Emily Prud'hommeaux
Data-driven Parsing Evaluation for Child-Parent Interactions
Sep 28, 2022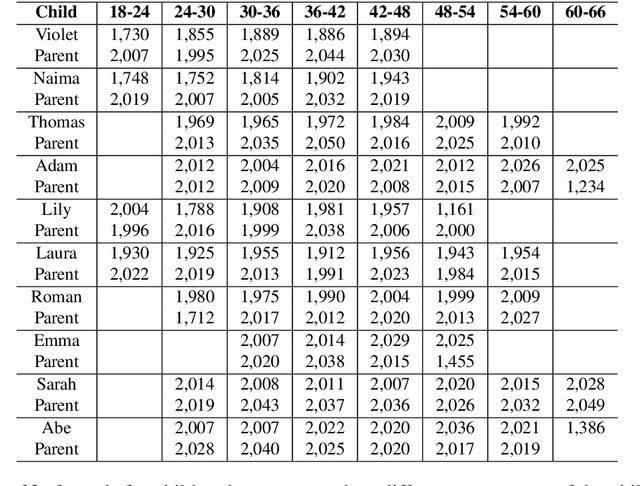
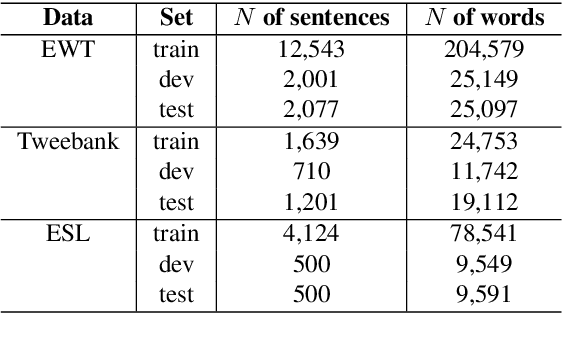
Abstract:We present a syntactic dependency treebank for naturalistic child and child-directed speech in English (MacWhinney, 2000). Our annotations largely followed the guidelines of the Universal Dependencies project (UD (Zeman et al., 2022)), with detailed extensions to lexical/syntactic structures unique to conversational speech (in opposition to written texts). Compared to existing UD-style spoken treebanks as well as other dependency corpora of child-parent interactions specifically, our dataset is of (much) larger size (N of utterances = 44,744; N of words = 233, 907) and contains speech from a total of 10 children covering a wide age range (18-66 months). With this dataset, we ask: (1) How well would state-of-the-art dependency parsers, tailored for the written domain, perform for speech of different interlocutors in spontaneous conversations? (2) What is the relationship between parser performance and the developmental stage of the child? To address these questions, in ongoing work, we are conducting thorough dependency parser evaluations using both graph-based and transition-based parsers with different hyperparameterization, trained from three different types of out-of-domain written texts: news, tweets, and learner data.
Investigating data partitioning strategies for crosslinguistic low-resource ASR evaluation
Aug 26, 2022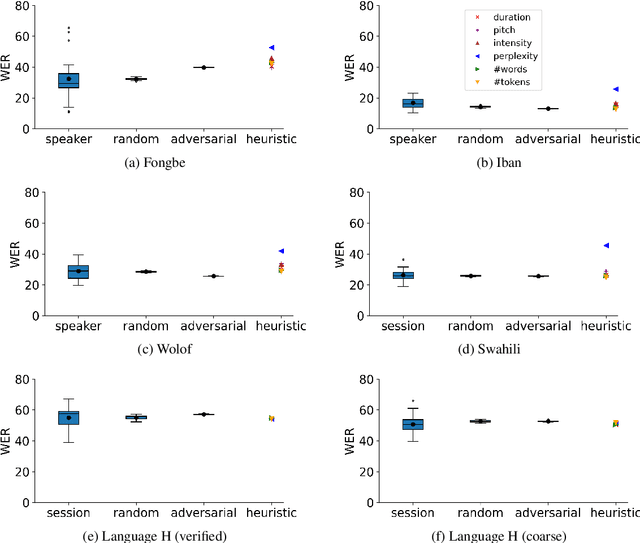
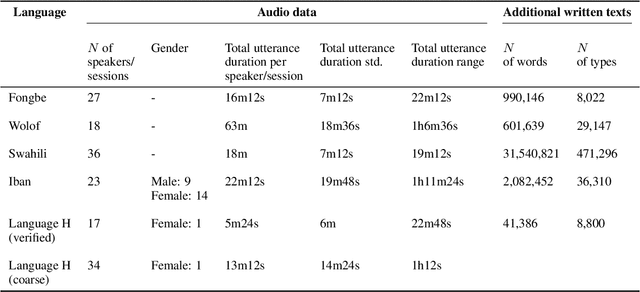
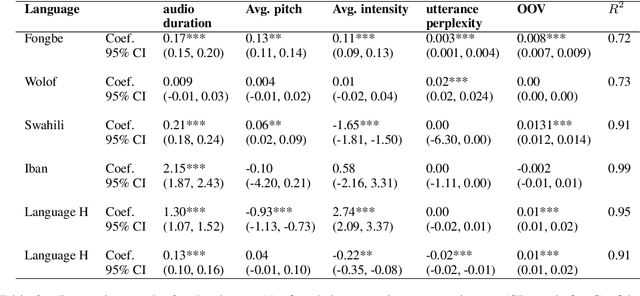
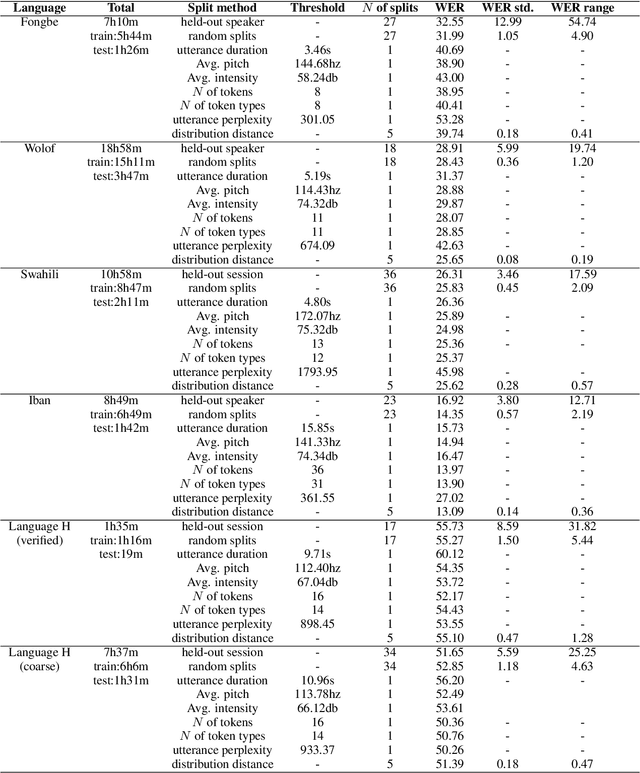
Abstract:Many automatic speech recognition (ASR) data sets include a single pre-defined test set consisting of one or more speakers whose speech never appears in the training set. This "hold-speaker(s)-out" data partitioning strategy, however, may not be ideal for data sets in which the number of speakers is very small. This study investigates ten different data split methods for five languages with minimal ASR training resources. We find that (1) model performance varies greatly depending on which speaker is selected for testing; (2) the average word error rate (WER) across all held-out speakers is comparable not only to the average WER over multiple random splits but also to any given individual random split; (3) WER is also generally comparable when the data is split heuristically or adversarially; (4) utterance duration and intensity are comparatively more predictive factors of variability regardless of the data split. These results suggest that the widely used hold-speakers-out approach to ASR data partitioning can yield results that do not reflect model performance on unseen data or speakers. Random splits can yield more reliable and generalizable estimates when facing data sparsity.
UniMorph 4.0: Universal Morphology
May 10, 2022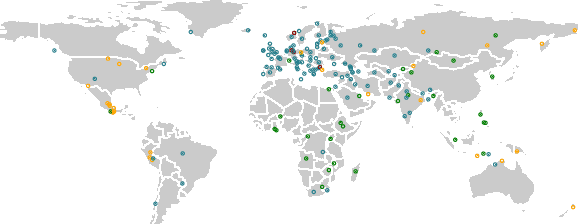
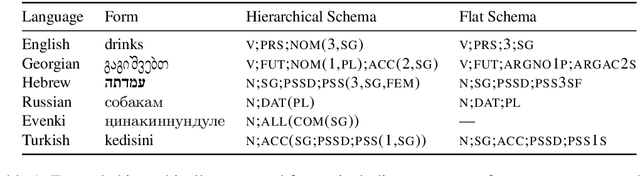
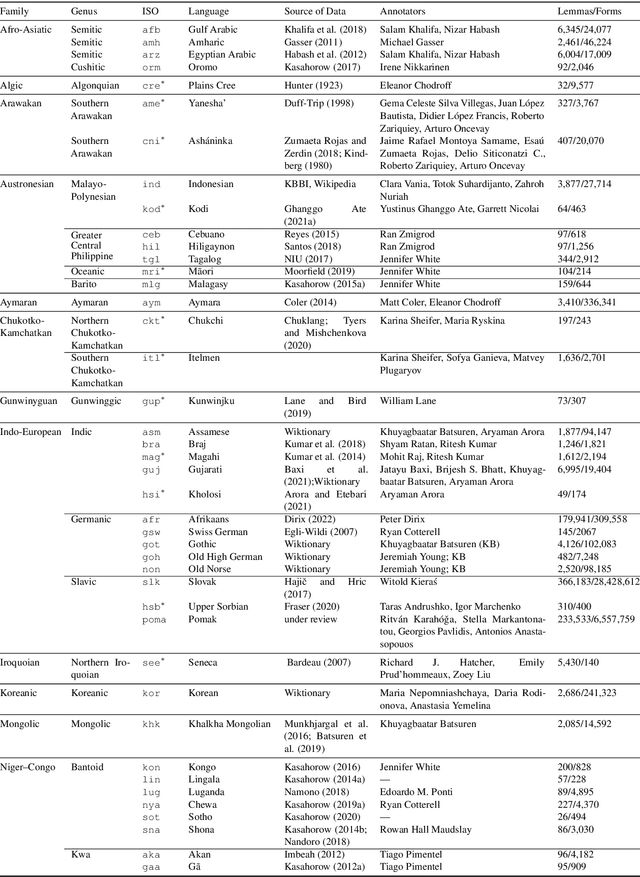
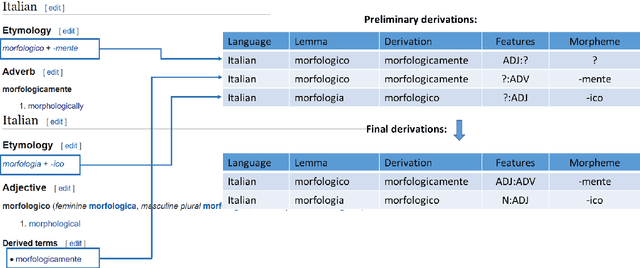
Abstract:The Universal Morphology (UniMorph) project is a collaborative effort providing broad-coverage instantiated normalized morphological inflection tables for hundreds of diverse world languages. The project comprises two major thrusts: a language-independent feature schema for rich morphological annotation and a type-level resource of annotated data in diverse languages realizing that schema. This paper presents the expansions and improvements made on several fronts over the last couple of years (since McCarthy et al. (2020)). Collaborative efforts by numerous linguists have added 67 new languages, including 30 endangered languages. We have implemented several improvements to the extraction pipeline to tackle some issues, e.g. missing gender and macron information. We have also amended the schema to use a hierarchical structure that is needed for morphological phenomena like multiple-argument agreement and case stacking, while adding some missing morphological features to make the schema more inclusive. In light of the last UniMorph release, we also augmented the database with morpheme segmentation for 16 languages. Lastly, this new release makes a push towards inclusion of derivational morphology in UniMorph by enriching the data and annotation schema with instances representing derivational processes from MorphyNet.
Not always about you: Prioritizing community needs when developing endangered language technology
Apr 12, 2022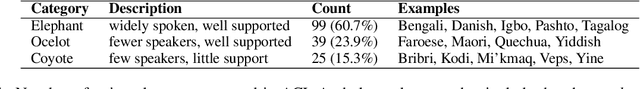

Abstract:Languages are classified as low-resource when they lack the quantity of data necessary for training statistical and machine learning tools and models. Causes of resource scarcity vary but can include poor access to technology for developing these resources, a relatively small population of speakers, or a lack of urgency for collecting such resources in bilingual populations where the second language is high-resource. As a result, the languages described as low-resource in the literature are as different as Finnish on the one hand, with millions of speakers using it in every imaginable domain, and Seneca, with only a small-handful of fluent speakers using the language primarily in a restricted domain. While issues stemming from the lack of resources necessary to train models unite this disparate group of languages, many other issues cut across the divide between widely-spoken low resource languages and endangered languages. In this position paper, we discuss the unique technological, cultural, practical, and ethical challenges that researchers and indigenous speech community members face when working together to develop language technology to support endangered language documentation and revitalization. We report the perspectives of language teachers, Master Speakers and elders from indigenous communities, as well as the point of view of academics. We describe an ongoing fruitful collaboration and make recommendations for future partnerships between academic researchers and language community stakeholders.
Data-driven Model Generalizability in Crosslinguistic Low-resource Morphological Segmentation
Jan 05, 2022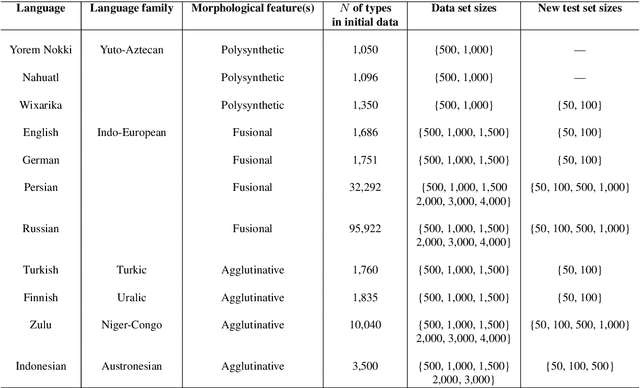
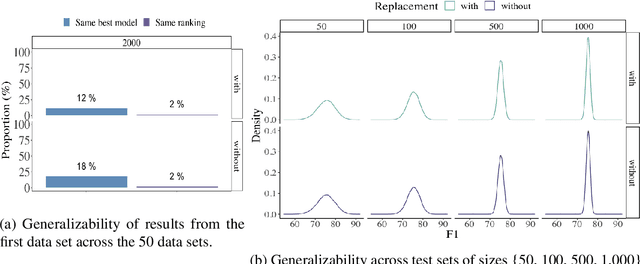
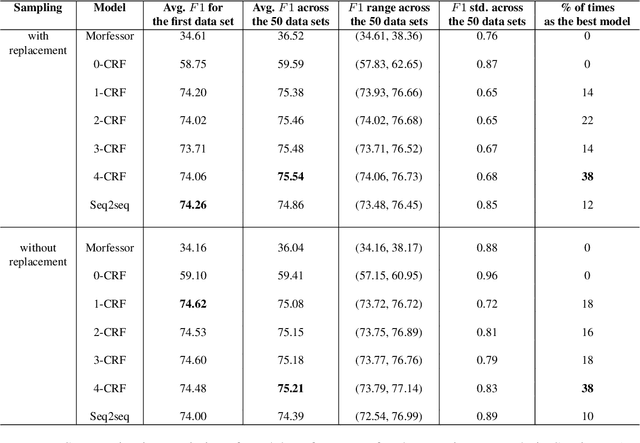
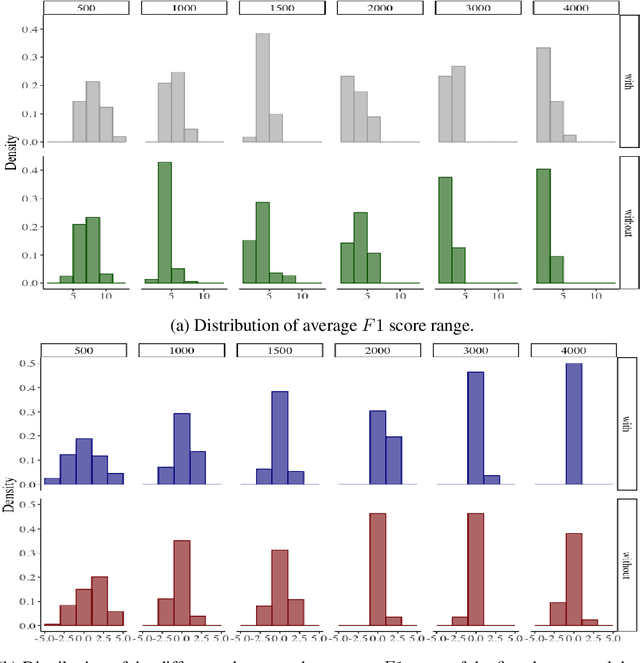
Abstract:Common designs of model evaluation typically focus on monolingual settings, where different models are compared according to their performance on a single data set that is assumed to be representative of all possible data for the task at hand. While this may be reasonable for a large data set, this assumption is difficult to maintain in low-resource scenarios, where artifacts of the data collection can yield data sets that are outliers, potentially making conclusions about model performance coincidental. To address these concerns, we investigate model generalizability in crosslinguistic low-resource scenarios. Using morphological segmentation as the test case, we compare three broad classes of models with different parameterizations, taking data from 11 languages across 6 language families. In each experimental setting, we evaluate all models on a first data set, then examine their performance consistency when introducing new randomly sampled data sets with the same size and when applying the trained models to unseen test sets of varying sizes. The results demonstrate that the extent of model generalization depends on the characteristics of the data set, and does not necessarily rely heavily on the data set size. Among the characteristics that we studied, the ratio of morpheme overlap and that of the average number of morphemes per word between the training and test sets are the two most prominent factors. Our findings suggest that future work should adopt random sampling to construct data sets with different sizes in order to make more responsible claims about model evaluation.
Neural Polysynthetic Language Modelling
May 13, 2020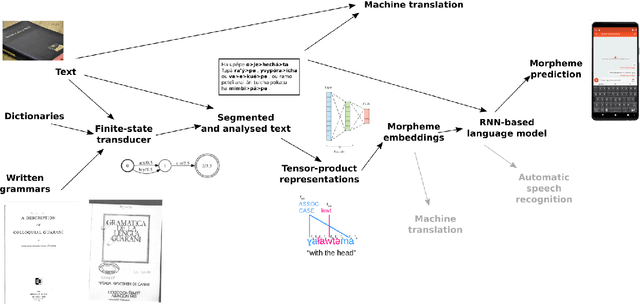

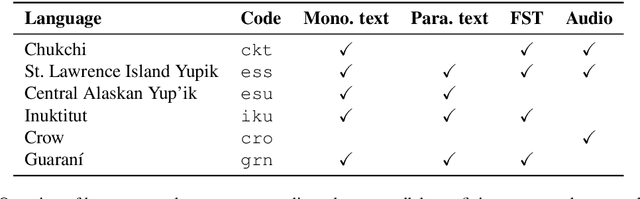
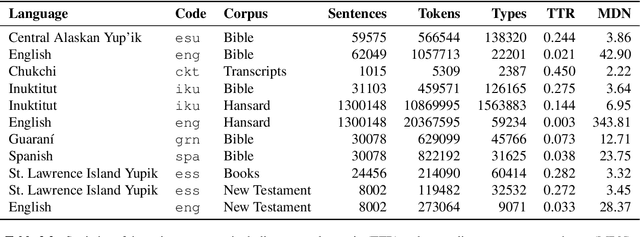
Abstract:Research in natural language processing commonly assumes that approaches that work well for English and and other widely-used languages are "language agnostic". In high-resource languages, especially those that are analytic, a common approach is to treat morphologically-distinct variants of a common root as completely independent word types. This assumes, that there are limited morphological inflections per root, and that the majority will appear in a large enough corpus, so that the model can adequately learn statistics about each form. Approaches like stemming, lemmatization, or subword segmentation are often used when either of those assumptions do not hold, particularly in the case of synthetic languages like Spanish or Russian that have more inflection than English. In the literature, languages like Finnish or Turkish are held up as extreme examples of complexity that challenge common modelling assumptions. Yet, when considering all of the world's languages, Finnish and Turkish are closer to the average case. When we consider polysynthetic languages (those at the extreme of morphological complexity), approaches like stemming, lemmatization, or subword modelling may not suffice. These languages have very high numbers of hapax legomena, showing the need for appropriate morphological handling of words, without which it is not possible for a model to capture enough word statistics. We examine the current state-of-the-art in language modelling, machine translation, and text prediction for four polysynthetic languages: Guaran\'i, St. Lawrence Island Yupik, Central Alaskan Yupik, and Inuktitut. We then propose a novel framework for language modelling that combines knowledge representations from finite-state morphological analyzers with Tensor Product Representations in order to enable neural language models capable of handling the full range of typologically variant languages.
A Summary of the First Workshop on Language Technology for Language Documentation and Revitalization
Apr 27, 2020

Abstract:Despite recent advances in natural language processing and other language technology, the application of such technology to language documentation and conservation has been limited. In August 2019, a workshop was held at Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh to attempt to bring together language community members, documentary linguists, and technologists to discuss how to bridge this gap and create prototypes of novel and practical language revitalization technologies. This paper reports the results of this workshop, including issues discussed, and various conceived and implemented technologies for nine languages: Arapaho, Cayuga, Inuktitut, Irish Gaelic, Kidaw'ida, Kwak'wala, Ojibwe, San Juan Quiahije Chatino, and Seneca.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge