, regression, hidden Markov measure field (HMMF) model-based segmentation, and volume-adjusted lung density. Despite some promising results, previous studies either required a tedious workflow or limited opportunities for downstream emphysema subtyping, limiting efficient adaptation on a large-scale study. To alleviate this dilemma, we developed an end-to-end deep learning framework based on an existing HMMF segmentation framework. We first demonstrate that a regular UNet cannot replicate the existing HMMF results because of the lack of scanner priors. We then design a novel domain attention block to fuse image feature with quantitative scanner priors which significantly improves the results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge