Darryl Hannan
Seeing Beyond Redundancy: Task Complexity's Role in Vision Token Specialization in VLLMs
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Vision capabilities in vision large language models (VLLMs) have consistently lagged behind their linguistic capabilities. In particular, numerous benchmark studies have demonstrated that VLLMs struggle when fine-grained visual information or spatial reasoning is required. However, we do not yet understand exactly why VLLMs struggle so much with these tasks relative to others. Some works have focused on visual redundancy as an explanation, where high-level visual information is uniformly spread across numerous tokens and specific, fine-grained visual information is discarded. In this work, we investigate this premise in greater detail, seeking to better understand exactly how various types of visual information are processed by the model and what types of visual information are discarded. To do so, we introduce a simple synthetic benchmark dataset that is specifically constructed to probe various visual features, along with a set of metrics for measuring visual redundancy, allowing us to better understand the nuances of their relationship. Then, we explore fine-tuning VLLMs on a number of complex visual tasks to better understand how redundancy and compression change based upon the complexity of the data that a model is trained on. We find that there is a connection between task complexity and visual compression, implying that having a sufficient ratio of high complexity visual data is crucial for altering the way that VLLMs distribute their visual representation and consequently improving their performance on complex visual tasks. We hope that this work will provide valuable insights for training the next generation of VLLMs.
FMG-Det: Foundation Model Guided Robust Object Detection
May 29, 2025Abstract:Collecting high quality data for object detection tasks is challenging due to the inherent subjectivity in labeling the boundaries of an object. This makes it difficult to not only collect consistent annotations across a dataset but also to validate them, as no two annotators are likely to label the same object using the exact same coordinates. These challenges are further compounded when object boundaries are partially visible or blurred, which can be the case in many domains. Training on noisy annotations significantly degrades detector performance, rendering them unusable, particularly in few-shot settings, where just a few corrupted annotations can impact model performance. In this work, we propose FMG-Det, a simple, efficient methodology for training models with noisy annotations. More specifically, we propose combining a multiple instance learning (MIL) framework with a pre-processing pipeline that leverages powerful foundation models to correct labels prior to training. This pre-processing pipeline, along with slight modifications to the detector head, results in state-of-the-art performance across a number of datasets, for both standard and few-shot scenarios, while being much simpler and more efficient than other approaches.
Foundation Models for Remote Sensing: An Analysis of MLLMs for Object Localization
Apr 14, 2025


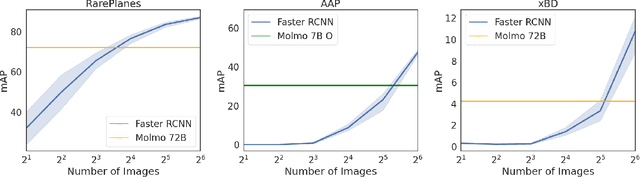
Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have altered the landscape of computer vision, obtaining impressive results across a wide range of tasks, especially in zero-shot settings. Unfortunately, their strong performance does not always transfer to out-of-distribution domains, such as earth observation (EO) imagery. Prior work has demonstrated that MLLMs excel at some EO tasks, such as image captioning and scene understanding, while failing at tasks that require more fine-grained spatial reasoning, such as object localization. However, MLLMs are advancing rapidly and insights quickly become out-dated. In this work, we analyze more recent MLLMs that have been explicitly trained to include fine-grained spatial reasoning capabilities, benchmarking them on EO object localization tasks. We demonstrate that these models are performant in certain settings, making them well suited for zero-shot scenarios. Additionally, we provide a detailed discussion focused on prompt selection, ground sample distance (GSD) optimization, and analyzing failure cases. We hope that this work will prove valuable as others evaluate whether an MLLM is well suited for a given EO localization task and how to optimize it.
The Impact of an XAI-Augmented Approach on Binary Classification with Scarce Data
Jul 01, 2024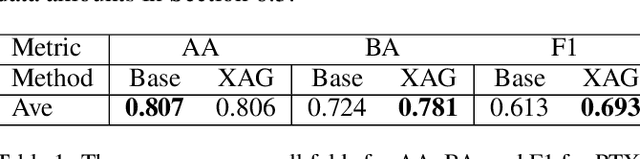
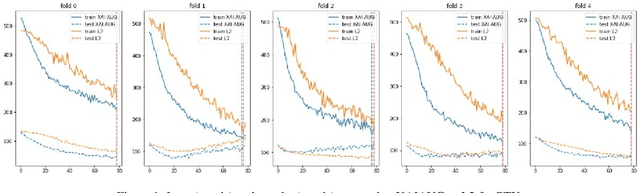
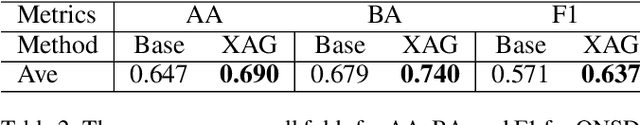
Abstract:Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) is the practice of clinicians conducting and interpreting ultrasound scans right at the patient's bedside. However, the expertise needed to interpret these images is considerable and may not always be present in emergency situations. This reality makes algorithms such as machine learning classifiers extremely valuable to augment human decisions. POCUS devices are becoming available at a reasonable cost in the size of a mobile phone. The challenge of turning POCUS devices into life-saving tools is that interpretation of ultrasound images requires specialist training and experience. Unfortunately, the difficulty to obtain positive training images represents an important obstacle to building efficient and accurate classifiers. Hence, the problem we try to investigate is how to explore strategies to increase accuracy of classifiers trained with scarce data. We hypothesize that training with a few data instances may not suffice for classifiers to generalize causing them to overfit. Our approach uses an Explainable AI-Augmented approach to help the algorithm learn more from less and potentially help the classifier better generalize.
Interpretable Models for Detecting and Monitoring Elevated Intracranial Pressure
Mar 04, 2024


Abstract:Detecting elevated intracranial pressure (ICP) is crucial in diagnosing and managing various neurological conditions. These fluctuations in pressure are transmitted to the optic nerve sheath (ONS), resulting in changes to its diameter, which can then be detected using ultrasound imaging devices. However, interpreting sonographic images of the ONS can be challenging. In this work, we propose two systems that actively monitor the ONS diameter throughout an ultrasound video and make a final prediction as to whether ICP is elevated. To construct our systems, we leverage subject matter expert (SME) guidance, structuring our processing pipeline according to their collection procedure, while also prioritizing interpretability and computational efficiency. We conduct a number of experiments, demonstrating that our proposed systems are able to outperform various baselines. One of our SMEs then manually validates our top system's performance, lending further credibility to our approach while demonstrating its potential utility in a clinical setting.
Event-to-Video Conversion for Overhead Object Detection
Feb 09, 2024
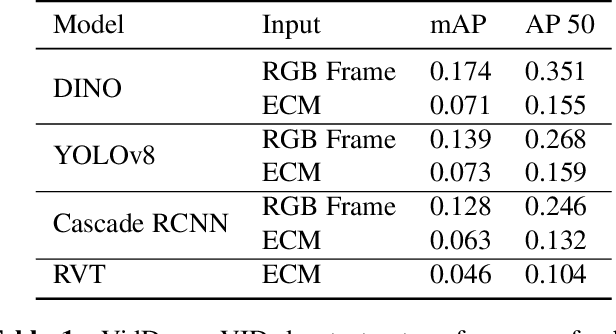
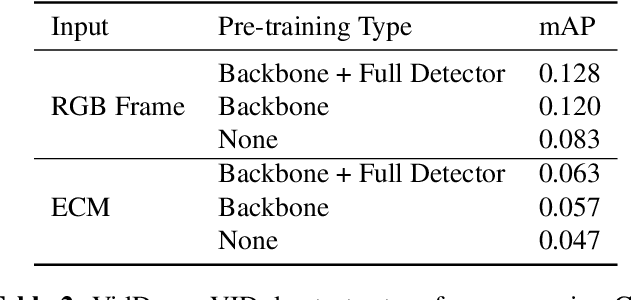
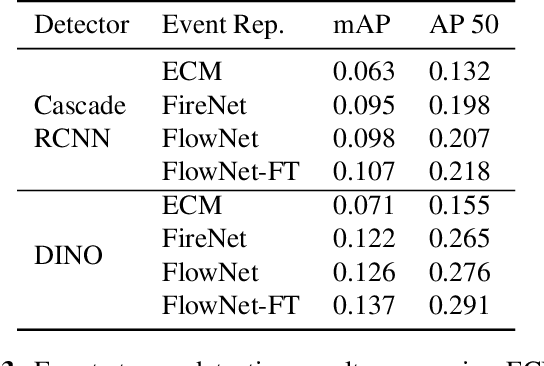
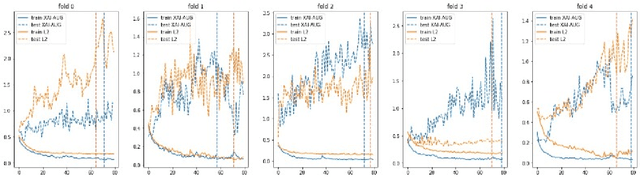
Abstract:Collecting overhead imagery using an event camera is desirable due to the energy efficiency of the image sensor compared to standard cameras. However, event cameras complicate downstream image processing, especially for complex tasks such as object detection. In this paper, we investigate the viability of event streams for overhead object detection. We demonstrate that across a number of standard modeling approaches, there is a significant gap in performance between dense event representations and corresponding RGB frames. We establish that this gap is, in part, due to a lack of overlap between the event representations and the pre-training data used to initialize the weights of the object detectors. Then, we apply event-to-video conversion models that convert event streams into gray-scale video to close this gap. We demonstrate that this approach results in a large performance increase, outperforming even event-specific object detection techniques on our overhead target task. These results suggest that better alignment between event representations and existing large pre-trained models may result in greater short-term performance gains compared to end-to-end event-specific architectural improvements.
MobilePTX: Sparse Coding for Pneumothorax Detection Given Limited Training Examples
Dec 08, 2022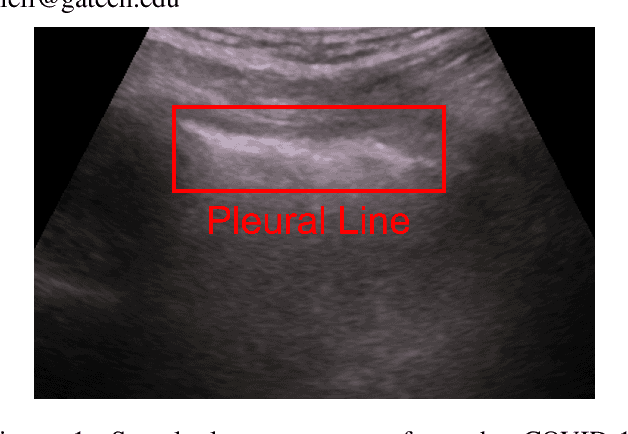
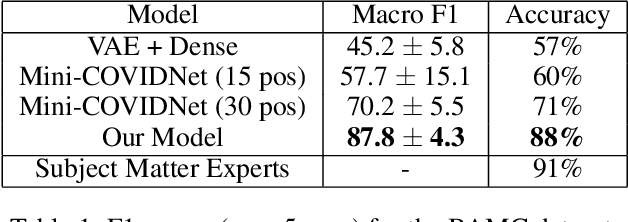
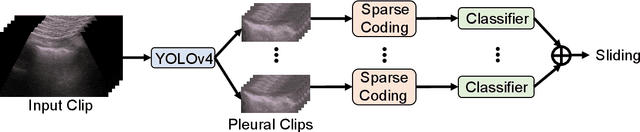

Abstract:Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) refers to clinician-performed and interpreted ultrasonography at the patient's bedside. Interpreting these images requires a high level of expertise, which may not be available during emergencies. In this paper, we support POCUS by developing classifiers that can aid medical professionals by diagnosing whether or not a patient has pneumothorax. We decomposed the task into multiple steps, using YOLOv4 to extract relevant regions of the video and a 3D sparse coding model to represent video features. Given the difficulty in acquiring positive training videos, we trained a small-data classifier with a maximum of 15 positive and 32 negative examples. To counteract this limitation, we leveraged subject matter expert (SME) knowledge to limit the hypothesis space, thus reducing the cost of data collection. We present results using two lung ultrasound datasets and demonstrate that our model is capable of achieving performance on par with SMEs in pneumothorax identification. We then developed an iOS application that runs our full system in less than 4 seconds on an iPad Pro, and less than 8 seconds on an iPhone 13 Pro, labeling key regions in the lung sonogram to provide interpretable diagnoses.
StoryDALL-E: Adapting Pretrained Text-to-Image Transformers for Story Continuation
Sep 13, 2022
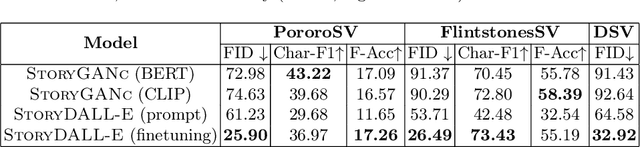
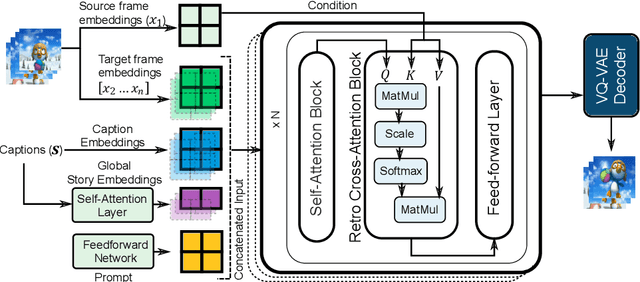
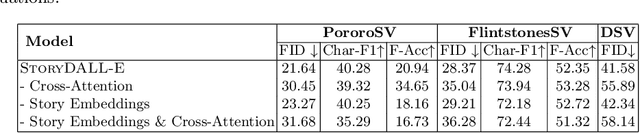
Abstract:Recent advances in text-to-image synthesis have led to large pretrained transformers with excellent capabilities to generate visualizations from a given text. However, these models are ill-suited for specialized tasks like story visualization, which requires an agent to produce a sequence of images given a corresponding sequence of captions, forming a narrative. Moreover, we find that the story visualization task fails to accommodate generalization to unseen plots and characters in new narratives. Hence, we first propose the task of story continuation, where the generated visual story is conditioned on a source image, allowing for better generalization to narratives with new characters. Then, we enhance or 'retro-fit' the pretrained text-to-image synthesis models with task-specific modules for (a) sequential image generation and (b) copying relevant elements from an initial frame. Then, we explore full-model finetuning, as well as prompt-based tuning for parameter-efficient adaptation, of the pre-trained model. We evaluate our approach StoryDALL-E on two existing datasets, PororoSV and FlintstonesSV, and introduce a new dataset DiDeMoSV collected from a video-captioning dataset. We also develop a model StoryGANc based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) for story continuation, and compare it with the StoryDALL-E model to demonstrate the advantages of our approach. We show that our retro-fitting approach outperforms GAN-based models for story continuation and facilitates copying of visual elements from the source image, thereby improving continuity in the generated visual story. Finally, our analysis suggests that pretrained transformers struggle to comprehend narratives containing several characters. Overall, our work demonstrates that pretrained text-to-image synthesis models can be adapted for complex and low-resource tasks like story continuation.
Improving Generation and Evaluation of Visual Stories via Semantic Consistency
May 20, 2021
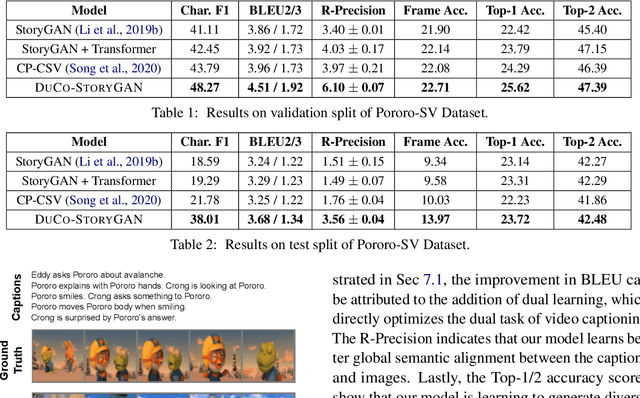
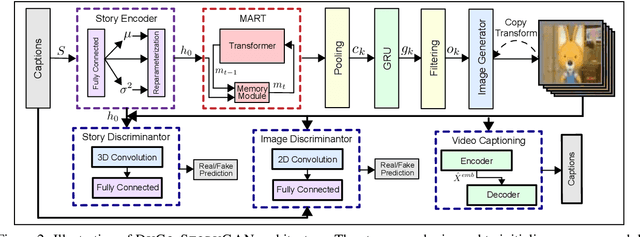
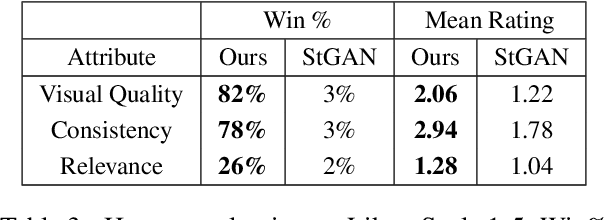
Abstract:Story visualization is an under-explored task that falls at the intersection of many important research directions in both computer vision and natural language processing. In this task, given a series of natural language captions which compose a story, an agent must generate a sequence of images that correspond to the captions. Prior work has introduced recurrent generative models which outperform text-to-image synthesis models on this task. However, there is room for improvement of generated images in terms of visual quality, coherence and relevance. We present a number of improvements to prior modeling approaches, including (1) the addition of a dual learning framework that utilizes video captioning to reinforce the semantic alignment between the story and generated images, (2) a copy-transform mechanism for sequentially-consistent story visualization, and (3) MART-based transformers to model complex interactions between frames. We present ablation studies to demonstrate the effect of each of these techniques on the generative power of the model for both individual images as well as the entire narrative. Furthermore, due to the complexity and generative nature of the task, standard evaluation metrics do not accurately reflect performance. Therefore, we also provide an exploration of evaluation metrics for the model, focused on aspects of the generated frames such as the presence/quality of generated characters, the relevance to captions, and the diversity of the generated images. We also present correlation experiments of our proposed automated metrics with human evaluations. Code and data available at: https://github.com/adymaharana/StoryViz
ManyModalQA: Modality Disambiguation and QA over Diverse Inputs
Jan 22, 2020



Abstract:We present a new multimodal question answering challenge, ManyModalQA, in which an agent must answer a question by considering three distinct modalities: text, images, and tables. We collect our data by scraping Wikipedia and then utilize crowdsourcing to collect question-answer pairs. Our questions are ambiguous, in that the modality that contains the answer is not easily determined based solely upon the question. To demonstrate this ambiguity, we construct a modality selector (or disambiguator) network, and this model gets substantially lower accuracy on our challenge set, compared to existing datasets, indicating that our questions are more ambiguous. By analyzing this model, we investigate which words in the question are indicative of the modality. Next, we construct a simple baseline ManyModalQA model, which, based on the prediction from the modality selector, fires a corresponding pre-trained state-of-the-art unimodal QA model. We focus on providing the community with a new manymodal evaluation set and only provide a fine-tuning set, with the expectation that existing datasets and approaches will be transferred for most of the training, to encourage low-resource generalization without large, monolithic training sets for each new task. There is a significant gap between our baseline models and human performance; therefore, we hope that this challenge encourages research in end-to-end modality disambiguation and multimodal QA models, as well as transfer learning. Code and data available at: https://github.com/hannandarryl/ManyModalQA
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge