Enrico Palumbo
Text2Tracks: Prompt-based Music Recommendation via Generative Retrieval
Mar 31, 2025



Abstract:In recent years, Large Language Models (LLMs) have enabled users to provide highly specific music recommendation requests using natural language prompts (e.g. "Can you recommend some old classics for slow dancing?"). In this setup, the recommended tracks are predicted by the LLM in an autoregressive way, i.e. the LLM generates the track titles one token at a time. While intuitive, this approach has several limitation. First, it is based on a general purpose tokenization that is optimized for words rather than for track titles. Second, it necessitates an additional entity resolution layer that matches the track title to the actual track identifier. Third, the number of decoding steps scales linearly with the length of the track title, slowing down inference. In this paper, we propose to address the task of prompt-based music recommendation as a generative retrieval task. Within this setting, we introduce novel, effective, and efficient representations of track identifiers that significantly outperform commonly used strategies. We introduce Text2Tracks, a generative retrieval model that learns a mapping from a user's music recommendation prompt to the relevant track IDs directly. Through an offline evaluation on a dataset of playlists with language inputs, we find that (1) the strategy to create IDs for music tracks is the most important factor for the effectiveness of Text2Tracks and semantic IDs significantly outperform commonly used strategies that rely on song titles as identifiers (2) provided with the right choice of track identifiers, Text2Tracks outperforms sparse and dense retrieval solutions trained to retrieve tracks from language prompts.
Bridging Search and Recommendation in Generative Retrieval: Does One Task Help the Other?
Oct 22, 2024Abstract:Generative retrieval for search and recommendation is a promising paradigm for retrieving items, offering an alternative to traditional methods that depend on external indexes and nearest-neighbor searches. Instead, generative models directly associate inputs with item IDs. Given the breakthroughs of Large Language Models (LLMs), these generative systems can play a crucial role in centralizing a variety of Information Retrieval (IR) tasks in a single model that performs tasks such as query understanding, retrieval, recommendation, explanation, re-ranking, and response generation. Despite the growing interest in such a unified generative approach for IR systems, the advantages of using a single, multi-task model over multiple specialized models are not well established in the literature. This paper investigates whether and when such a unified approach can outperform task-specific models in the IR tasks of search and recommendation, broadly co-existing in multiple industrial online platforms, such as Spotify, YouTube, and Netflix. Previous work shows that (1) the latent representations of items learned by generative recommenders are biased towards popularity, and (2) content-based and collaborative-filtering-based information can improve an item's representations. Motivated by this, our study is guided by two hypotheses: [H1] the joint training regularizes the estimation of each item's popularity, and [H2] the joint training regularizes the item's latent representations, where search captures content-based aspects of an item and recommendation captures collaborative-filtering aspects. Our extensive experiments with both simulated and real-world data support both [H1] and [H2] as key contributors to the effectiveness improvements observed in the unified search and recommendation generative models over the single-task approaches.
Generating Query Recommendations via LLMs
Jun 04, 2024Abstract:Query recommendation systems are ubiquitous in modern search engines, assisting users in producing effective queries to meet their information needs. However, these systems require a large amount of data to produce good recommendations, such as a large collection of documents to index and query logs. In particular, query logs and user data are not available in cold start scenarios. Query logs are expensive to collect and maintain and require complex and time-consuming cascading pipelines for creating, combining, and ranking recommendations. To address these issues, we frame the query recommendation problem as a generative task, proposing a novel approach called Generative Query Recommendation (GQR). GQR uses an LLM as its foundation and does not require to be trained or fine-tuned to tackle the query recommendation problem. We design a prompt that enables the LLM to understand the specific recommendation task, even using a single example. We then improved our system by proposing a version that exploits query logs called Retriever-Augmented GQR (RA-GQR). RA-GQr dynamically composes its prompt by retrieving similar queries from query logs. GQR approaches reuses a pre-existing neural architecture resulting in a simpler and more ready-to-market approach, even in a cold start scenario. Our proposed GQR obtains state-of-the-art performance in terms of NDCG@10 and clarity score against two commercial search engines and the previous state-of-the-art approach on the Robust04 and ClueWeb09B collections, improving on average the NDCG@10 performance up to ~4% on Robust04 and ClueWeb09B w.r.t the previous best competitor. RA-GQR further improve the NDCG@10 obtaining an increase of ~11%, ~6\% on Robust04 and ClueWeb09B w.r.t the best competitor. Furthermore, our system obtained ~59% of user preferences in a blind user study, proving that our method produces the most engaging queries.
Towards Graph Foundation Models for Personalization
Mar 12, 2024Abstract:In the realm of personalization, integrating diverse information sources such as consumption signals and content-based representations is becoming increasingly critical to build state-of-the-art solutions. In this regard, two of the biggest trends in research around this subject are Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and Foundation Models (FMs). While GNNs emerged as a popular solution in industry for powering personalization at scale, FMs have only recently caught attention for their promising performance in personalization tasks like ranking and retrieval. In this paper, we present a graph-based foundation modeling approach tailored to personalization. Central to this approach is a Heterogeneous GNN (HGNN) designed to capture multi-hop content and consumption relationships across a range of recommendable item types. To ensure the generality required from a Foundation Model, we employ a Large Language Model (LLM) text-based featurization of nodes that accommodates all item types, and construct the graph using co-interaction signals, which inherently transcend content specificity. To facilitate practical generalization, we further couple the HGNN with an adaptation mechanism based on a two-tower (2T) architecture, which also operates agnostically to content type. This multi-stage approach ensures high scalability; while the HGNN produces general purpose embeddings, the 2T component models in a continuous space the sheer size of user-item interaction data. Our comprehensive approach has been rigorously tested and proven effective in delivering recommendations across a diverse array of products within a real-world, industrial audio streaming platform.
Improving Content Retrievability in Search with Controllable Query Generation
Mar 21, 2023Abstract:An important goal of online platforms is to enable content discovery, i.e. allow users to find a catalog entity they were not familiar with. A pre-requisite to discover an entity, e.g. a book, with a search engine is that the entity is retrievable, i.e. there are queries for which the system will surface such entity in the top results. However, machine-learned search engines have a high retrievability bias, where the majority of the queries return the same entities. This happens partly due to the predominance of narrow intent queries, where users create queries using the title of an already known entity, e.g. in book search 'harry potter'. The amount of broad queries where users want to discover new entities, e.g. in music search 'chill lyrical electronica with an atmospheric feeling to it', and have a higher tolerance to what they might find, is small in comparison. We focus here on two factors that have a negative impact on the retrievability of the entities (I) the training data used for dense retrieval models and (II) the distribution of narrow and broad intent queries issued in the system. We propose CtrlQGen, a method that generates queries for a chosen underlying intent-narrow or broad. We can use CtrlQGen to improve factor (I) by generating training data for dense retrieval models comprised of diverse synthetic queries. CtrlQGen can also be used to deal with factor (II) by suggesting queries with broader intents to users. Our results on datasets from the domains of music, podcasts, and books reveal that we can significantly decrease the retrievability bias of a dense retrieval model when using CtrlQGen. First, by using the generated queries as training data for dense models we make 9% of the entities retrievable (go from zero to non-zero retrievability). Second, by suggesting broader queries to users, we can make 12% of the entities retrievable in the best case.
Alexa Teacher Model: Pretraining and Distilling Multi-Billion-Parameter Encoders for Natural Language Understanding Systems
Jun 15, 2022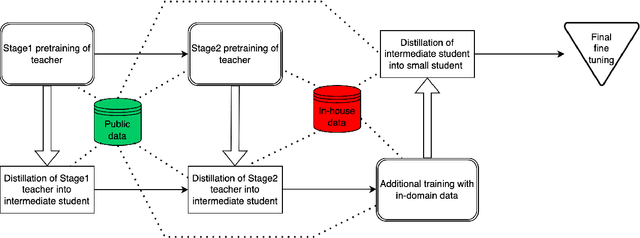
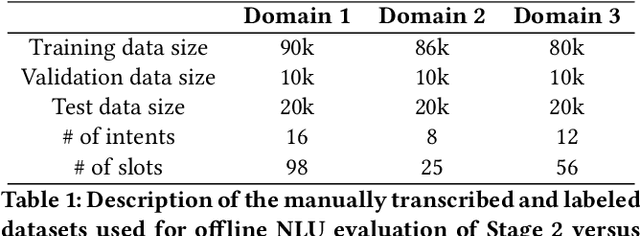
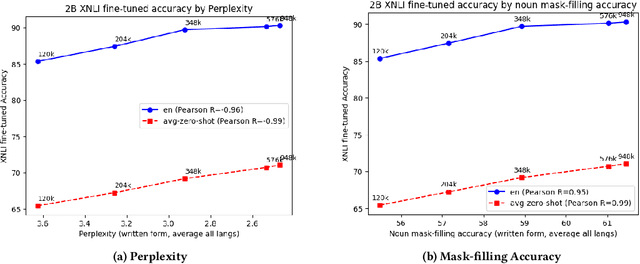
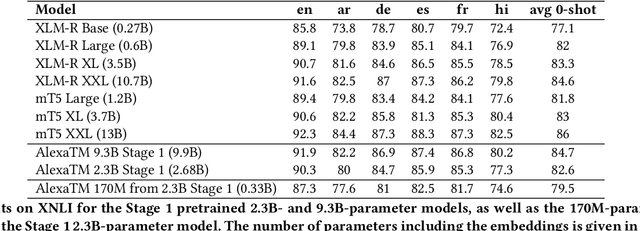
Abstract:We present results from a large-scale experiment on pretraining encoders with non-embedding parameter counts ranging from 700M to 9.3B, their subsequent distillation into smaller models ranging from 17M-170M parameters, and their application to the Natural Language Understanding (NLU) component of a virtual assistant system. Though we train using 70% spoken-form data, our teacher models perform comparably to XLM-R and mT5 when evaluated on the written-form Cross-lingual Natural Language Inference (XNLI) corpus. We perform a second stage of pretraining on our teacher models using in-domain data from our system, improving error rates by 3.86% relative for intent classification and 7.01% relative for slot filling. We find that even a 170M-parameter model distilled from our Stage 2 teacher model has 2.88% better intent classification and 7.69% better slot filling error rates when compared to the 2.3B-parameter teacher trained only on public data (Stage 1), emphasizing the importance of in-domain data for pretraining. When evaluated offline using labeled NLU data, our 17M-parameter Stage 2 distilled model outperforms both XLM-R Base (85M params) and DistillBERT (42M params) by 4.23% to 6.14%, respectively. Finally, we present results from a full virtual assistant experimentation platform, where we find that models trained using our pretraining and distillation pipeline outperform models distilled from 85M-parameter teachers by 3.74%-4.91% on an automatic measurement of full-system user dissatisfaction.
* KDD 2022
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge