Jeremie Zumer
Institute for Research in Immunology and Cancer, Department of Computer Science and Operations Research, Université de Montréal
Holographic Neural Architectures
Jun 04, 2018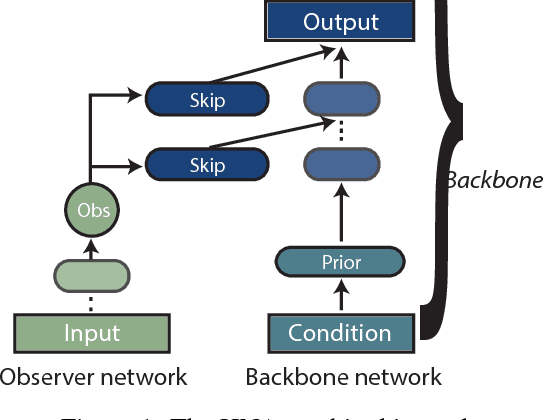
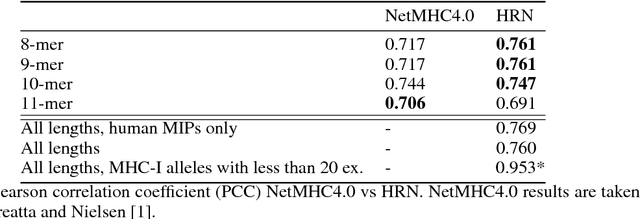
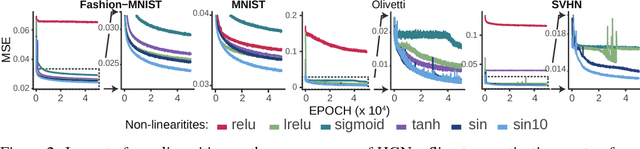

Abstract:Representation learning is at the heart of what makes deep learning effective. In this work, we introduce a new framework for representation learning that we call "Holographic Neural Architectures" (HNAs). In the same way that an observer can experience the 3D structure of a holographed object by looking at its hologram from several angles, HNAs derive Holographic Representations from the training set. These representations can then be explored by moving along a continuous bounded single dimension. We show that HNAs can be used to make generative networks, state-of-the-art regression models and that they are inherently highly resistant to noise. Finally, we argue that because of their denoising abilities and their capacity to generalize well from very few examples, models based upon HNAs are particularly well suited for biological applications where training examples are rare or noisy.
Relevance of Unsupervised Metrics in Task-Oriented Dialogue for Evaluating Natural Language Generation
Jun 29, 2017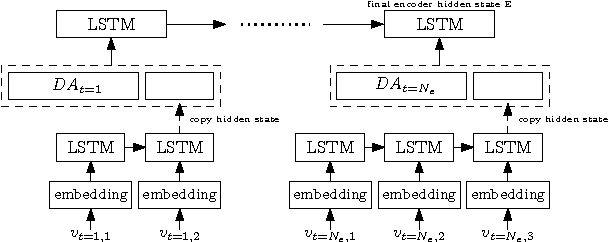
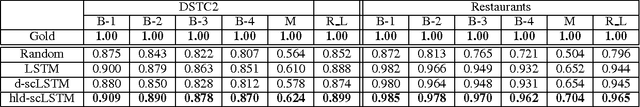
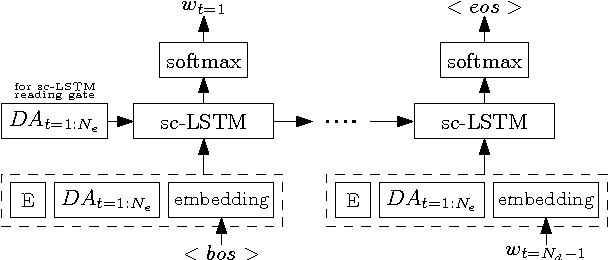
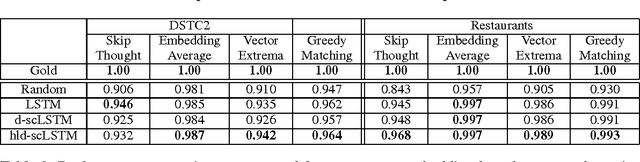
Abstract:Automated metrics such as BLEU are widely used in the machine translation literature. They have also been used recently in the dialogue community for evaluating dialogue response generation. However, previous work in dialogue response generation has shown that these metrics do not correlate strongly with human judgment in the non task-oriented dialogue setting. Task-oriented dialogue responses are expressed on narrower domains and exhibit lower diversity. It is thus reasonable to think that these automated metrics would correlate well with human judgment in the task-oriented setting where the generation task consists of translating dialogue acts into a sentence. We conduct an empirical study to confirm whether this is the case. Our findings indicate that these automated metrics have stronger correlation with human judgments in the task-oriented setting compared to what has been observed in the non task-oriented setting. We also observe that these metrics correlate even better for datasets which provide multiple ground truth reference sentences. In addition, we show that some of the currently available corpora for task-oriented language generation can be solved with simple models and advocate for more challenging datasets.
A Frame Tracking Model for Memory-Enhanced Dialogue Systems
Jun 06, 2017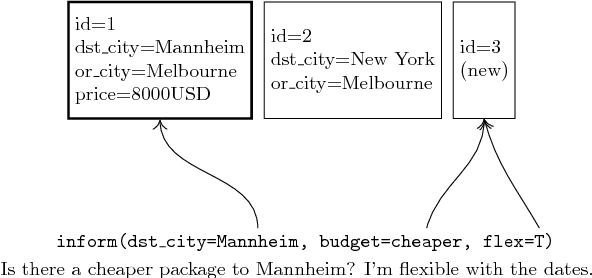
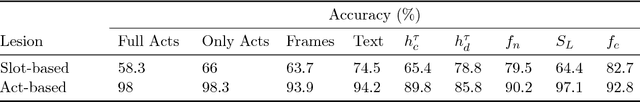
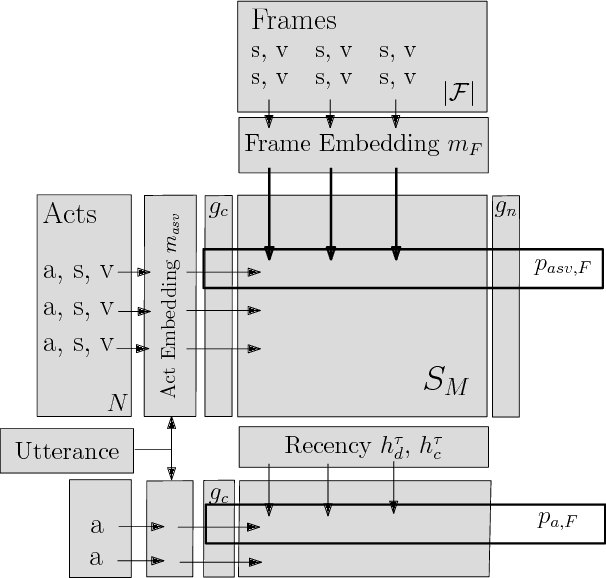

Abstract:Recently, resources and tasks were proposed to go beyond state tracking in dialogue systems. An example is the frame tracking task, which requires recording multiple frames, one for each user goal set during the dialogue. This allows a user, for instance, to compare items corresponding to different goals. This paper proposes a model which takes as input the list of frames created so far during the dialogue, the current user utterance as well as the dialogue acts, slot types, and slot values associated with this utterance. The model then outputs the frame being referenced by each triple of dialogue act, slot type, and slot value. We show that on the recently published Frames dataset, this model significantly outperforms a previously proposed rule-based baseline. In addition, we propose an extensive analysis of the frame tracking task by dividing it into sub-tasks and assessing their difficulty with respect to our model.
Frames: A Corpus for Adding Memory to Goal-Oriented Dialogue Systems
Apr 13, 2017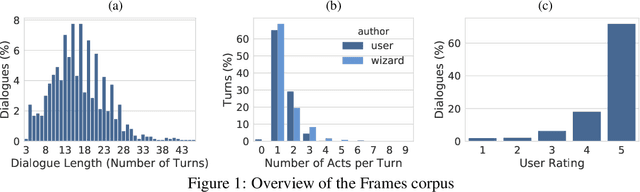

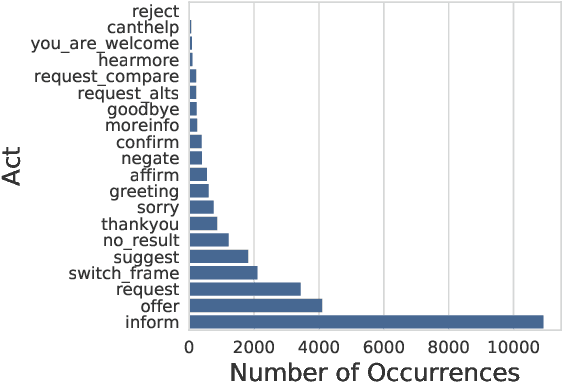

Abstract:This paper presents the Frames dataset (Frames is available at http://datasets.maluuba.com/Frames), a corpus of 1369 human-human dialogues with an average of 15 turns per dialogue. We developed this dataset to study the role of memory in goal-oriented dialogue systems. Based on Frames, we introduce a task called frame tracking, which extends state tracking to a setting where several states are tracked simultaneously. We propose a baseline model for this task. We show that Frames can also be used to study memory in dialogue management and information presentation through natural language generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge