Danielle Rothermel
Dungeons and Data: A Large-Scale NetHack Dataset
Nov 22, 2022Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in the development of agents to solve challenging sequential decision making problems such as Go, StarCraft, or DOTA, have relied on both simulated environments and large-scale datasets. However, progress on this research has been hindered by the scarcity of open-sourced datasets and the prohibitive computational cost to work with them. Here we present the NetHack Learning Dataset (NLD), a large and highly-scalable dataset of trajectories from the popular game of NetHack, which is both extremely challenging for current methods and very fast to run. NLD consists of three parts: 10 billion state transitions from 1.5 million human trajectories collected on the NAO public NetHack server from 2009 to 2020; 3 billion state-action-score transitions from 100,000 trajectories collected from the symbolic bot winner of the NetHack Challenge 2021; and, accompanying code for users to record, load and stream any collection of such trajectories in a highly compressed form. We evaluate a wide range of existing algorithms including online and offline RL, as well as learning from demonstrations, showing that significant research advances are needed to fully leverage large-scale datasets for challenging sequential decision making tasks.
Insights From the NeurIPS 2021 NetHack Challenge
Mar 22, 2022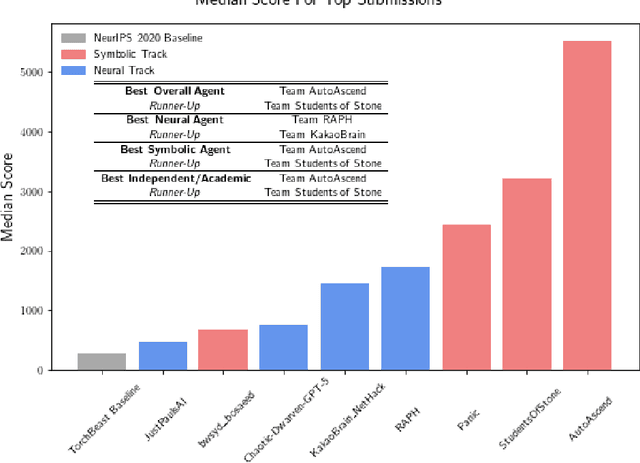
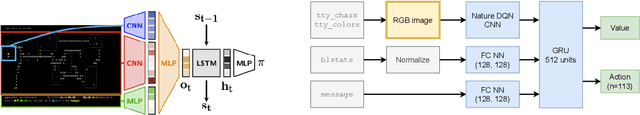
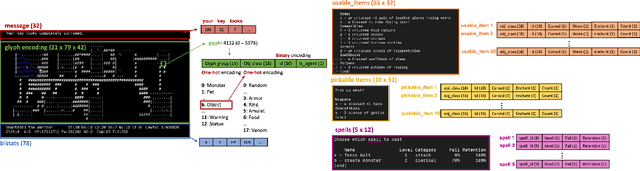
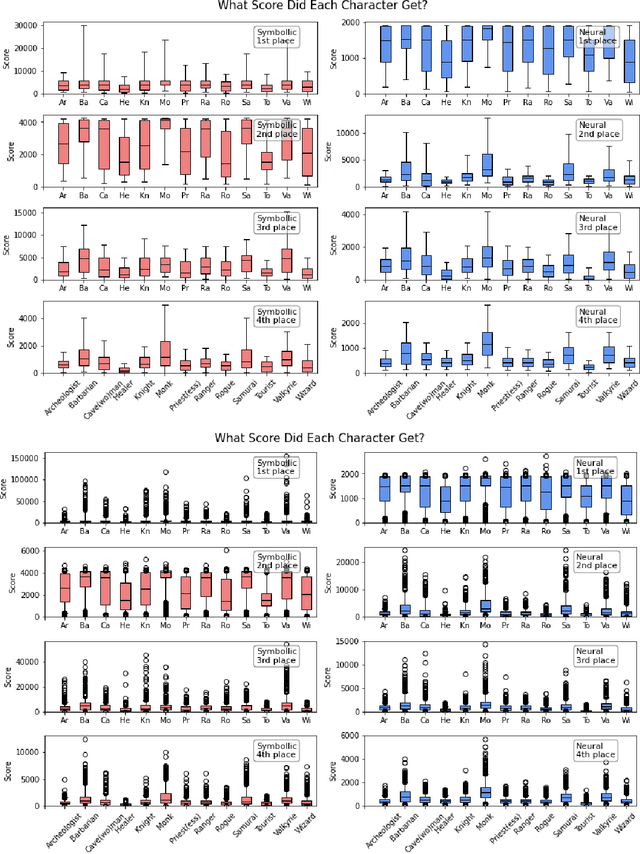
Abstract:In this report, we summarize the takeaways from the first NeurIPS 2021 NetHack Challenge. Participants were tasked with developing a program or agent that can win (i.e., 'ascend' in) the popular dungeon-crawler game of NetHack by interacting with the NetHack Learning Environment (NLE), a scalable, procedurally generated, and challenging Gym environment for reinforcement learning (RL). The challenge showcased community-driven progress in AI with many diverse approaches significantly beating the previously best results on NetHack. Furthermore, it served as a direct comparison between neural (e.g., deep RL) and symbolic AI, as well as hybrid systems, demonstrating that on NetHack symbolic bots currently outperform deep RL by a large margin. Lastly, no agent got close to winning the game, illustrating NetHack's suitability as a long-term benchmark for AI research.
Don't Sweep your Learning Rate under the Rug: A Closer Look at Cross-modal Transfer of Pretrained Transformers
Jul 26, 2021



Abstract:Self-supervised pre-training of large-scale transformer models on text corpora followed by finetuning has achieved state-of-the-art on a number of natural language processing tasks. Recently, Lu et al. (2021, arXiv:2103.05247) claimed that frozen pretrained transformers (FPTs) match or outperform training from scratch as well as unfrozen (fine-tuned) pretrained transformers in a set of transfer tasks to other modalities. In our work, we find that this result is, in fact, an artifact of not tuning the learning rates. After carefully redesigning the empirical setup, we find that when tuning learning rates properly, pretrained transformers do outperform or match training from scratch in all of our tasks, but only as long as the entire model is finetuned. Thus, while transfer from pretrained language models to other modalities does indeed provide gains and hints at exciting possibilities for future work, properly tuning hyperparameters is important for arriving at robust findings.
Why Build an Assistant in Minecraft?
Jul 25, 2019Abstract:In this document we describe a rationale for a research program aimed at building an open "assistant" in the game Minecraft, in order to make progress on the problems of natural language understanding and learning from dialogue.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge