Emery Fine
Selecting Better Samples from Pre-trained LLMs: A Case Study on Question Generation
Sep 22, 2022
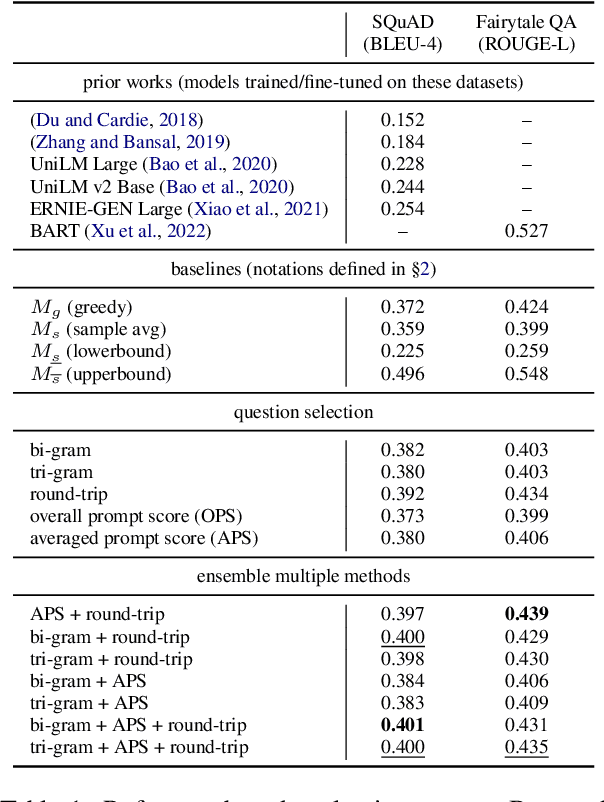
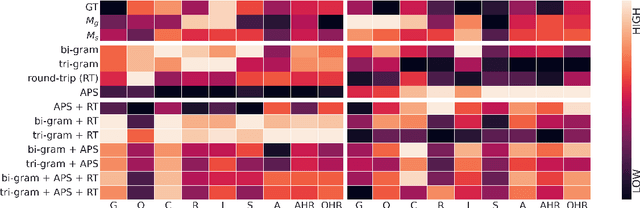
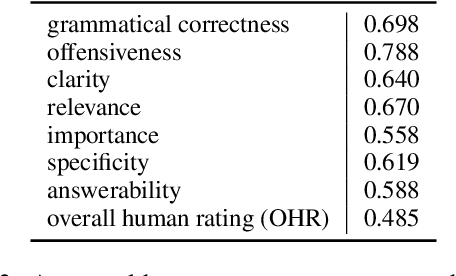
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have in recent years demonstrated impressive prowess in natural language generation. A common practice to improve generation diversity is to sample multiple outputs from the model. However, there lacks a simple and robust way of selecting the best output from these stochastic samples. As a case study framed in the context of question generation, we propose two prompt-based approaches to selecting high-quality questions from a set of LLM-generated candidates. Our method works under the constraints of 1) a black-box (non-modifiable) question generation model and 2) lack of access to human-annotated references -- both of which are realistic limitations for real-world deployment of LLMs. With automatic as well as human evaluations, we empirically demonstrate that our approach can effectively select questions of higher qualities than greedy generation.
Tip of the Tongue Known-Item Retrieval: A Case Study in Movie Identification
Jan 18, 2021



Abstract:While current information retrieval systems are effective for known-item retrieval where the searcher provides a precise name or identifier for the item being sought, systems tend to be much less effective for cases where the searcher is unable to express a precise name or identifier. We refer to this as tip of the tongue (TOT) known-item retrieval, named after the cognitive state of not being able to retrieve an item from memory. Using movie search as a case study, we explore the characteristics of questions posed by searchers in TOT states in a community question answering website. We analyze how searchers express their information needs during TOT states in the movie domain. Specifically, what information do searchers remember about the item being sought and how do they convey this information? Our results suggest that searchers use a combination of information about: (1) the content of the item sought, (2) the context in which they previously engaged with the item, and (3) previous attempts to find the item using other resources (e.g., search engines). Additionally, searchers convey information by sometimes expressing uncertainty (i.e., hedging), opinions, emotions, and by performing relative (vs. absolute) comparisons with attributes of the item. As a result of our analysis, we believe that searchers in TOT states may require specialized query understanding methods or document representations. Finally, our preliminary retrieval experiments show the impact of each information type presented in information requests on retrieval performance.
TextWorld: A Learning Environment for Text-based Games
Jun 29, 2018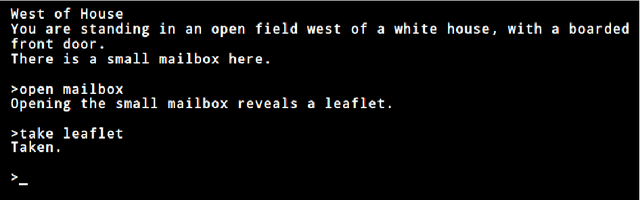
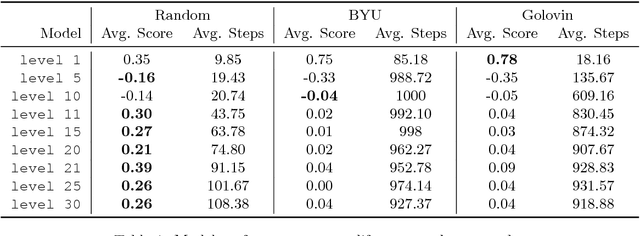

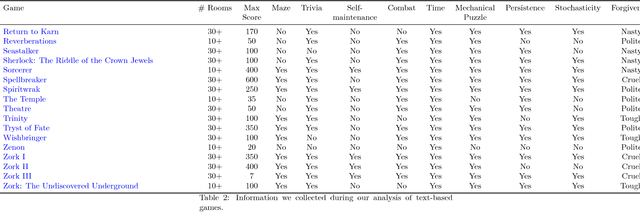
Abstract:We introduce TextWorld, a sandbox learning environment for the training and evaluation of RL agents on text-based games. TextWorld is a Python library that handles interactive play-through of text games, as well as backend functions like state tracking and reward assignment. It comes with a curated list of games whose features and challenges we have analyzed. More significantly, it enables users to handcraft or automatically generate new games. Its generative mechanisms give precise control over the difficulty, scope, and language of constructed games, and can be used to relax challenges inherent to commercial text games like partial observability and sparse rewards. By generating sets of varied but similar games, TextWorld can also be used to study generalization and transfer learning. We cast text-based games in the Reinforcement Learning formalism, use our framework to develop a set of benchmark games, and evaluate several baseline agents on this set and the curated list.
Frames: A Corpus for Adding Memory to Goal-Oriented Dialogue Systems
Apr 13, 2017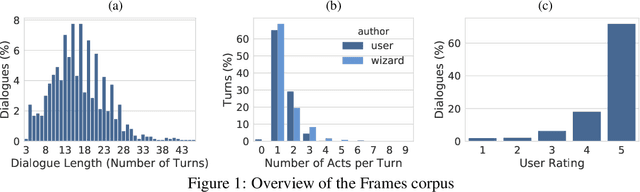

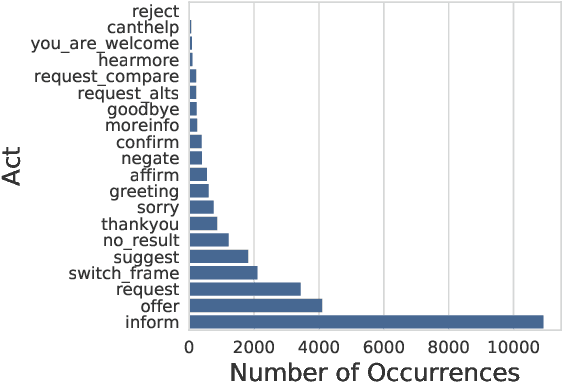

Abstract:This paper presents the Frames dataset (Frames is available at http://datasets.maluuba.com/Frames), a corpus of 1369 human-human dialogues with an average of 15 turns per dialogue. We developed this dataset to study the role of memory in goal-oriented dialogue systems. Based on Frames, we introduce a task called frame tracking, which extends state tracking to a setting where several states are tracked simultaneously. We propose a baseline model for this task. We show that Frames can also be used to study memory in dialogue management and information presentation through natural language generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge